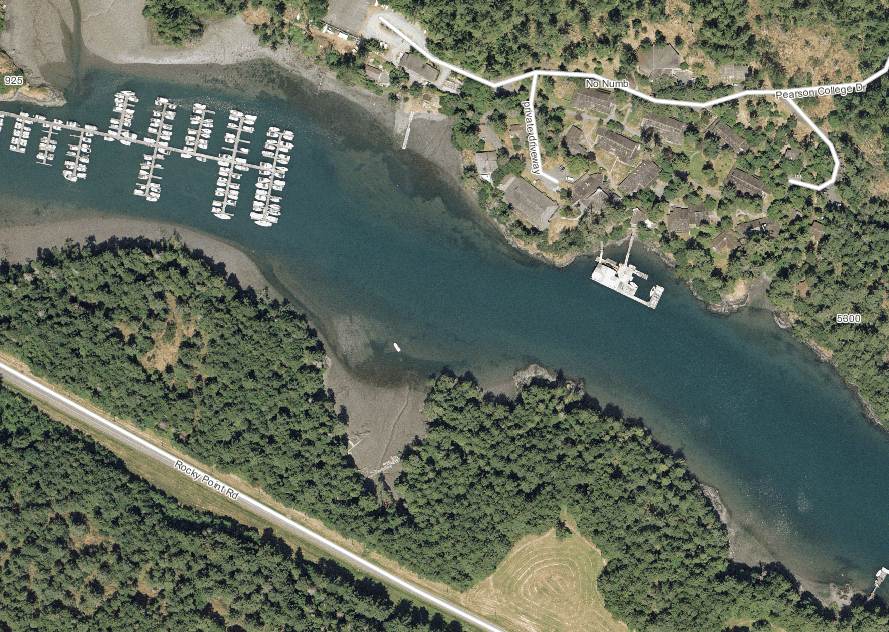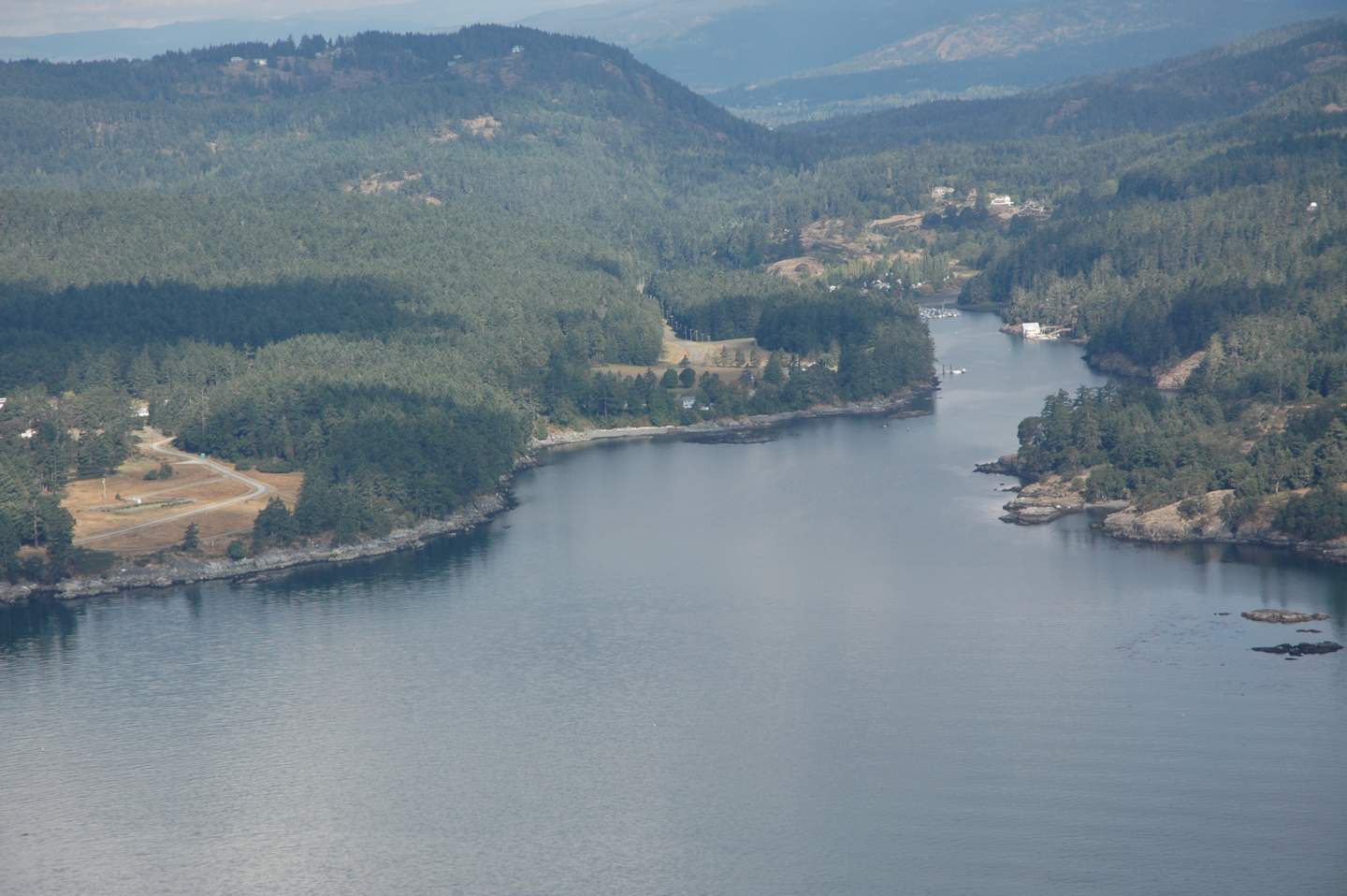
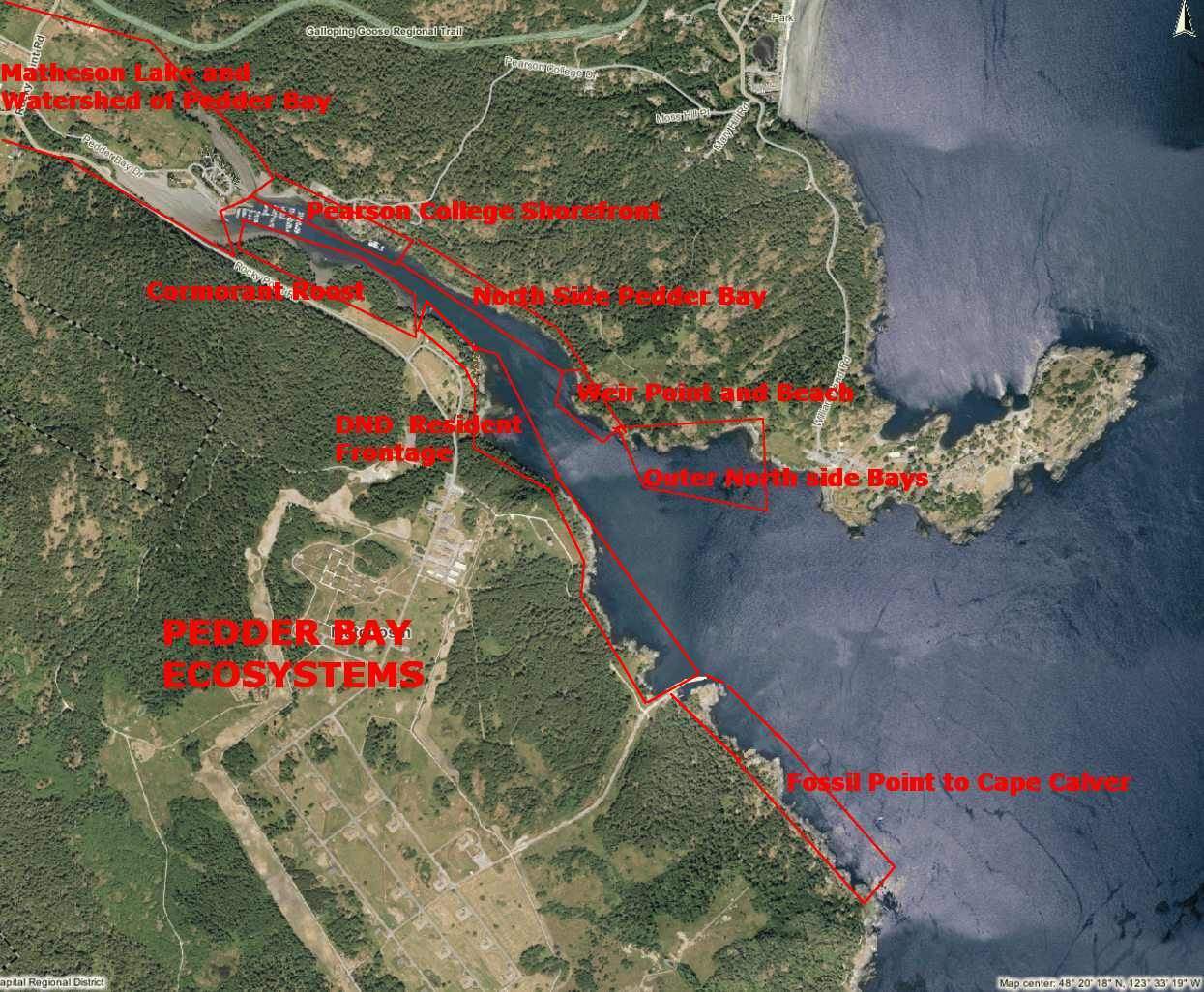
Aerial Map Courtesy of the CRD NATURAL AREAS ATLAS
Helicopter Images from GEOBC
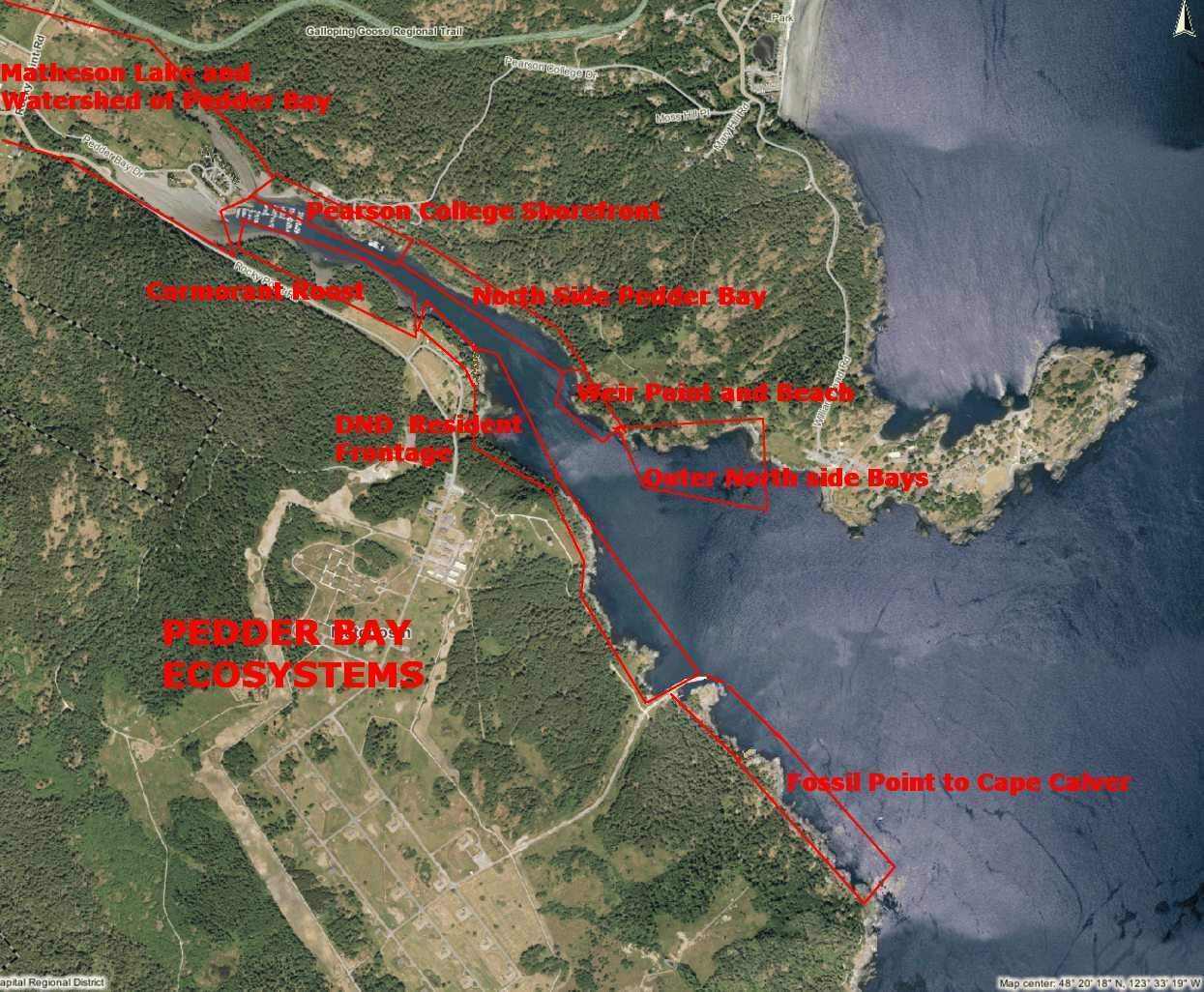
The geography of Pedder Bay and the exposure of its shores to the marine environment results in a number of contrasting ecosystems on the upland part of the shores. It also contributes significant materials to the marine environment and through four or five months of the year contributes a large volume of freshwater, acting more like an estuary than a regular bay.
Pedder Bay, British Columbia Wave Climate Study and Wave Protection Considerations
March 1991 Fisheries and Oceans report
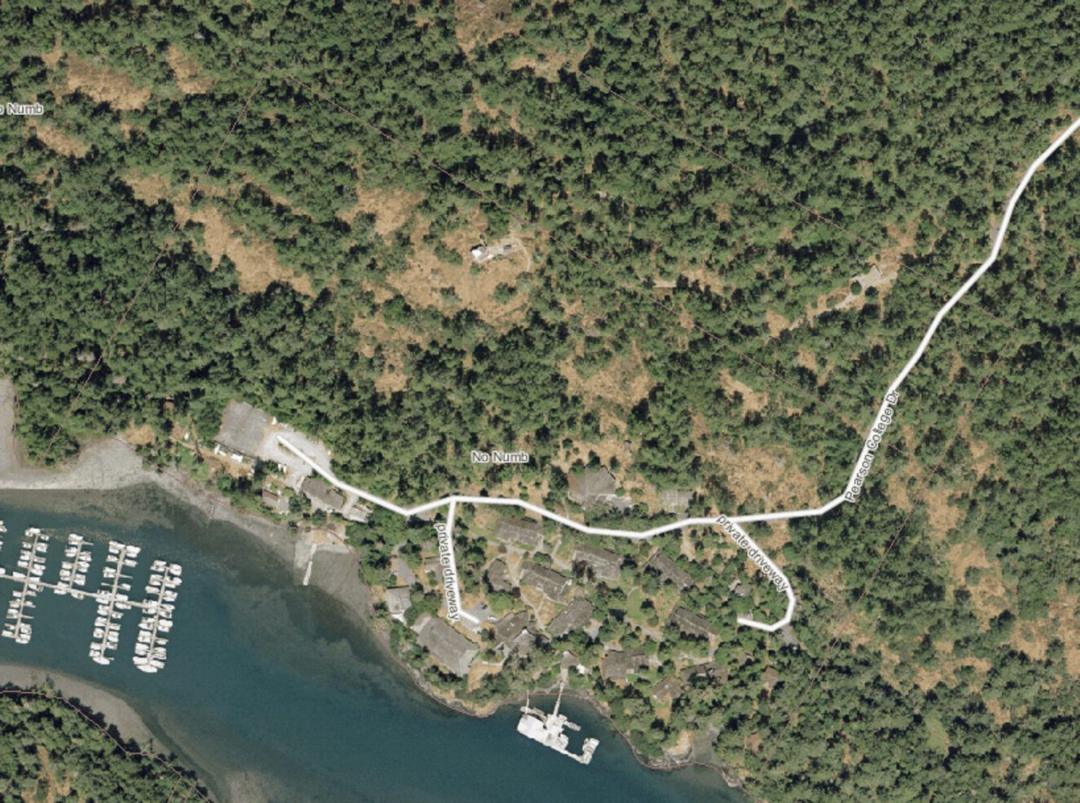
PEARSON COLLEGE SHOREFRONT
Lester B. Pearson College opened in 1974 on the north side of Pedder Bay on land formerly owned by the Department of National Defence . At high tide, most of the shoreline of the campus is rocky intertidal, however at low tide, mudflats appear along much of the shore.
-

-
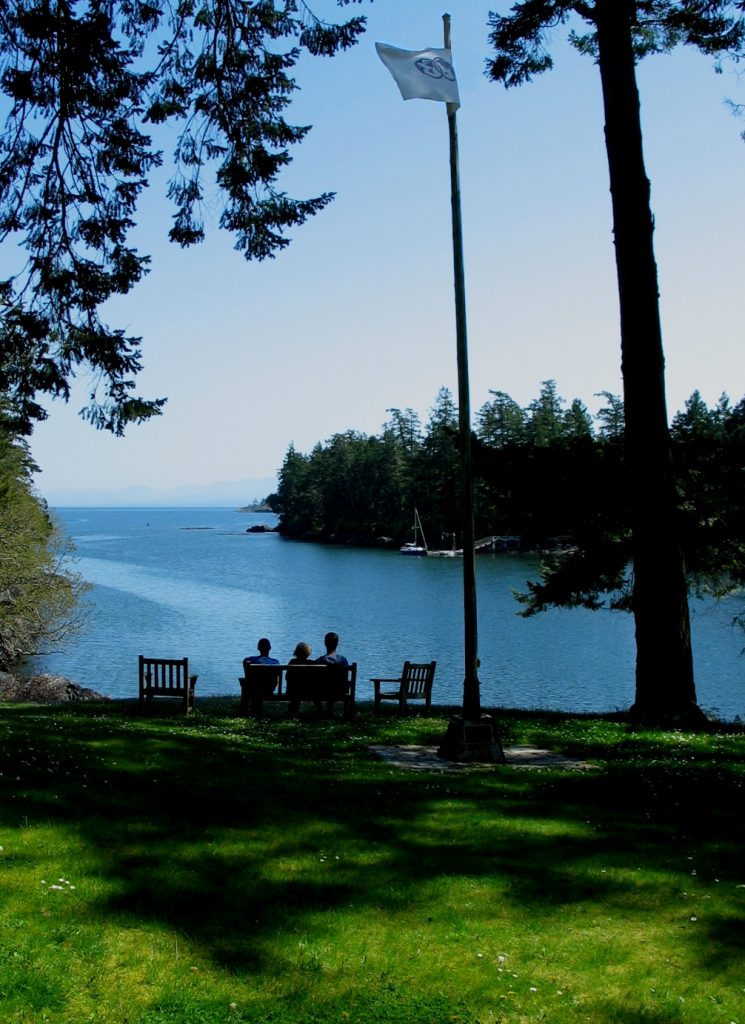
A view of Pedder Bay looking South East from “the Point “on Lester Pearson College Campus
-

-
“The Point” on Pearson College Campus
-

-
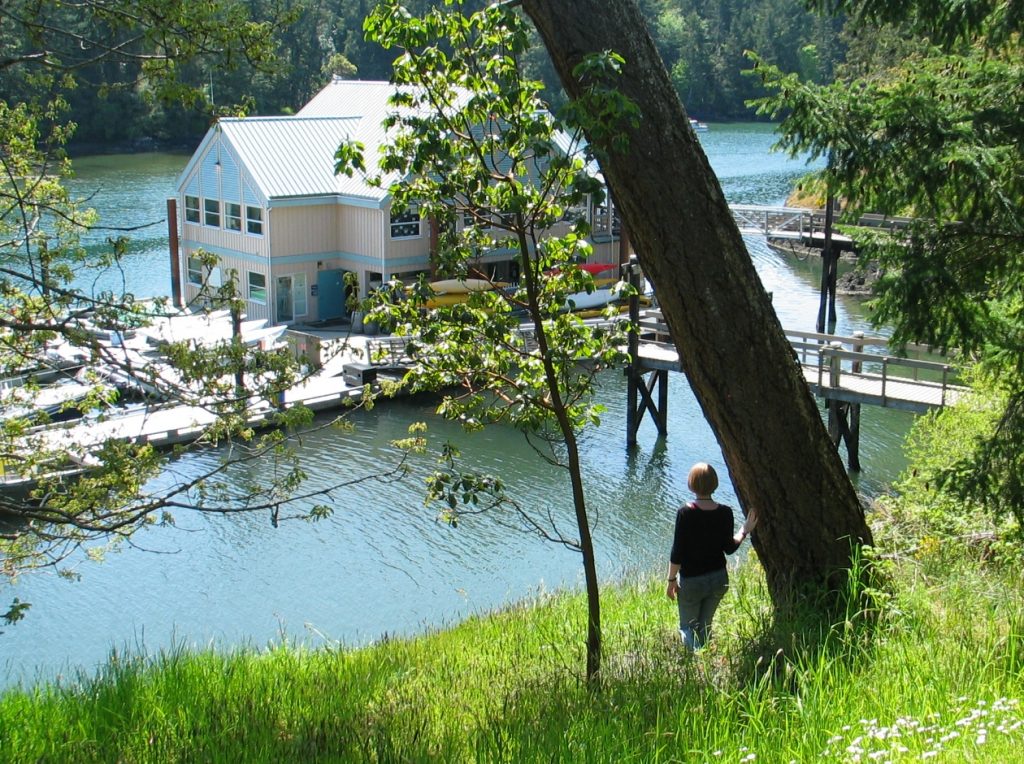
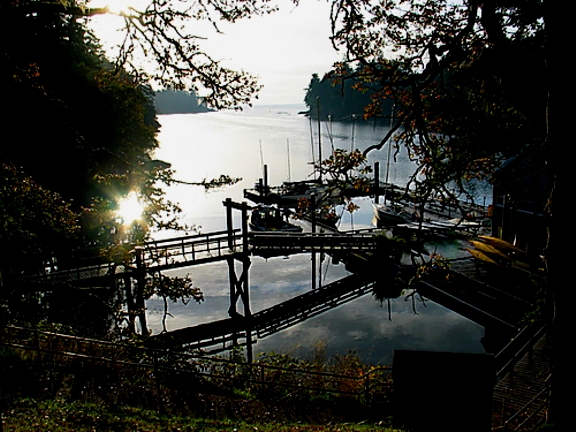
The docks at Pearson College with Marine Lab.
The following is excerpted from the College reference guide ” The Road Ends at Our Place: The Ecosystems of Pearson College.
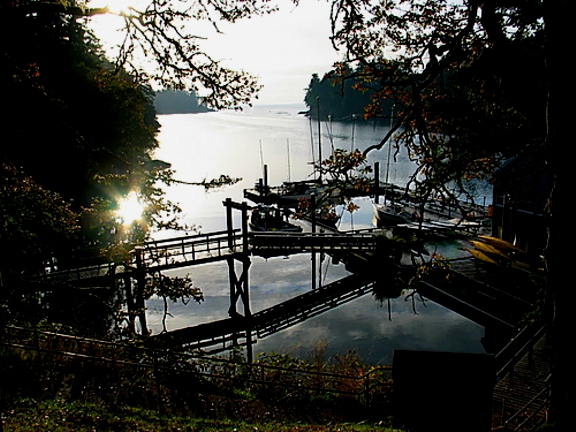 One of the first projects the students faced when the college was founded was to build the floating docks as their outlet to the sea. This provided for a rich marine environment program which has expanded since that time. College boats provide for field trips in the biology and marine science classes, and the afternoon activities in sailing, SCUBA diving and kayaking lead to an active seafront.
One of the first projects the students faced when the college was founded was to build the floating docks as their outlet to the sea. This provided for a rich marine environment program which has expanded since that time. College boats provide for field trips in the biology and marine science classes, and the afternoon activities in sailing, SCUBA diving and kayaking lead to an active seafront.
In 2003, the addition of the floating lab provided room for three more classrooms as well as a diving equipment room, workshop, office and storage space for the sea activities. The immediate access to the ecosystems of Pedder Bay make it an ideal facility for the life sciences.
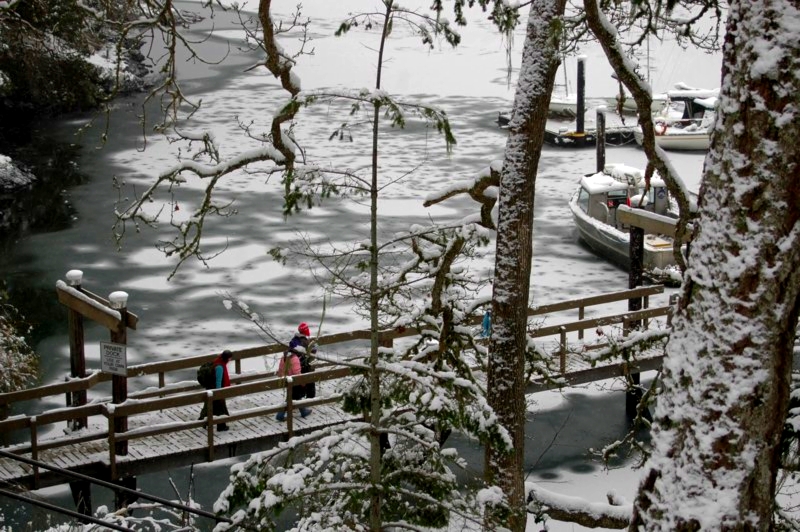
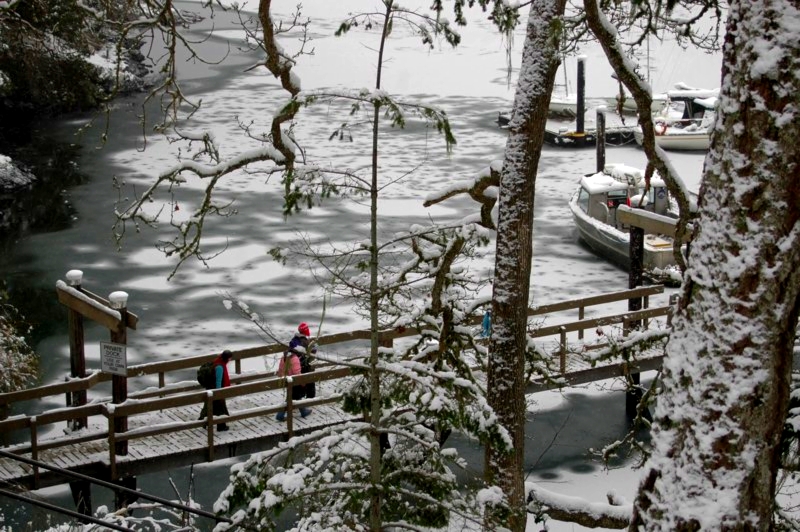 Only on rare occasions (once in ten years) do we get a week of cold weather and snow which causes the inner part of the bay up to the college docks to freeze over. The campus for a few brief days takes on a unique beauty when this happens. It also is a time when we can take advantage of the learning opportunity by having the students experience the unique aspects of “snow ecology”. For students from tropical countries who may never have experienced such conditions, there is a realization that snow has insulating features, can be breathed through, is variable in weight and density, and plants from temperate climates adapt to it in unique ways. Meanwhile down at the waterfront, unique patterns of salinity and fresh water can be discovered with ice formation.
Only on rare occasions (once in ten years) do we get a week of cold weather and snow which causes the inner part of the bay up to the college docks to freeze over. The campus for a few brief days takes on a unique beauty when this happens. It also is a time when we can take advantage of the learning opportunity by having the students experience the unique aspects of “snow ecology”. For students from tropical countries who may never have experienced such conditions, there is a realization that snow has insulating features, can be breathed through, is variable in weight and density, and plants from temperate climates adapt to it in unique ways. Meanwhile down at the waterfront, unique patterns of salinity and fresh water can be discovered with ice formation.
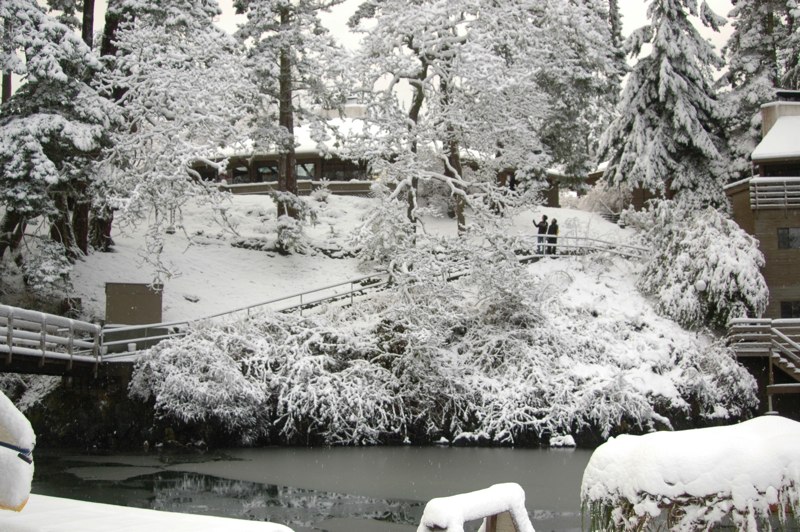
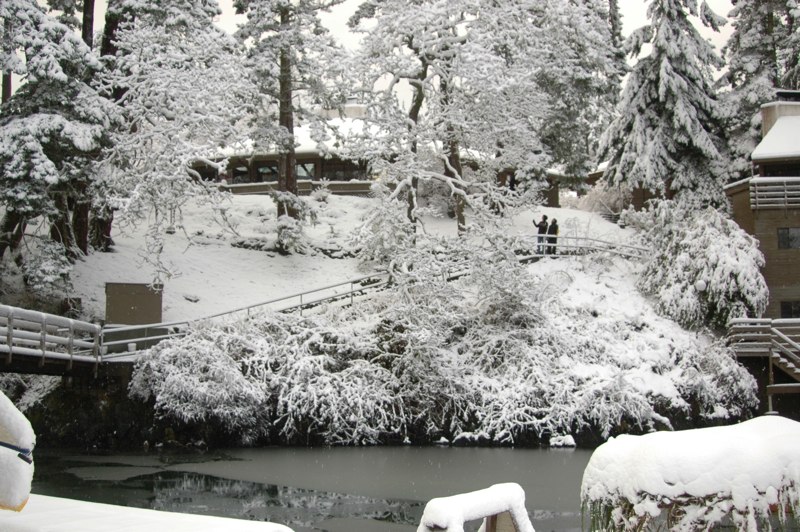 The academic building viewed from the docks after one of those rare snowfalls that we get in Pedder Bay.
The academic building viewed from the docks after one of those rare snowfalls that we get in Pedder Bay.
=====================================================
- Mudflats and RockyIntertidal Ecosystems of Pedder Bay
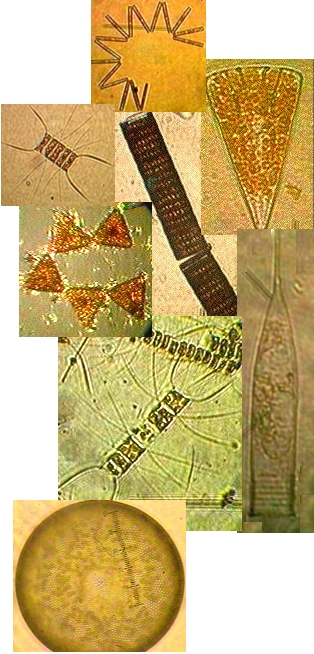 The shores of Pedder Bay provide more fascinating variety to our campus, and the profile of the bay changes considerably from low to high tide, a range of 3 meters. The water of the bay varies in temperature from 8 degrees Celsius in the winter to 13 degrees in the summer.
The shores of Pedder Bay provide more fascinating variety to our campus, and the profile of the bay changes considerably from low to high tide, a range of 3 meters. The water of the bay varies in temperature from 8 degrees Celsius in the winter to 13 degrees in the summer.
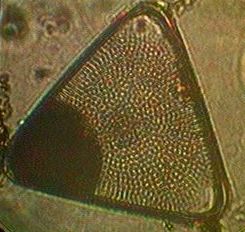
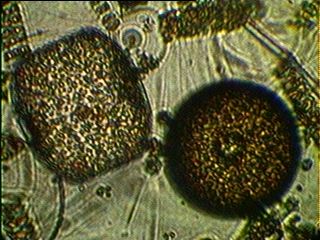
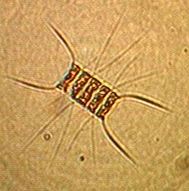
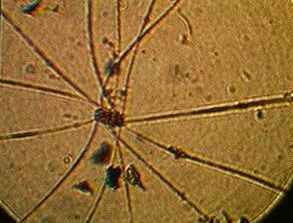
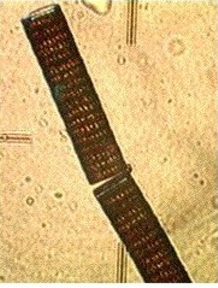
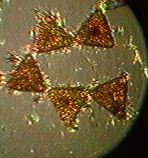
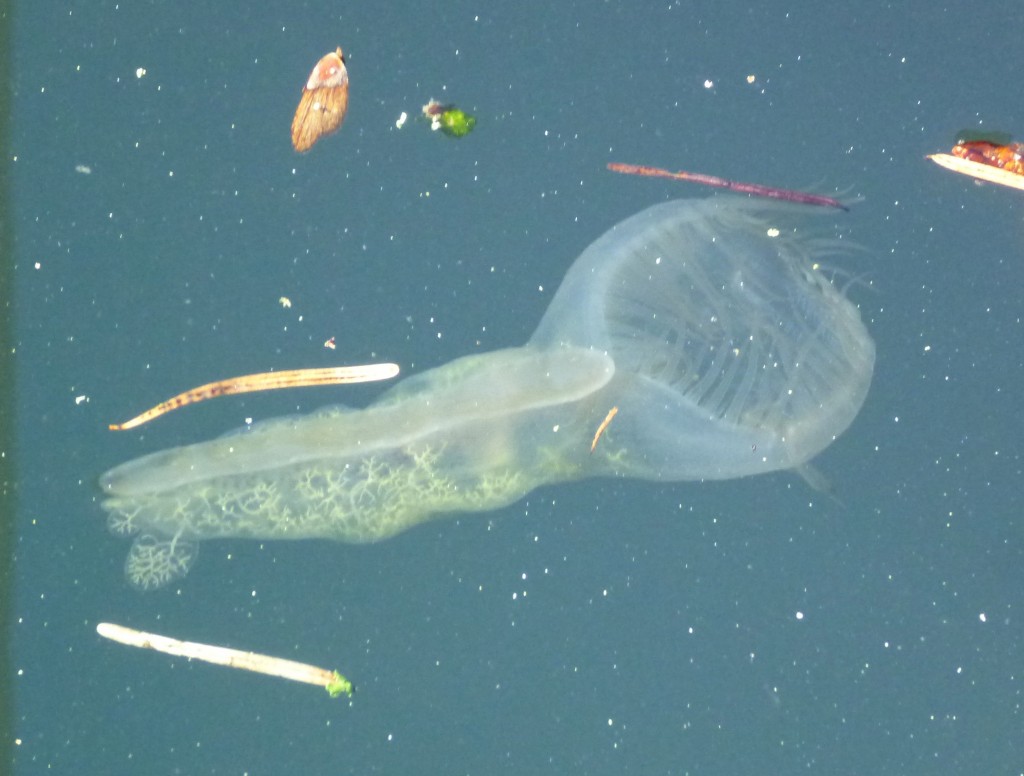
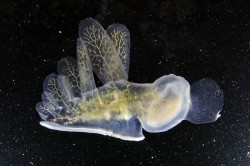
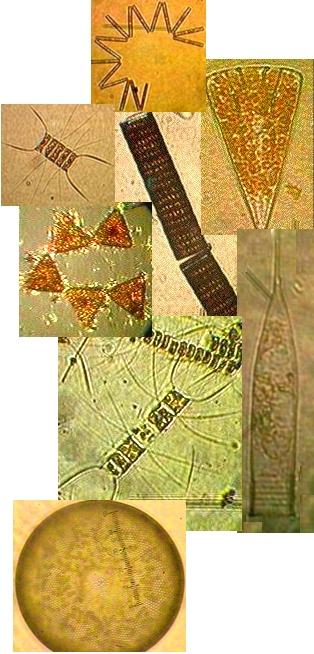
The mudflat in front of the sea front commons building is typical of the small inlets along the bay. It provides a rich habitat to mud-dwelling organisms and red-rock and dungeness crabs. Overhanging trees and trees which have fallen into the water provide the substrate for the bay mussel , Mytilus trossulus, and several barnacle species. Several species of limpet and littorine snails graze rocks in the intertidal zone and the large white anemone , Metridium farcimen, can be seen on the bottom of the bay, anchored to submerged branches or exposed rocks. All the invertebrates contribute their larva to the rich planktonic mix in the waters of the bay. The main producers in the bay are the large round centric diatoms, Coscinodiscus sp. but on different occasions under the microscopes of the biology students, a wide array of geometric shapes of other phytoplankton species will appear. Copepods and the nauplius larvae of barnacles make up the main zooplankton of the bay.
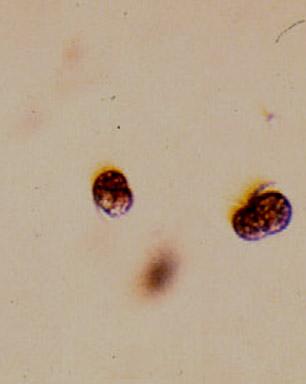
 Often in the spring when the sunlight levels are adequate, the nutrient laden water from winter run-off may support a non-poisonous red tide. A deep reddish bloom caused by the organism Mesodinium rubrum will cover parts of the bay. This is a unique marine photosynthetic ciliate which can fix energy because it has a cryptophyte endosymbiontic red algae inside it. A good example of a mutualistic relationship occurring on a massive scale within the bay.
Often in the spring when the sunlight levels are adequate, the nutrient laden water from winter run-off may support a non-poisonous red tide. A deep reddish bloom caused by the organism Mesodinium rubrum will cover parts of the bay. This is a unique marine photosynthetic ciliate which can fix energy because it has a cryptophyte endosymbiontic red algae inside it. A good example of a mutualistic relationship occurring on a massive scale within the bay.
The Floating lab and docks provide a great amount of substrate on which a variety of organisms attach. These areas have also been useful for the science classes in providing areas for hanging baskets for aquaculture experiments. Within easy access there is a rich fouling community which provides many specimens used in classes. Almost every invertebrate phylum is represented on the underside of these docks. The plankton of Pedder Bay form the nutritional and energy base of the ecosystem.The file in the list of exercises. below provides a lab assignment on quantification of plankton biodiversity .
===========================================================
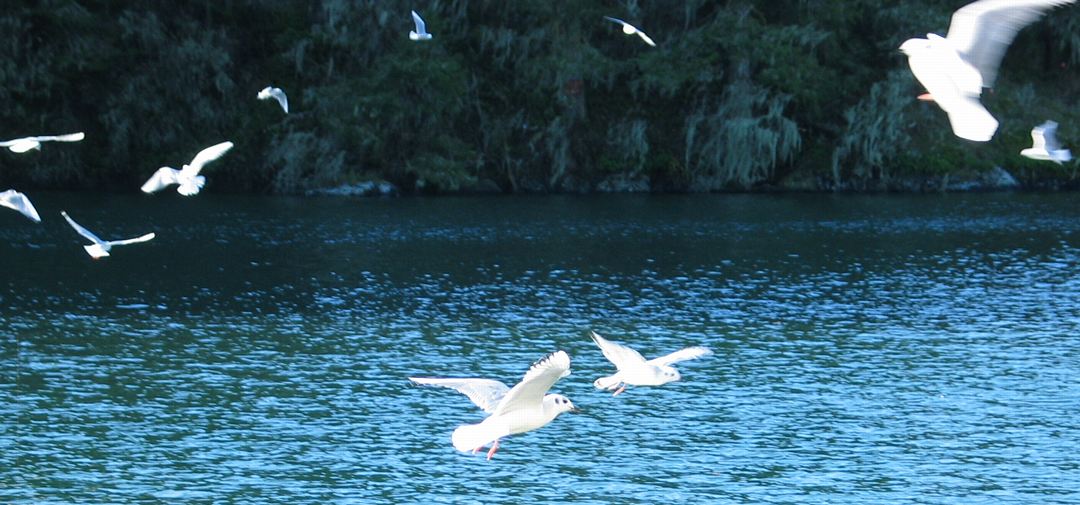
THE BIRDS of PEDDER BAY
-

-
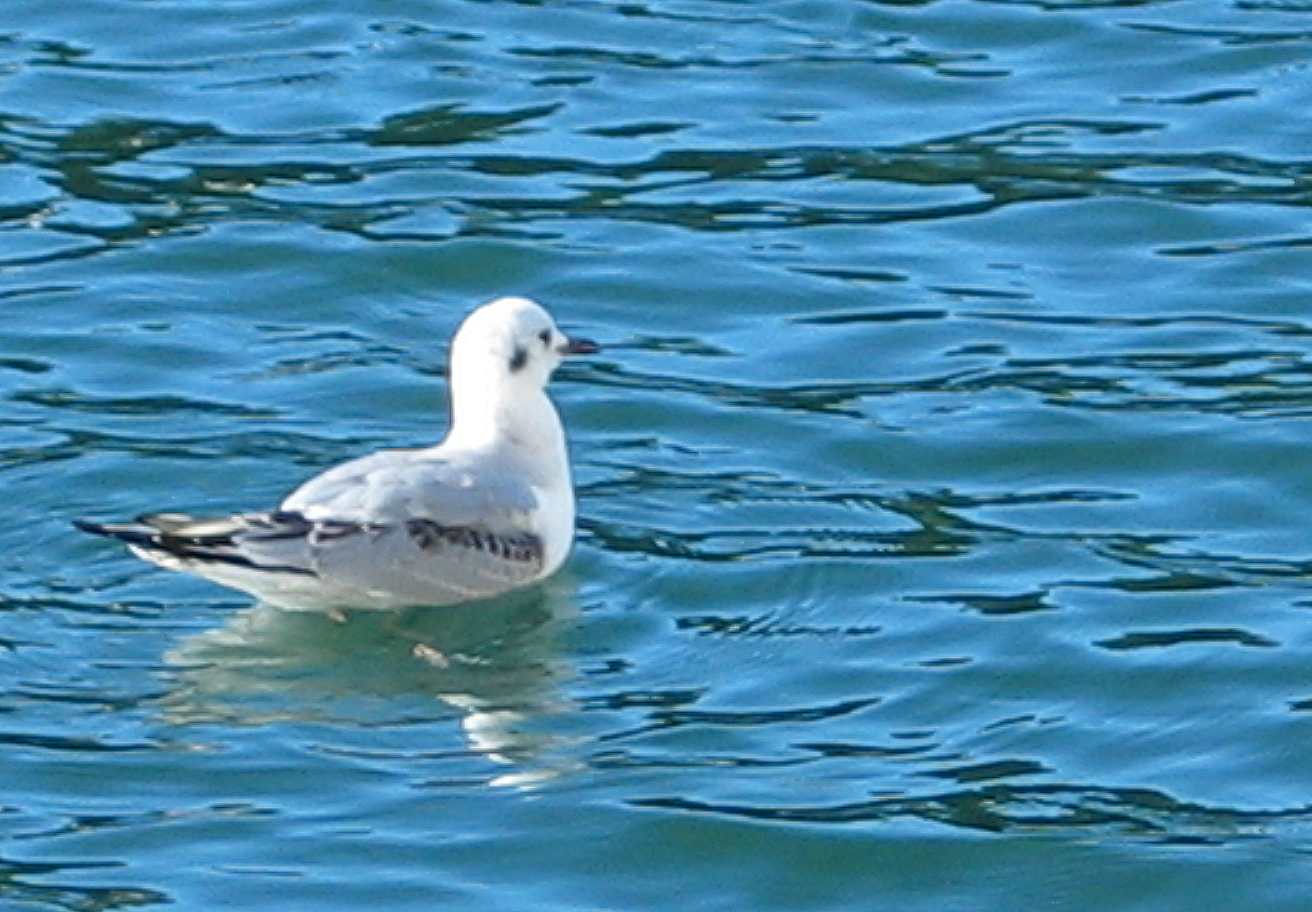
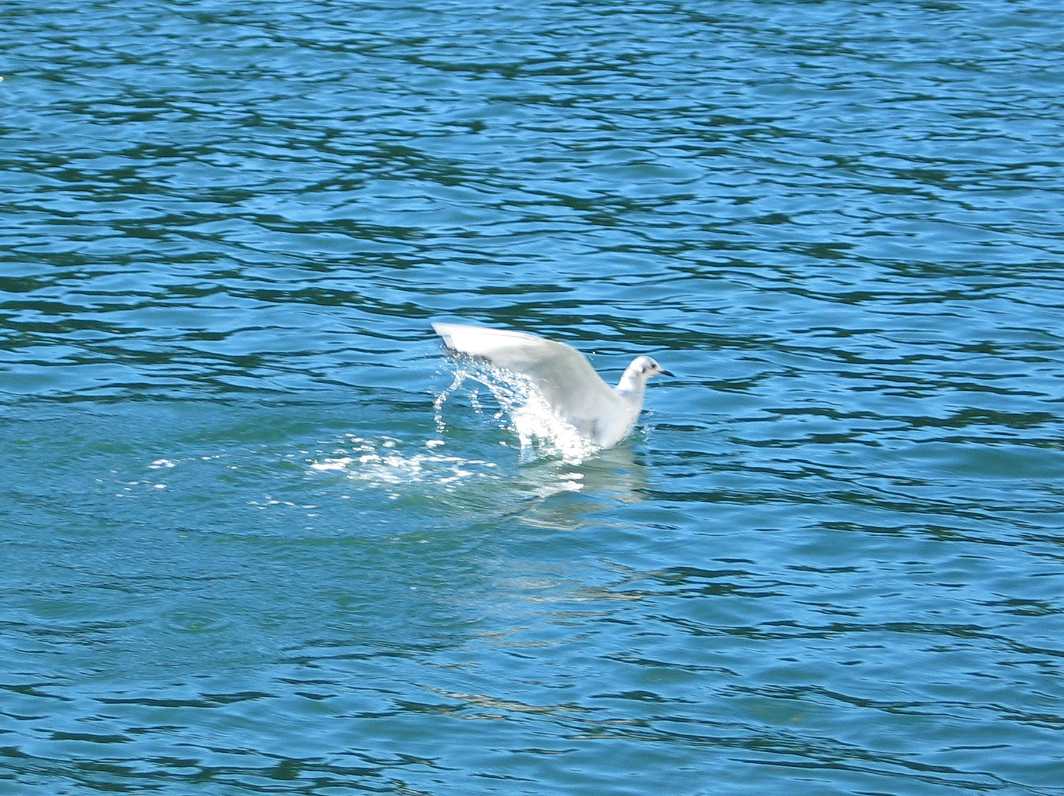
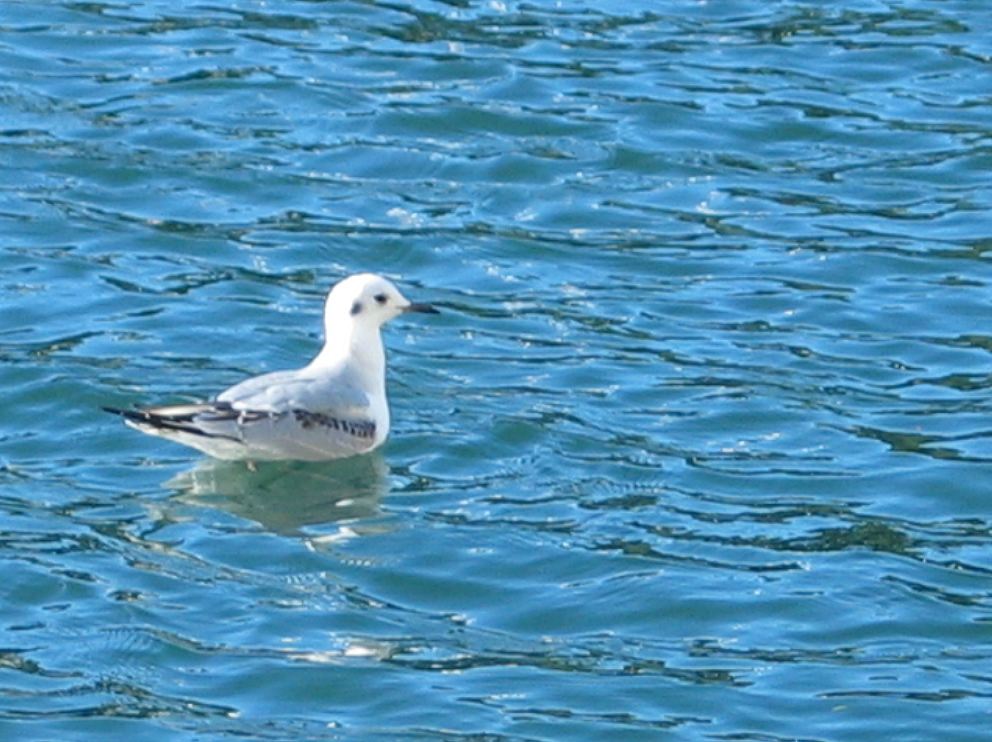
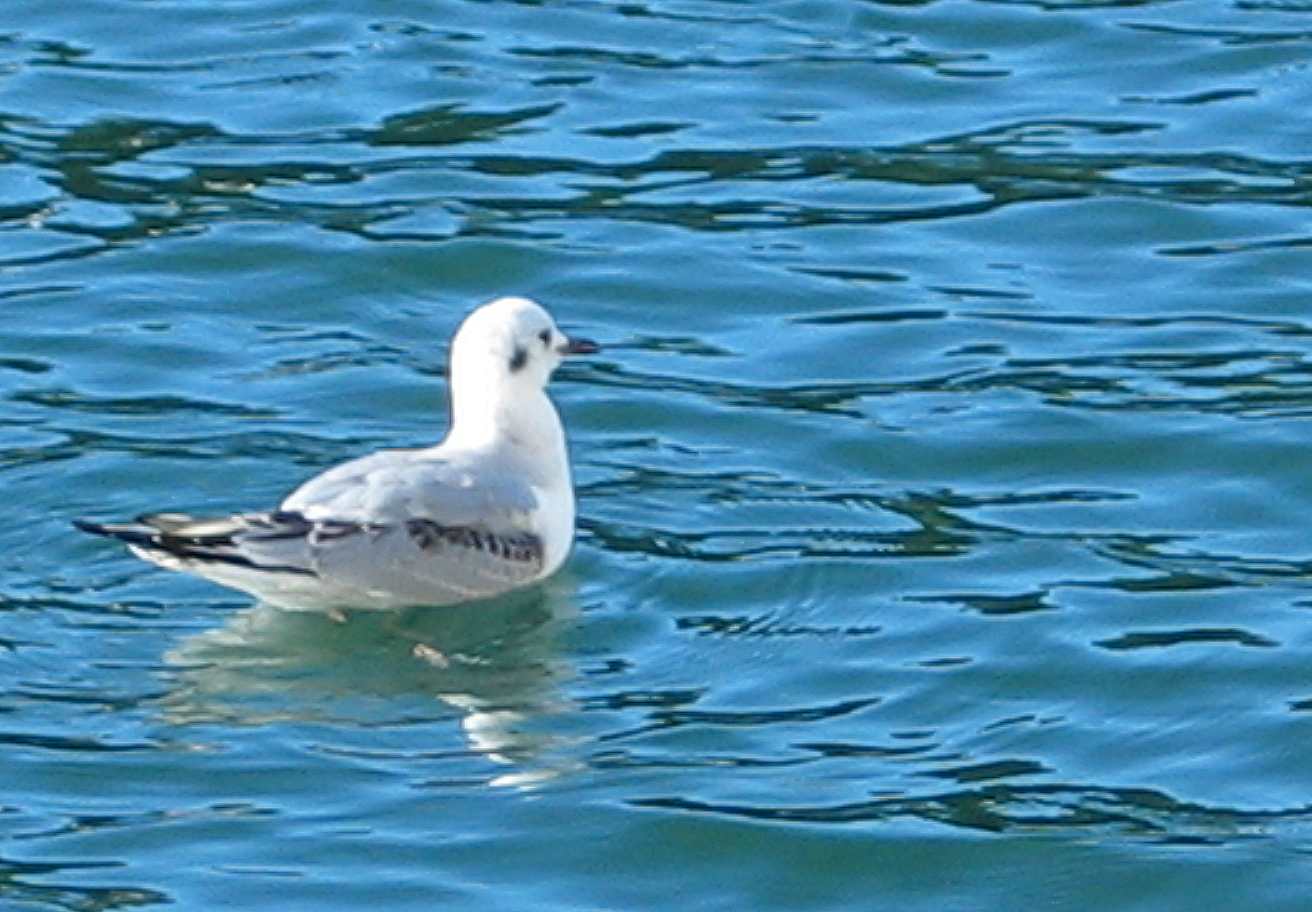
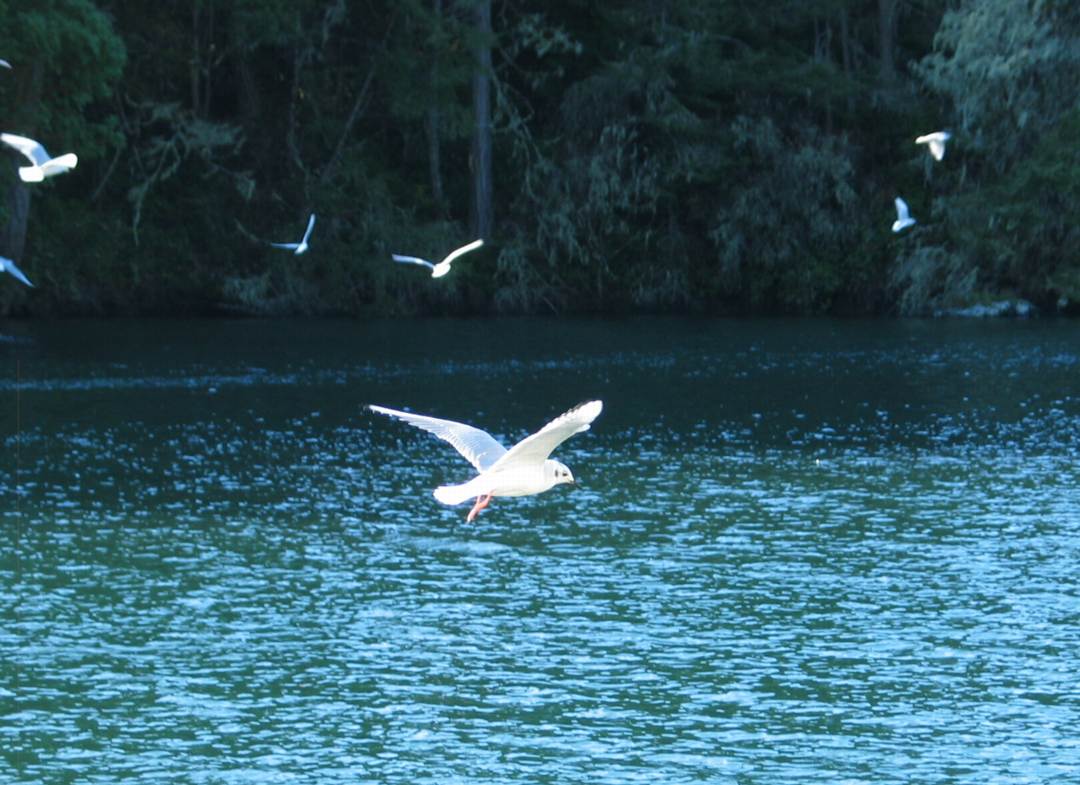
In November of 2008, The Bonapartes Gulls
-

-
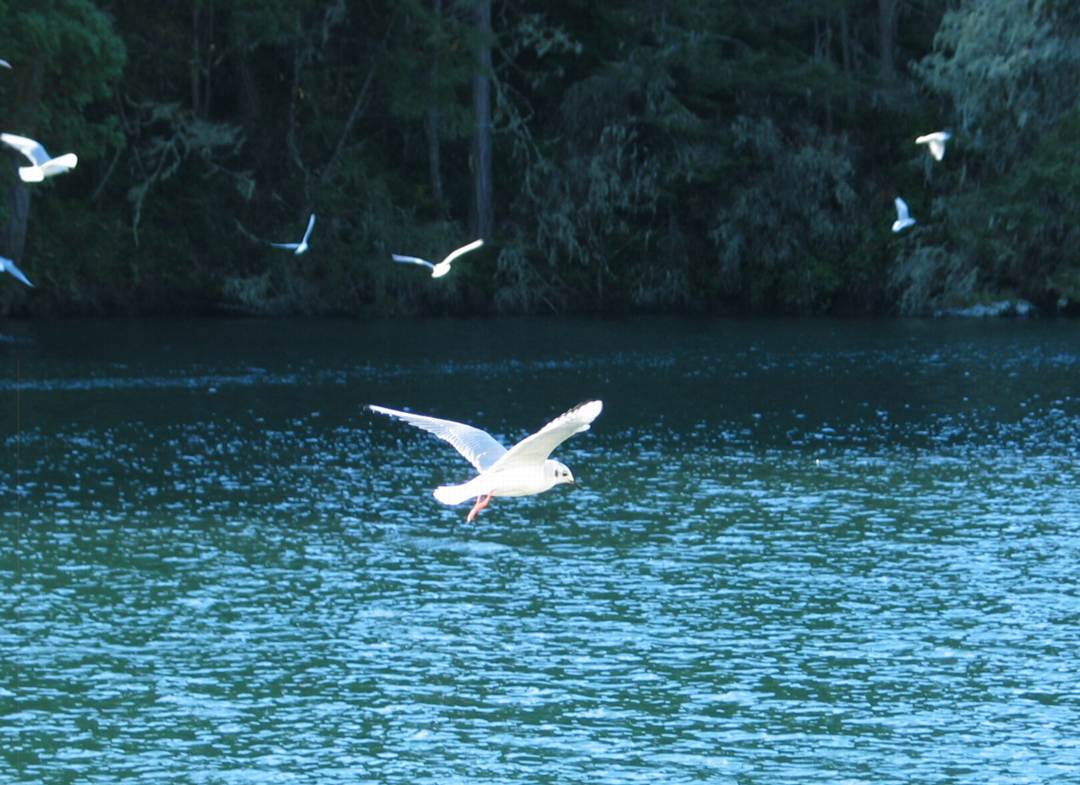
stayed for several days diving and feeding on the herring balls
-

-
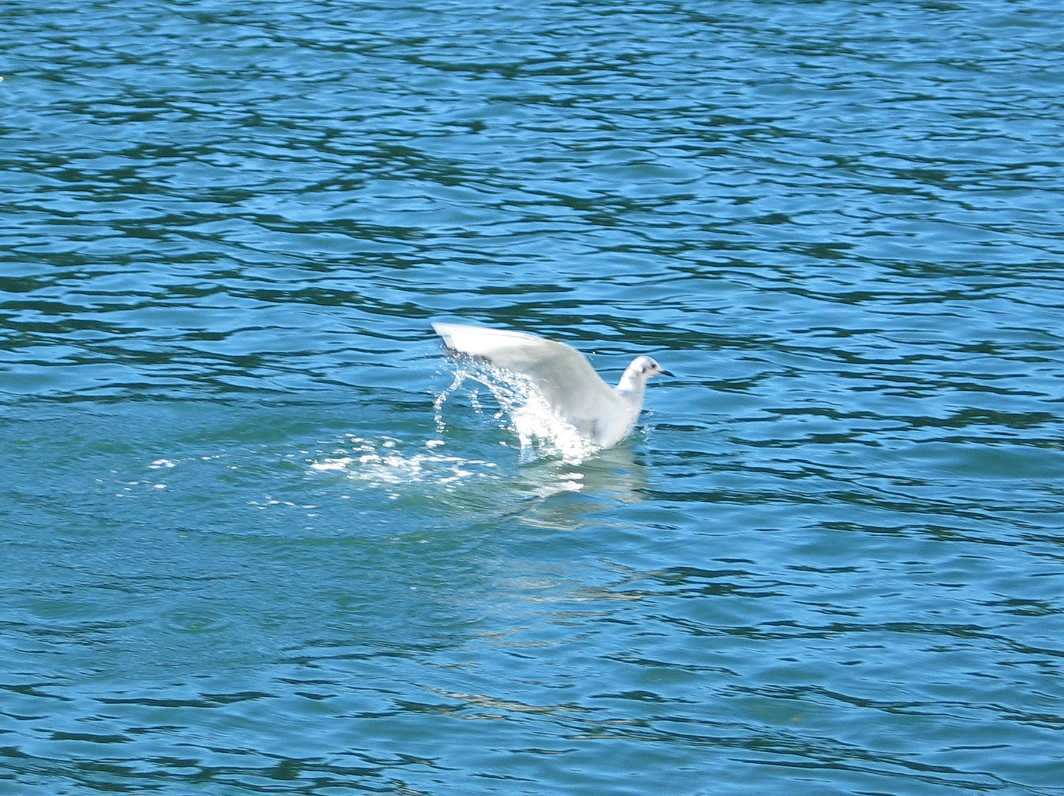
and other forage fish around the docks at Pearson College
-

-

-

-

-
Bufflehead, (Bucephala albeola) a common overwintering duck in the Bay.
-

-
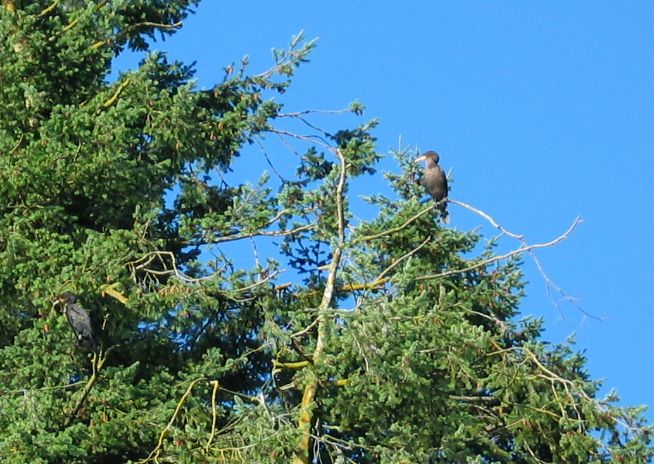
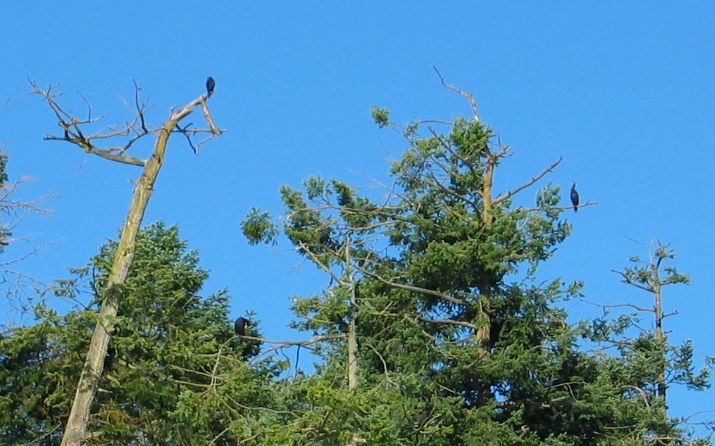
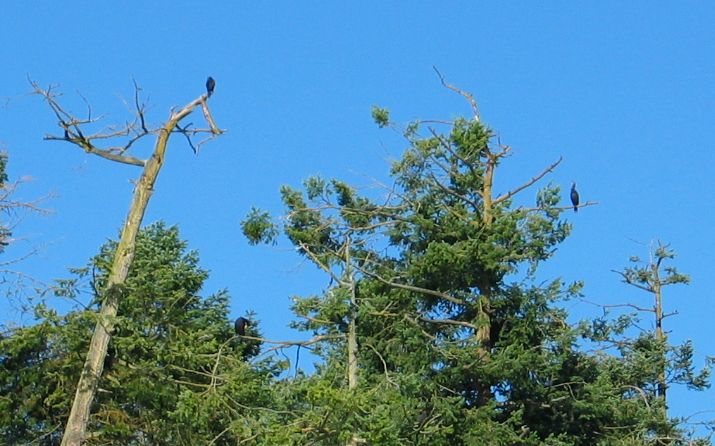
Cormorant Winter Roost: Note the trees are being stripped of the top branches as they make way for more comfortable perches
-

-
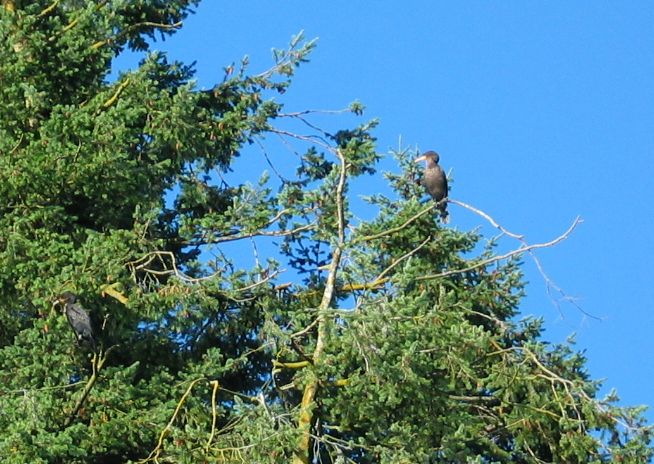
Juvenile Double Crested Cormorant on the right , adult , the darker one to the left.
-

-
Great Blue Heron standing on the docks at Pearson College
-

-
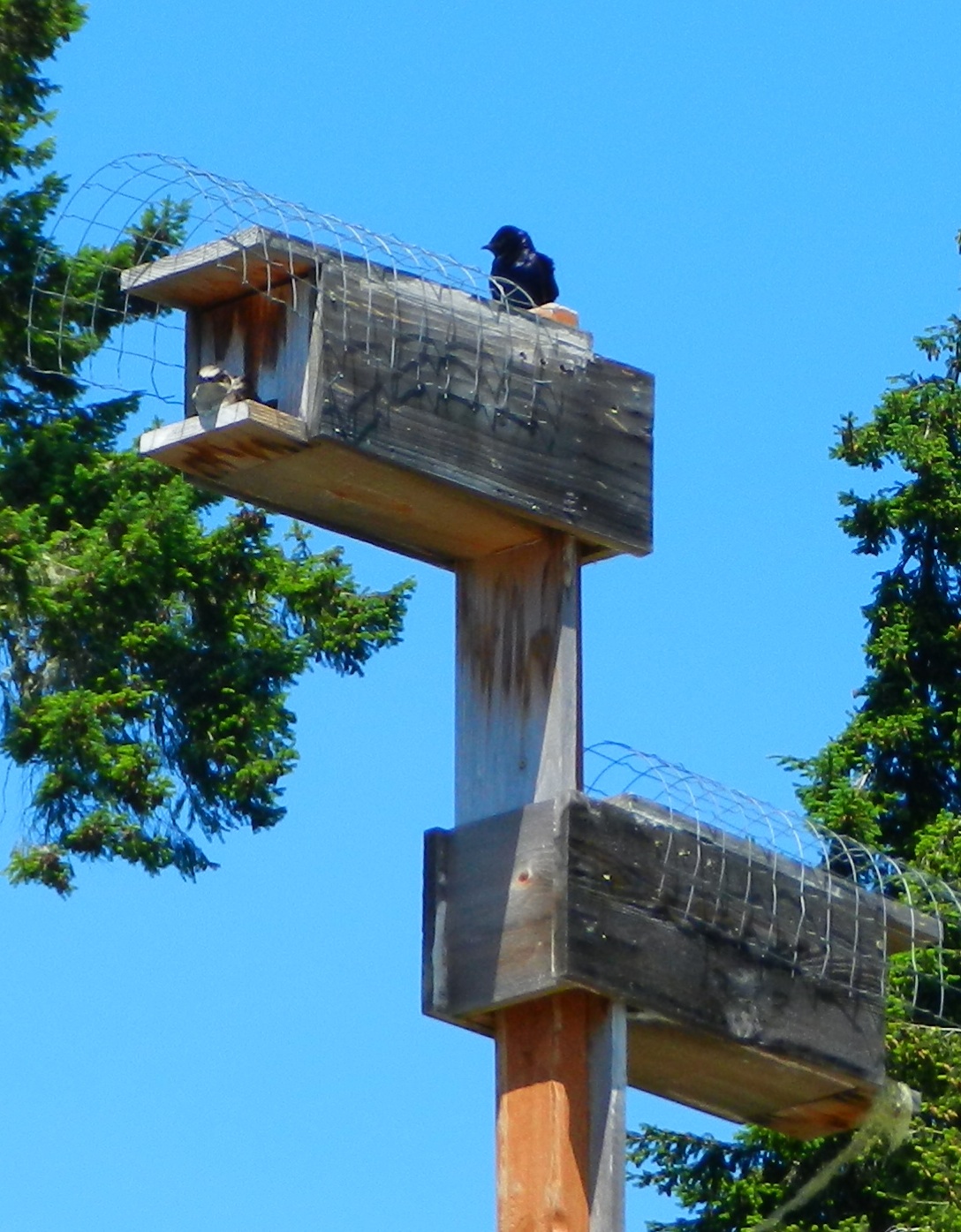
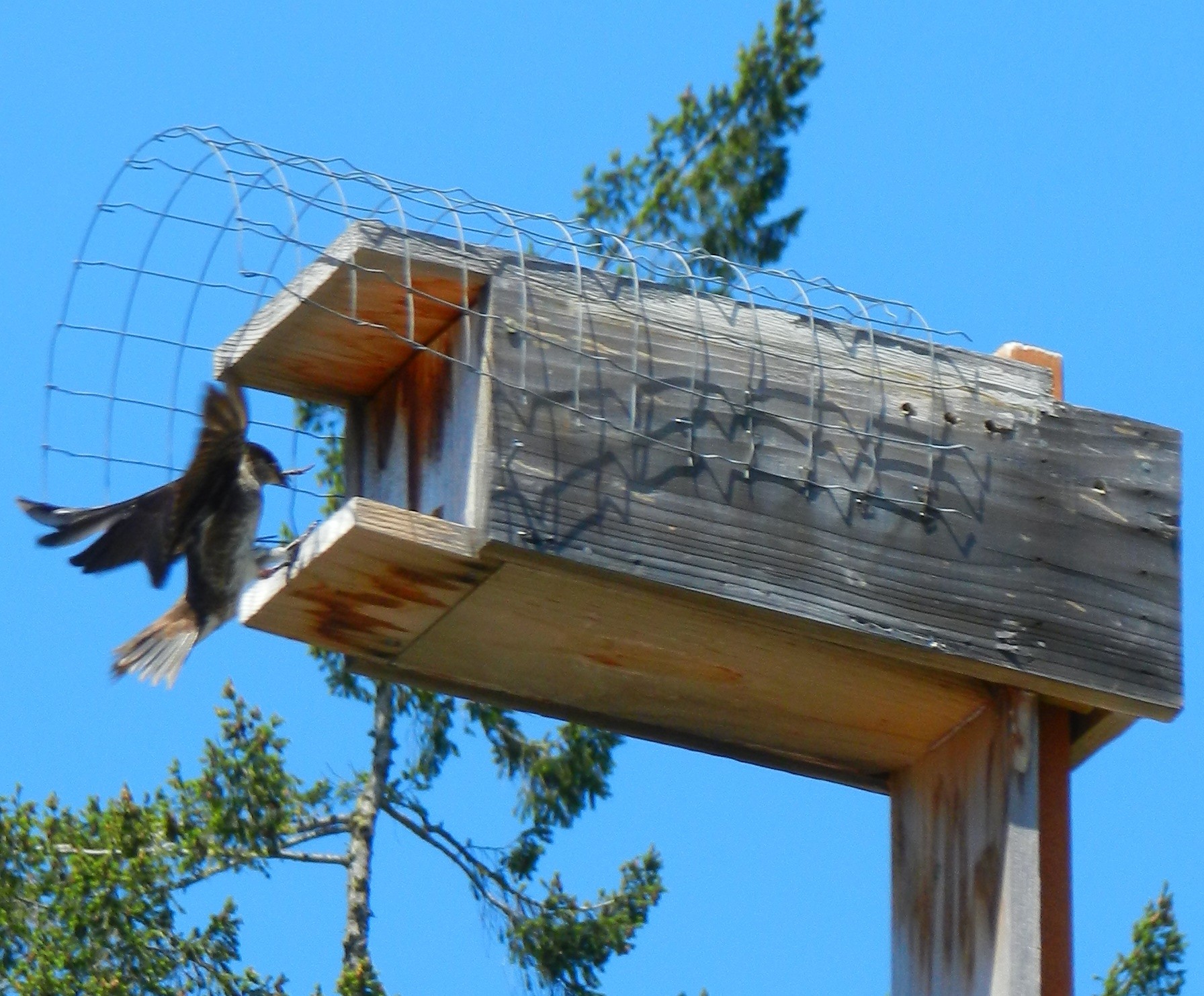
Purple martins in nest boxes
-

-
Pearson College Docks
========================================================
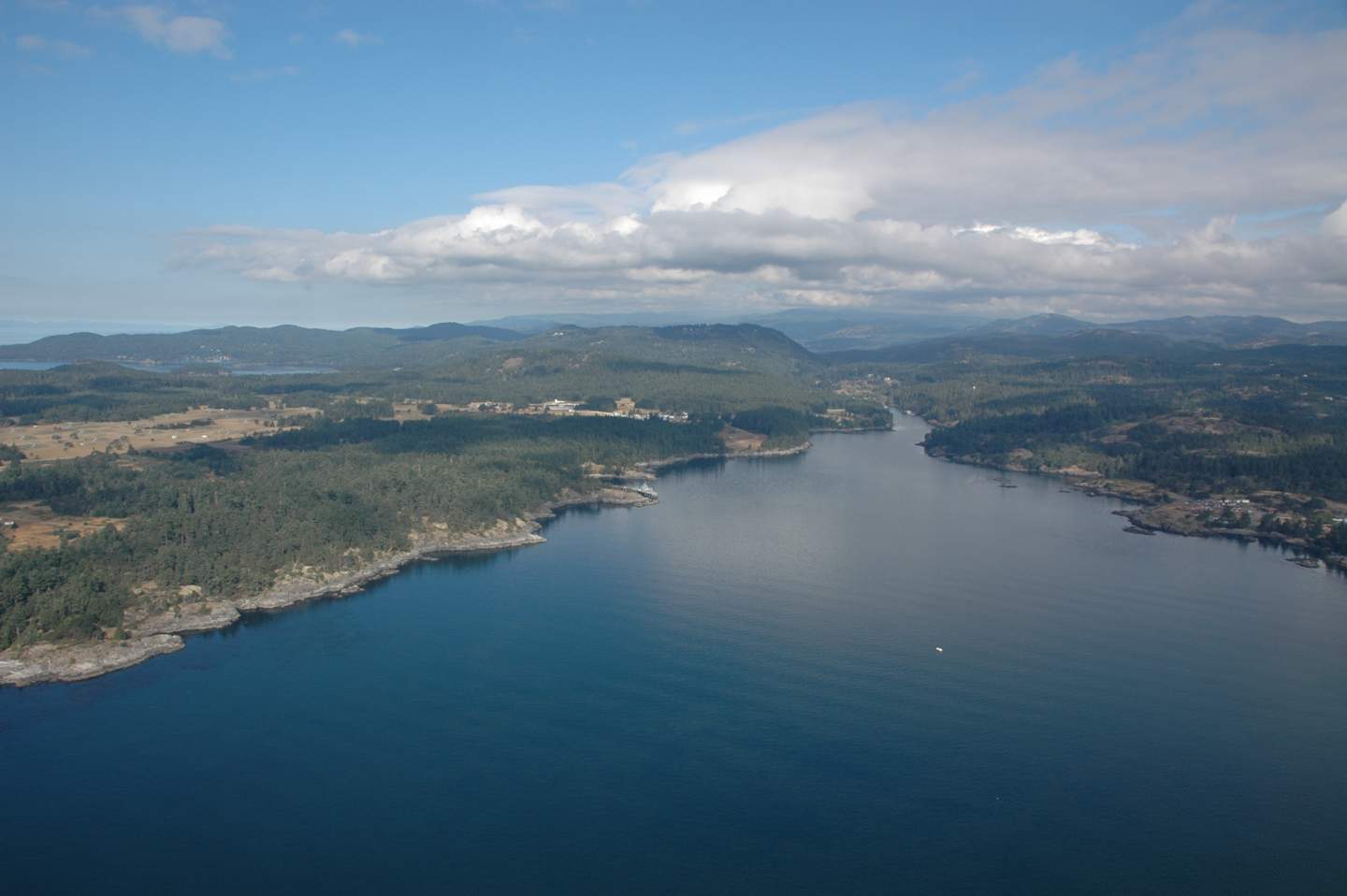
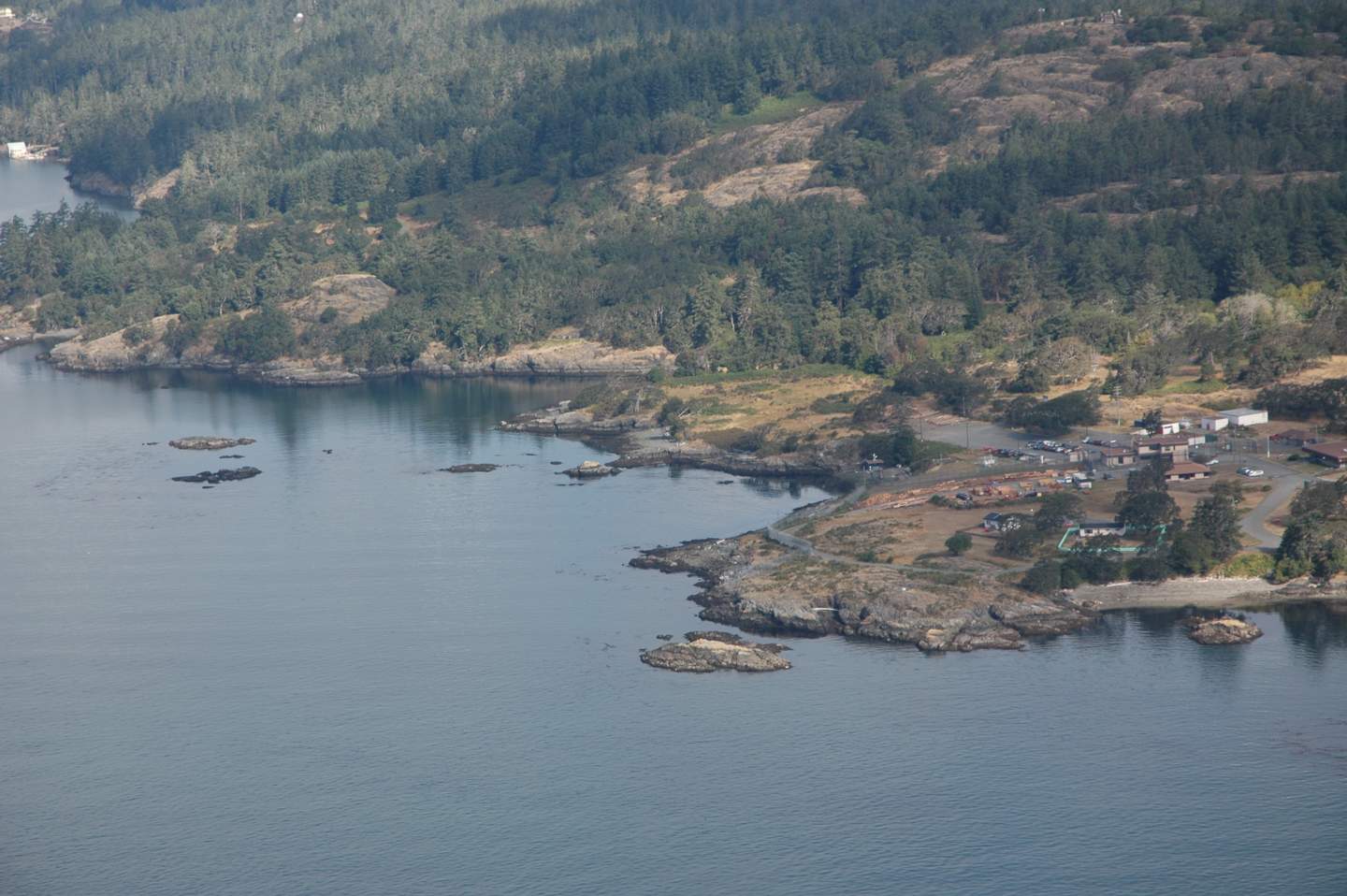
Starting on the outer South Shore of Pedder Bay at Cape Calver , this review will take you into the bay and around the shores and out to the North side and William Head
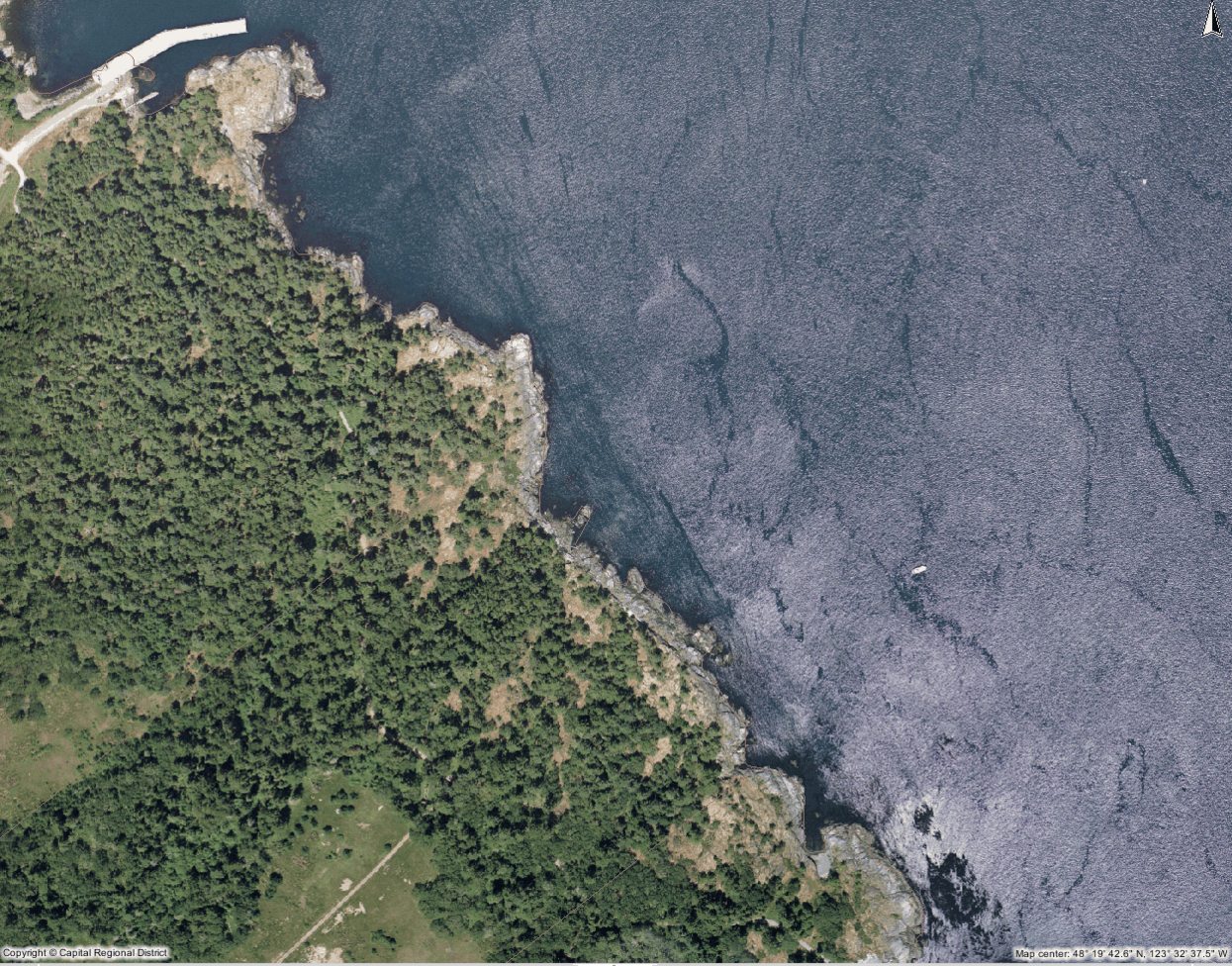 MANOR and FOSSIL POINT TO CAPE CALVER :
MANOR and FOSSIL POINT TO CAPE CALVER :
ROCKY COASTLINE..
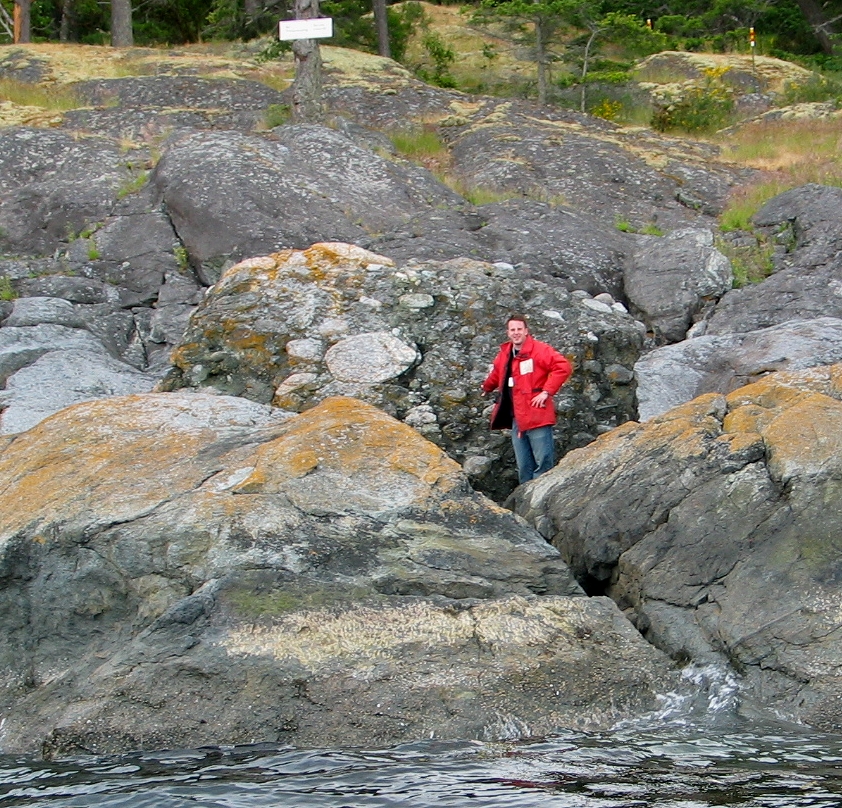
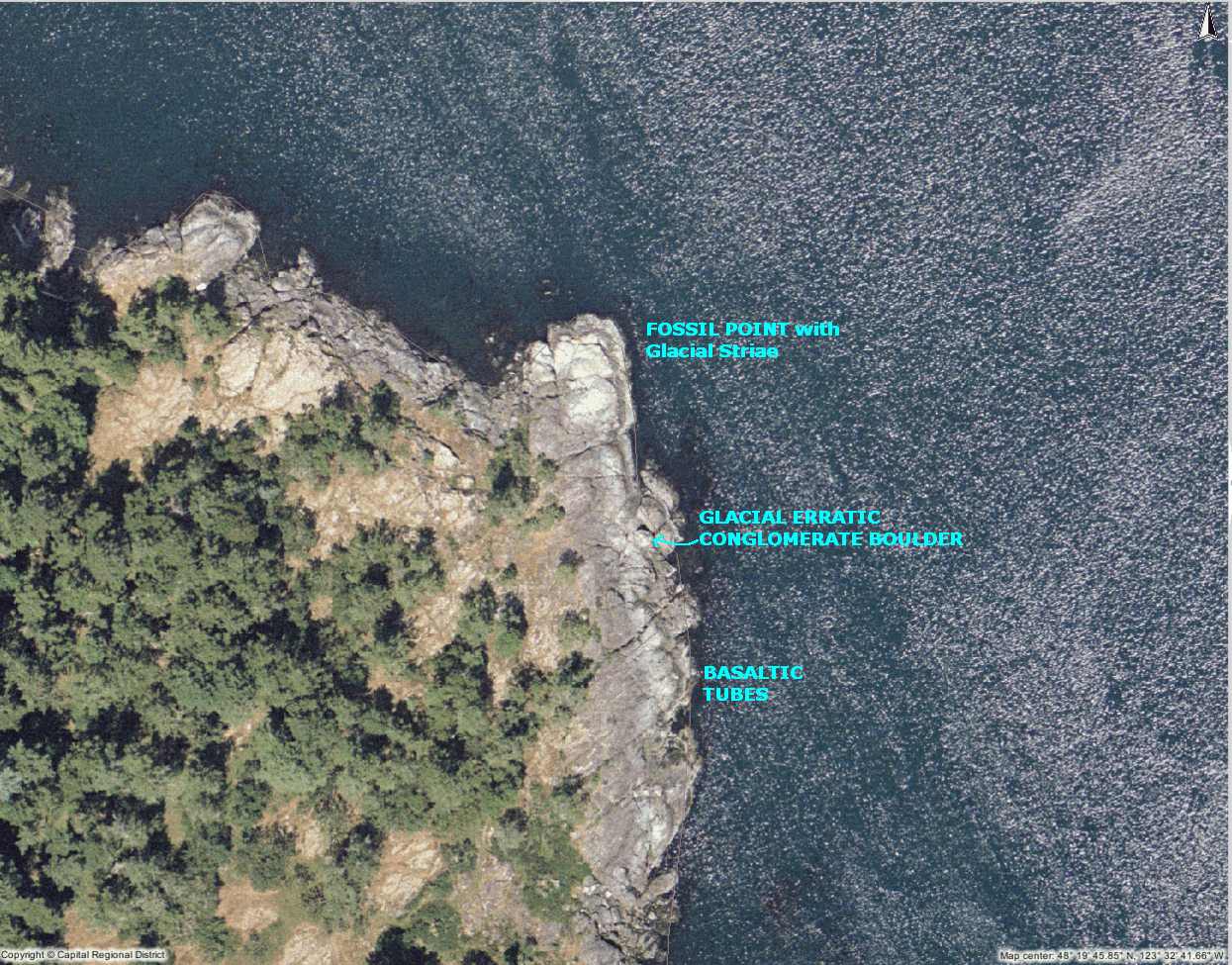
This section is notable mainly for its geological features. Here there is evidence of the most recent glaciation of 10,000 years ago: a massive conglomerate boulder on the shore and the glacial striae or grooves on the rock of the coastline. In other parts of the bay, granite boulders add to the collection of bits of glacial evidence
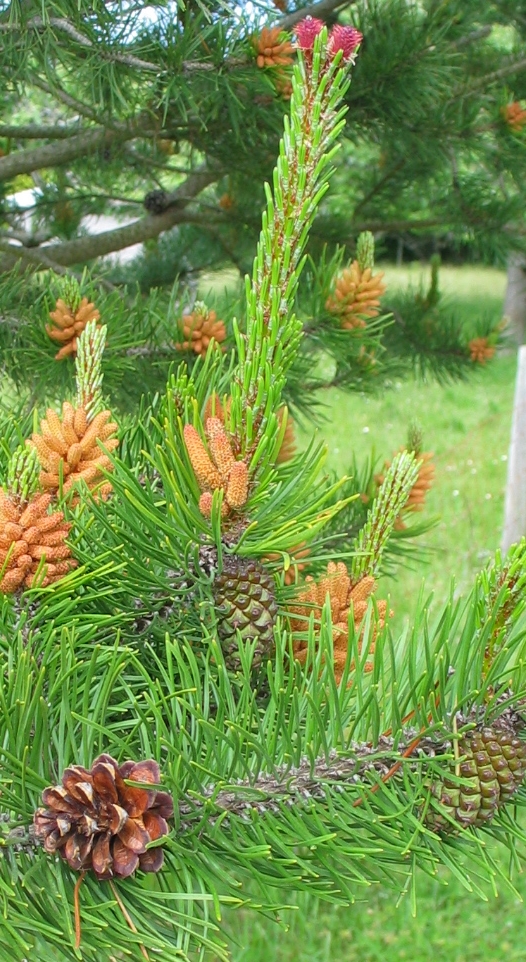
 Shore pine, Pinus contorta , penetrates along the shore into Pedder Bay from the outer parts of Rocky Point. In this outer section, salt spray is received above the intertidal zone in winter storms from the north east. The fetch, or distance across the ocean upon which the wind can impart energy in a storm is well over 50 kilometers for this outer section if a line is drawn from Cape Calver to a point in the open ocean beyond Victoria. Further into the bay from Fossil Point where there are more protected shores, the predominant tree cover is Douglas fir, and trees can grow closer to the water.
Shore pine, Pinus contorta , penetrates along the shore into Pedder Bay from the outer parts of Rocky Point. In this outer section, salt spray is received above the intertidal zone in winter storms from the north east. The fetch, or distance across the ocean upon which the wind can impart energy in a storm is well over 50 kilometers for this outer section if a line is drawn from Cape Calver to a point in the open ocean beyond Victoria. Further into the bay from Fossil Point where there are more protected shores, the predominant tree cover is Douglas fir, and trees can grow closer to the water.
-

-
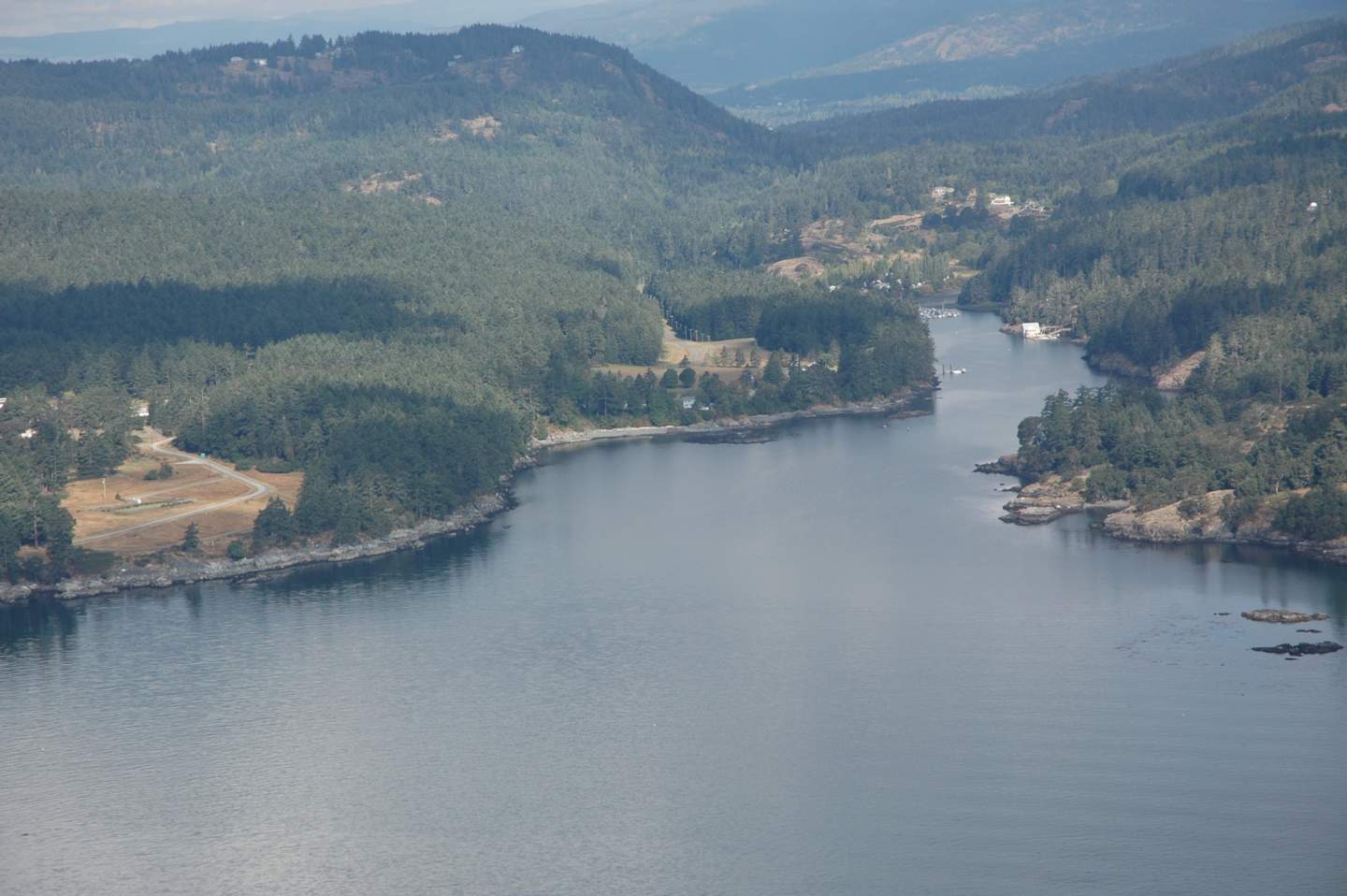

-
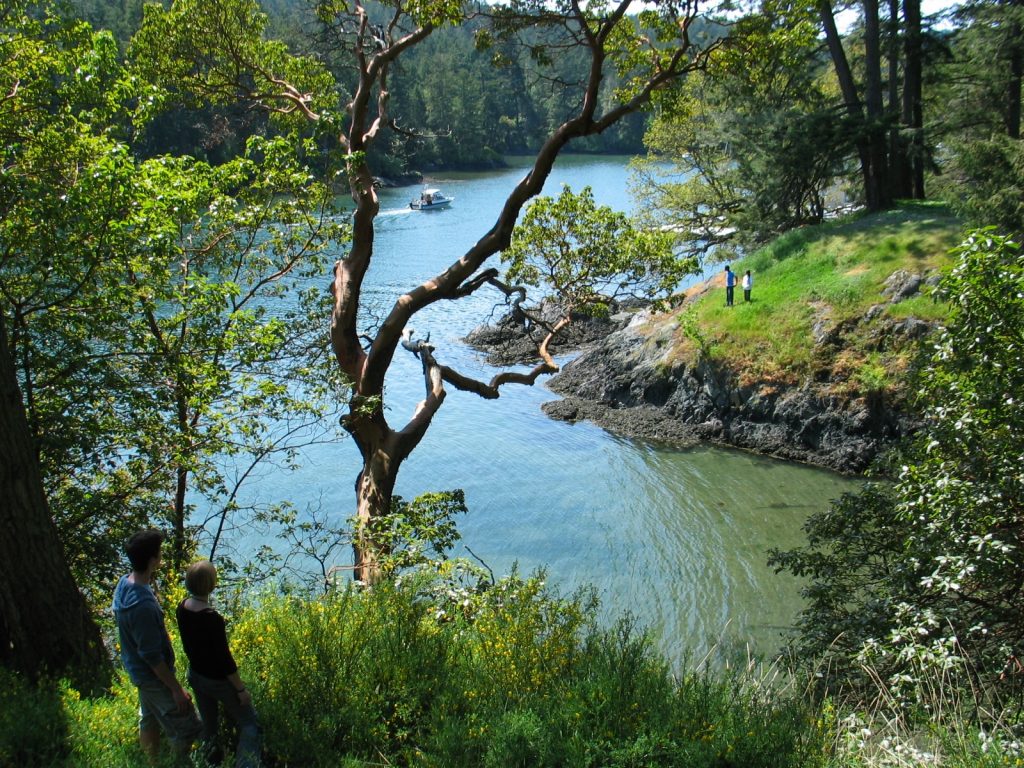
The inner mouth of Pedder bay with Pearson College docks on the right,
-
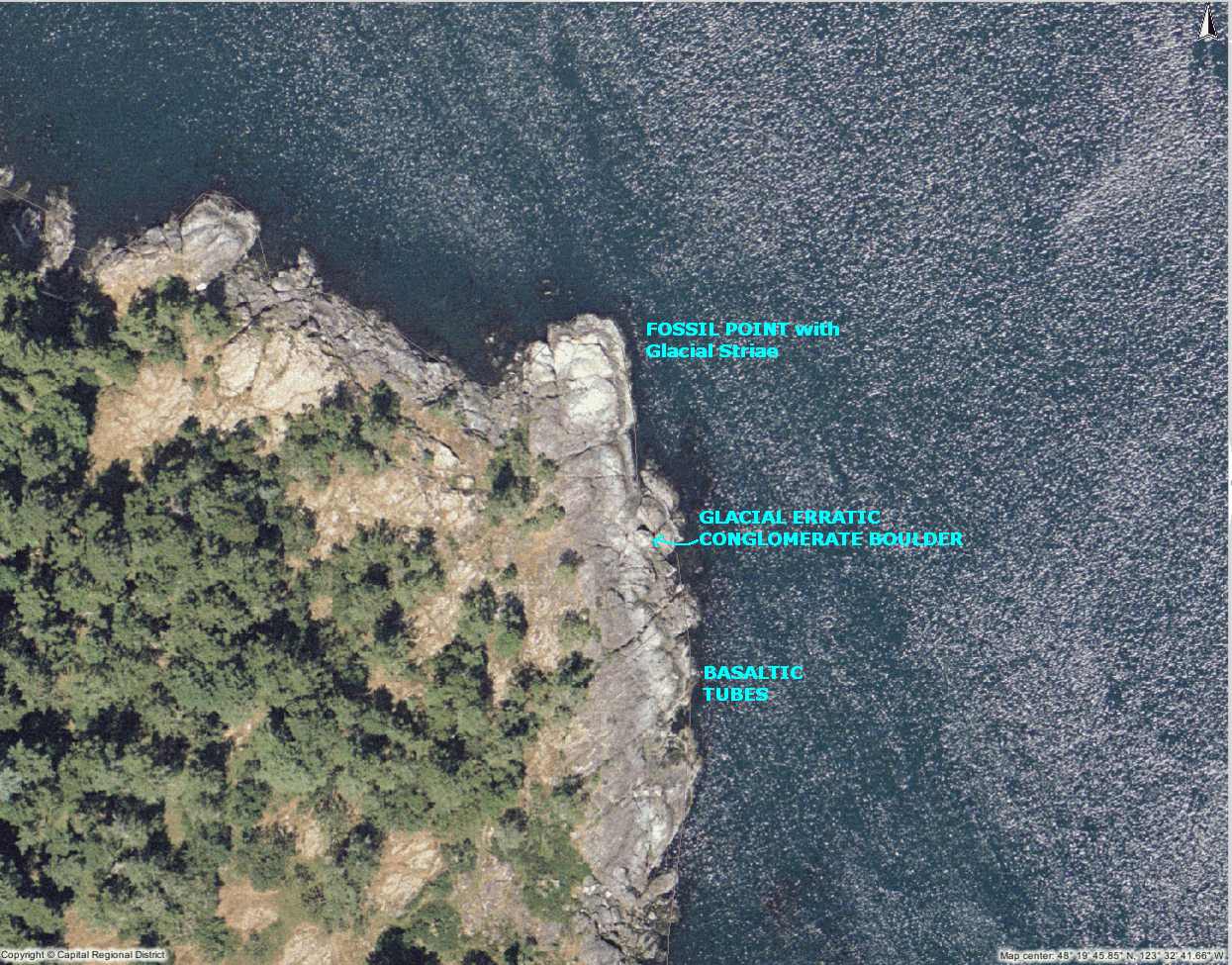

-
Map of Fossil Point and Area
-
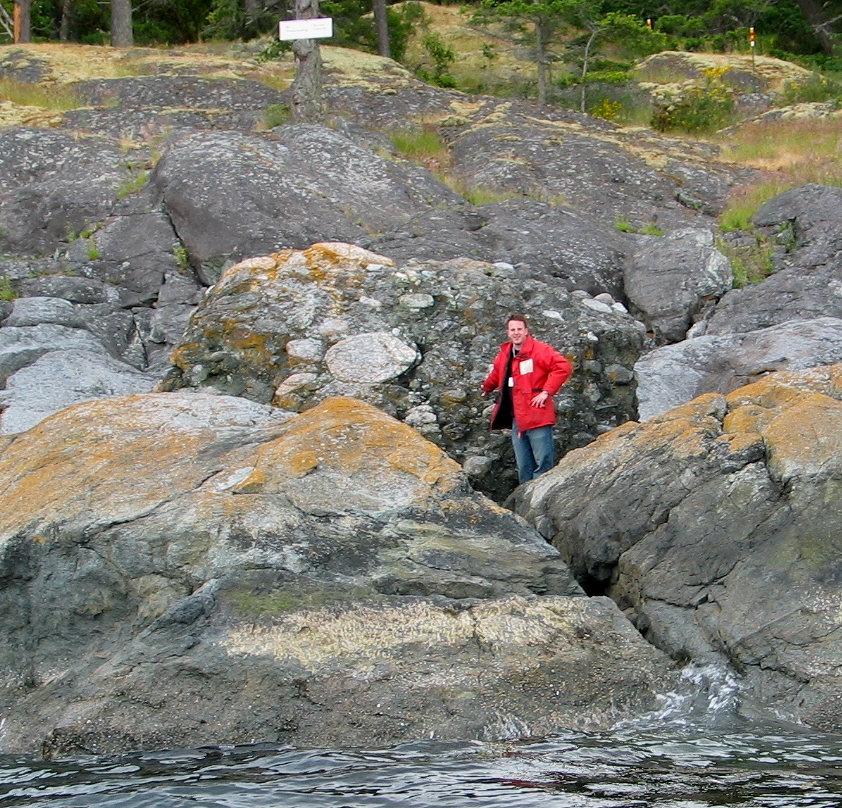

-
Glacial erratic : A large conglomerate boulder near Fossil Point.
-
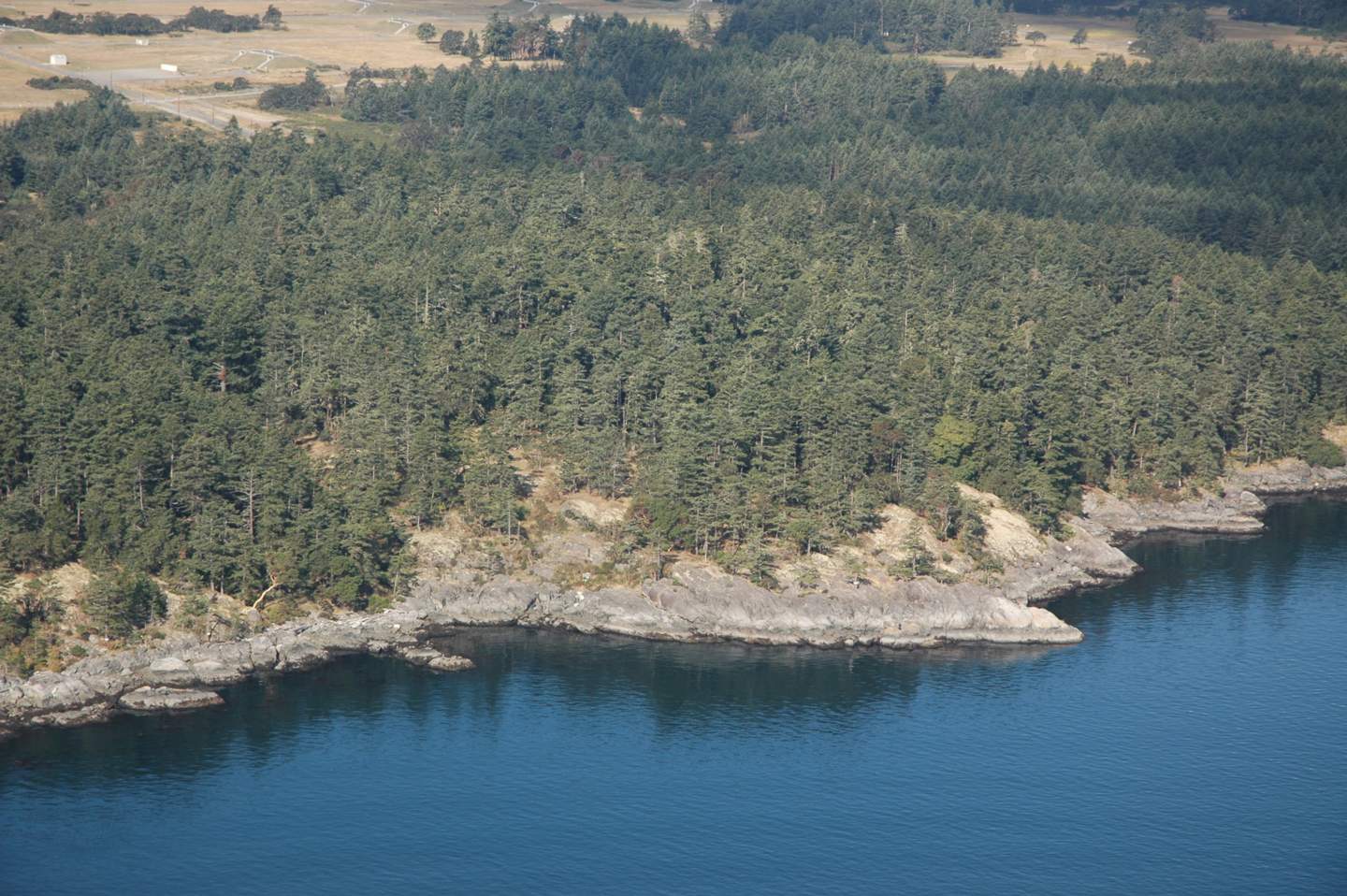

-
Cape Cal;ver to Fossil Point
-

-
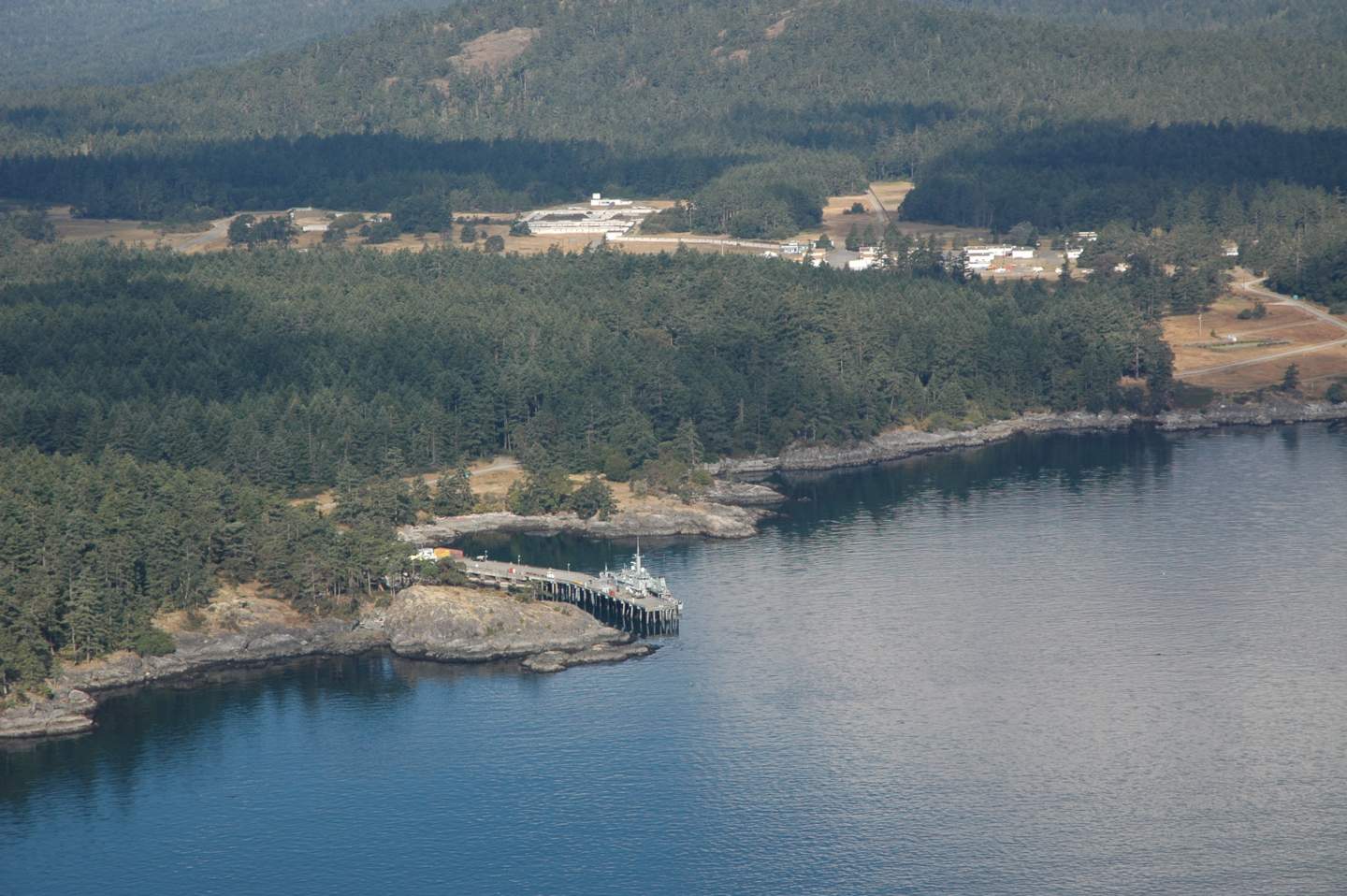
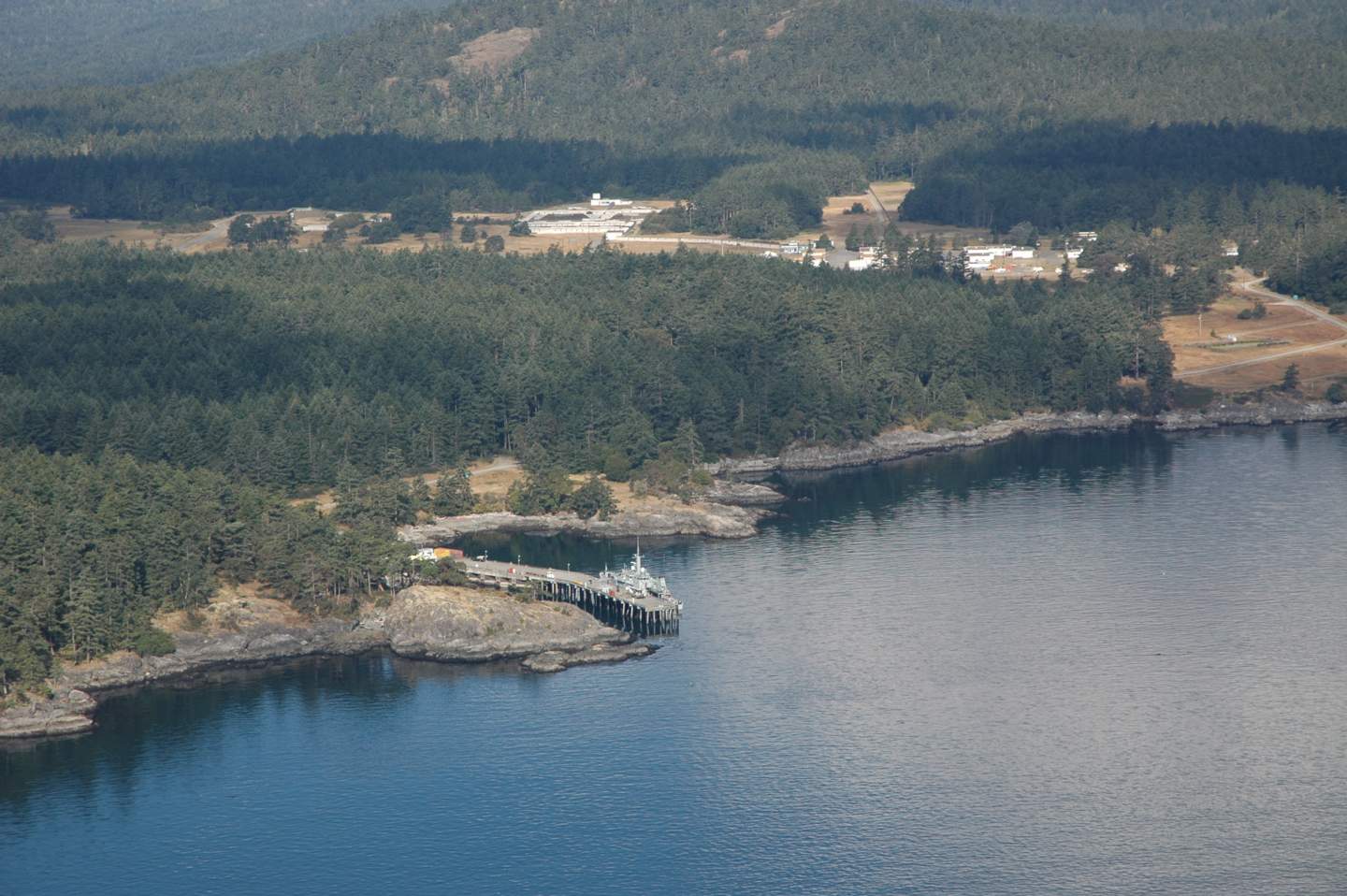
DND Jetty
-

-
Helgesen Point
-

-
The inner mouth of Pedder bay with Pearson College docks on the right
-
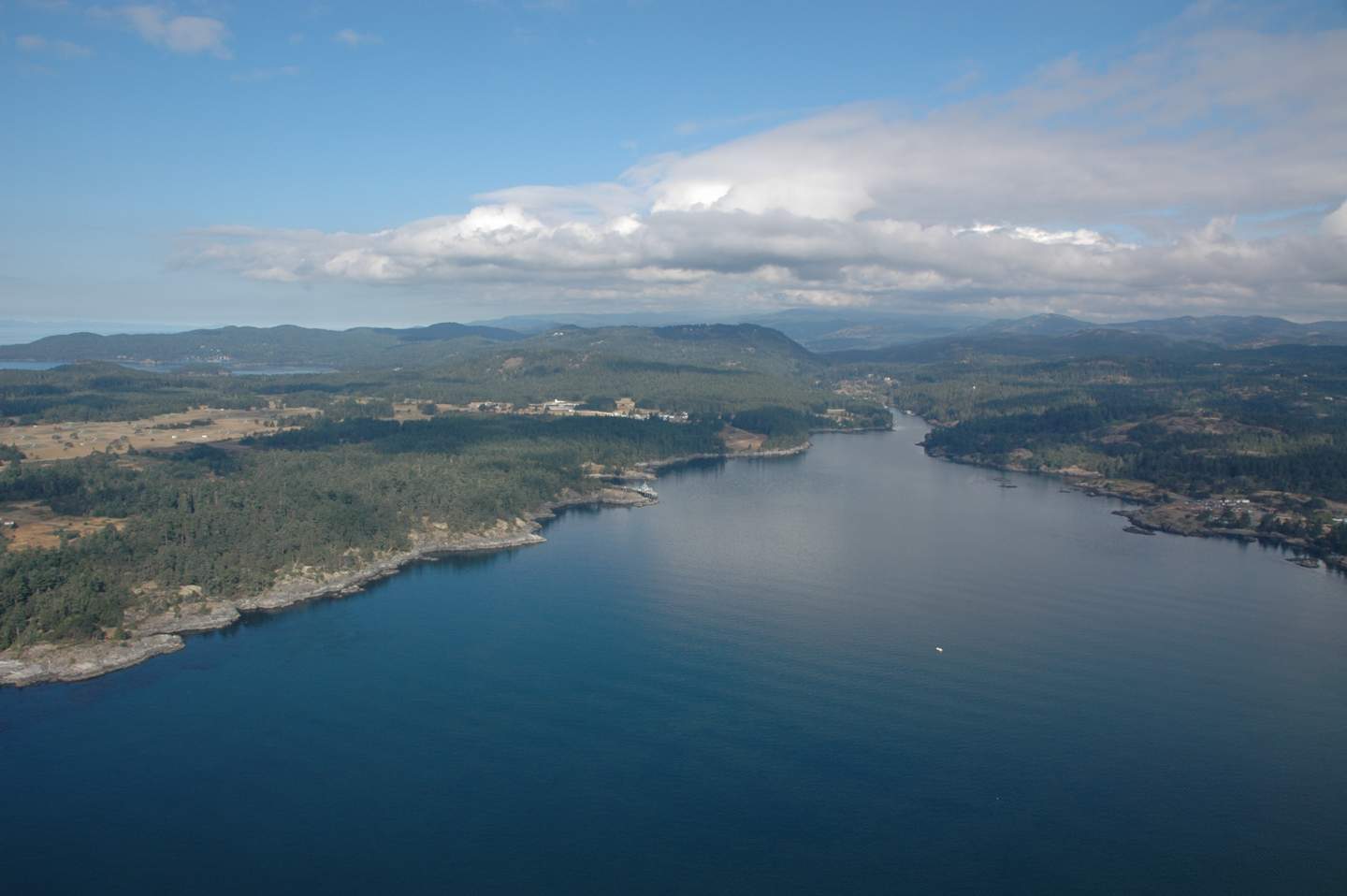

-
The outer mouth of Pedder Bay, Cape Calver on the left
=======================================================
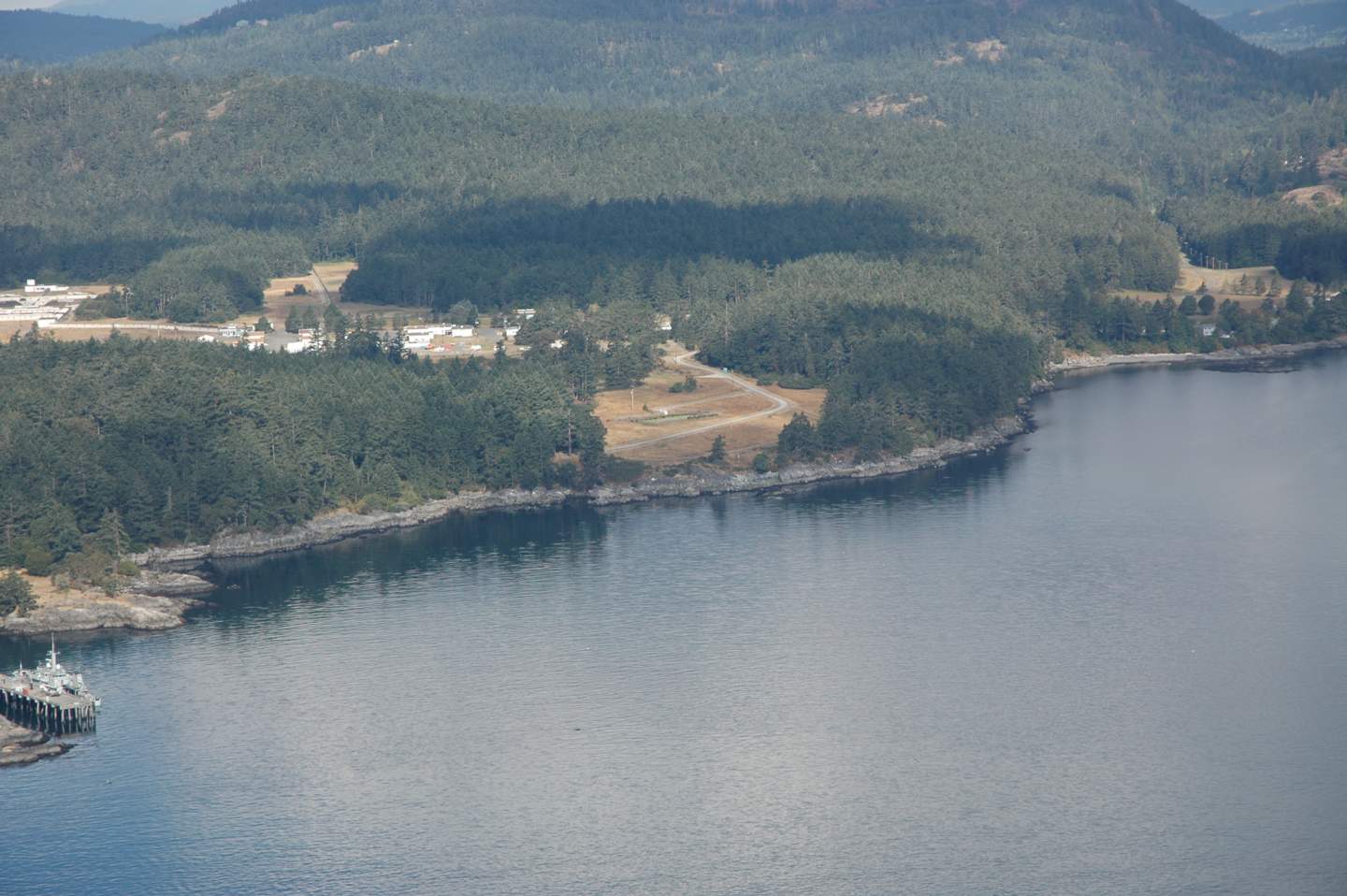
 DND RESIDENCES TO JETTY SHORELINE
DND RESIDENCES TO JETTY SHORELINE
======================================================
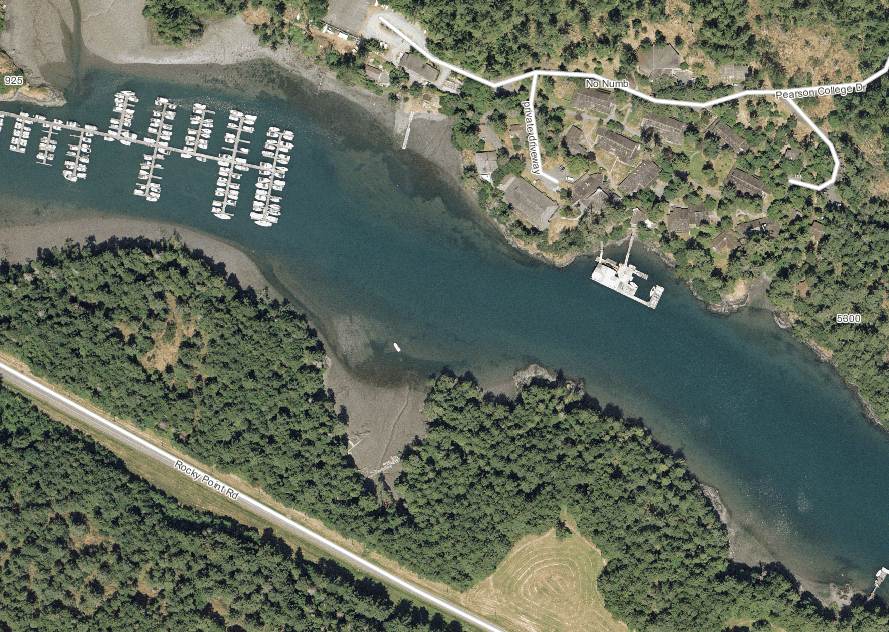 PEARSON COLLEGE DOCKS AND SHORELINE
PEARSON COLLEGE DOCKS AND SHORELINE
========================================================
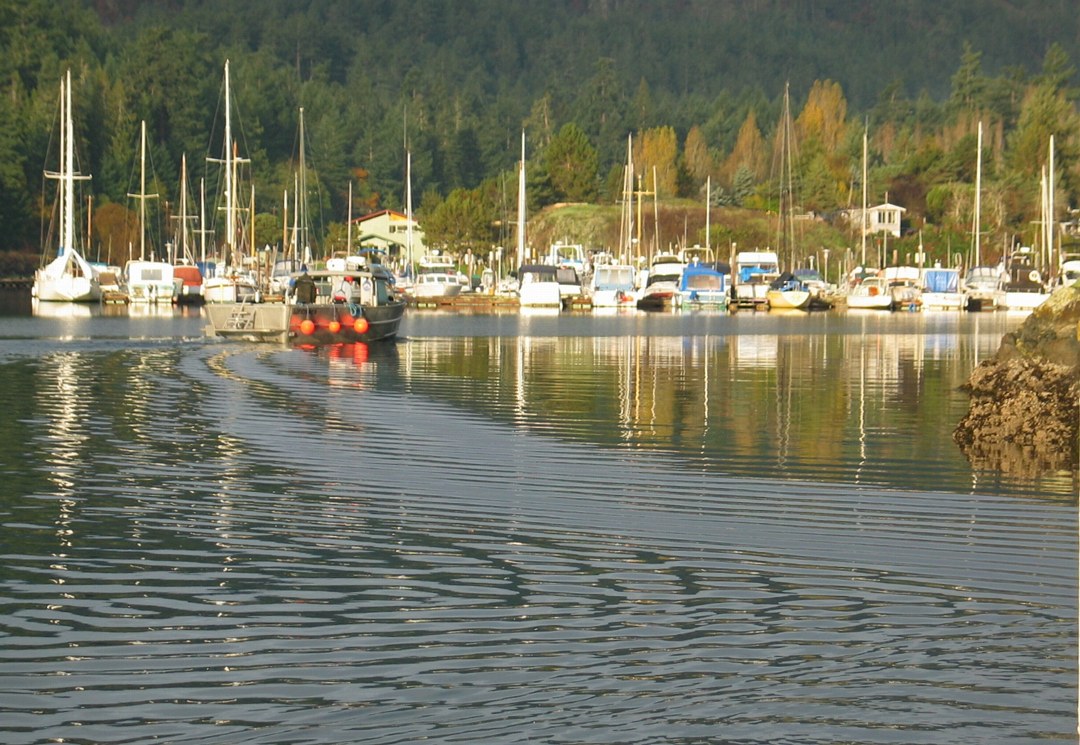
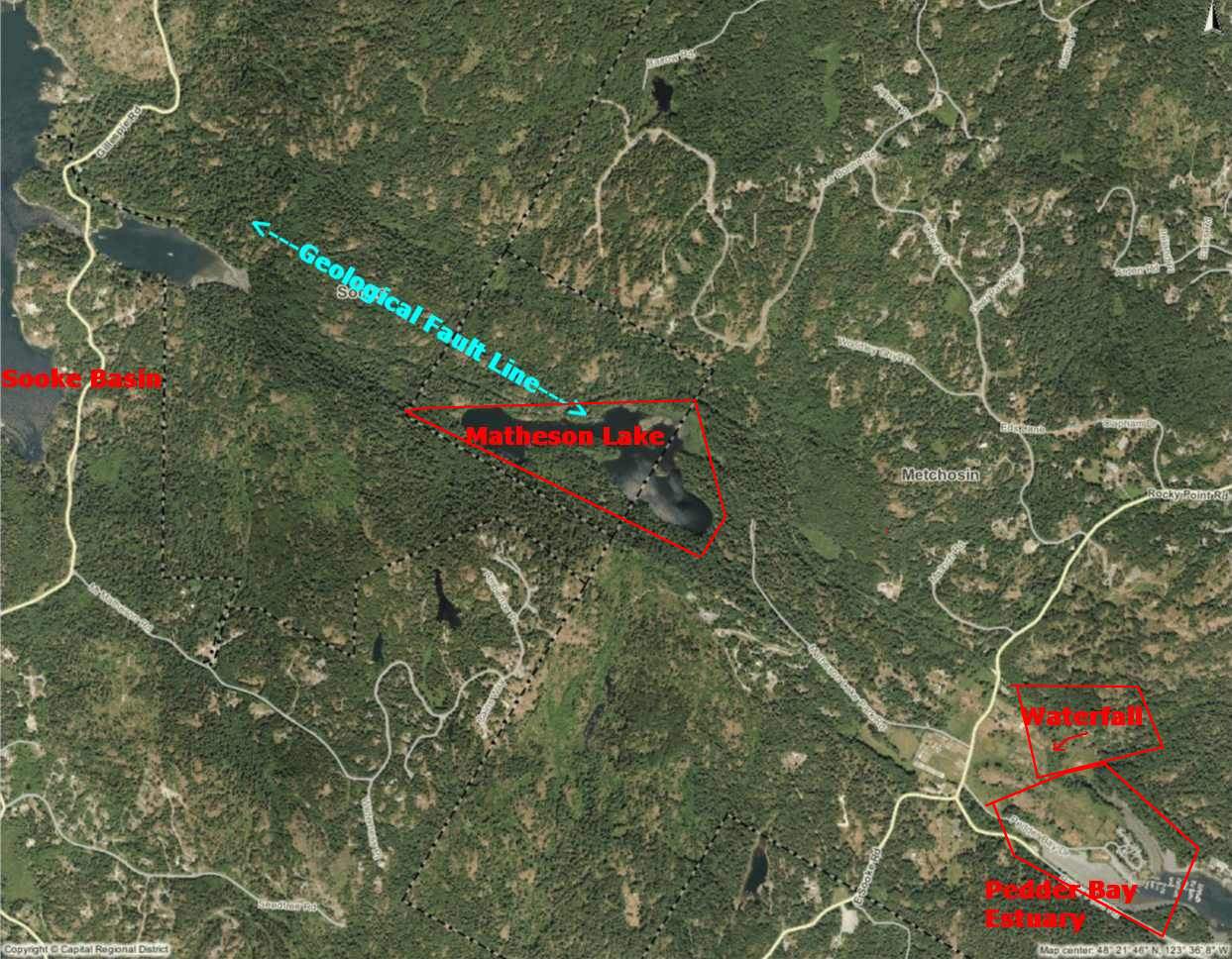 Pedder Bay Marina to estuary , waterfall and Matheson Lake
Pedder Bay Marina to estuary , waterfall and Matheson Lake
Aerial Map Courtesy of the CRD Natural Areas Atlas
-

-
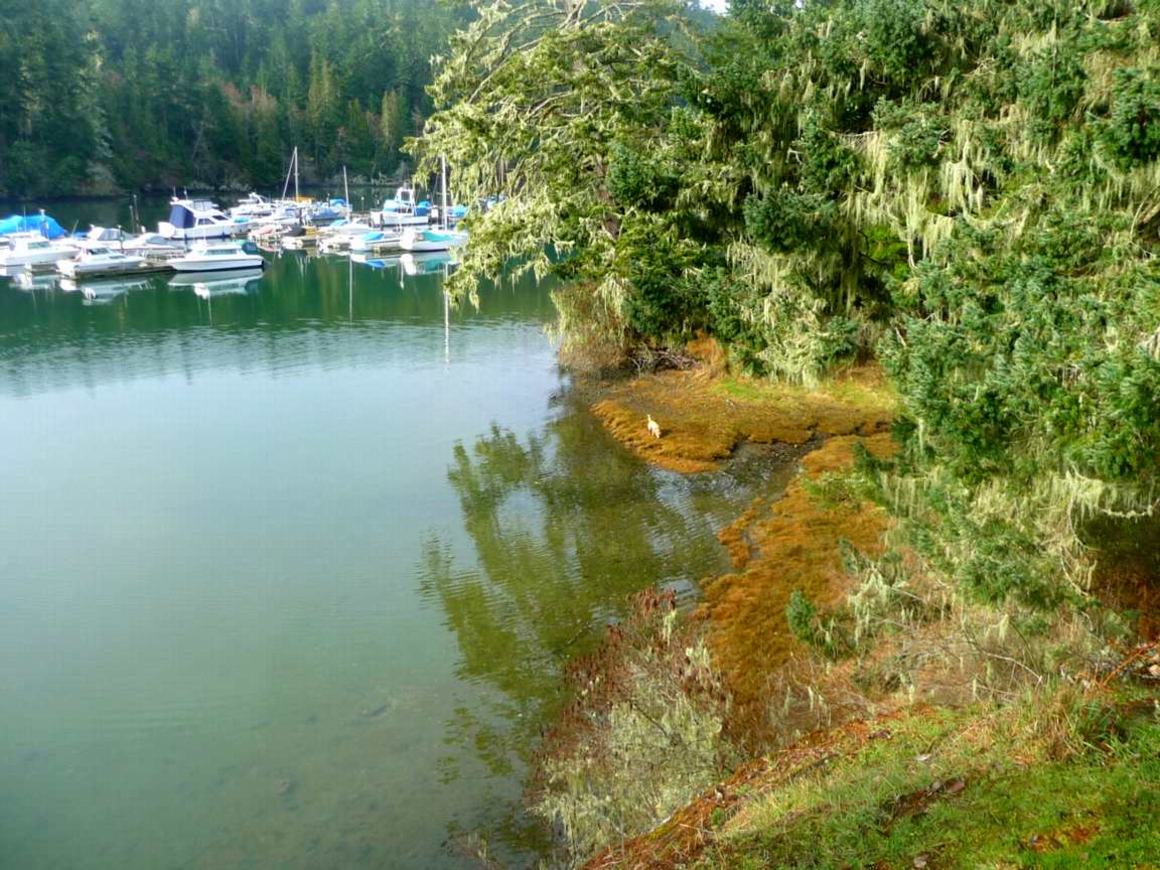
North side estuary looking west inland at high tide.
-

-
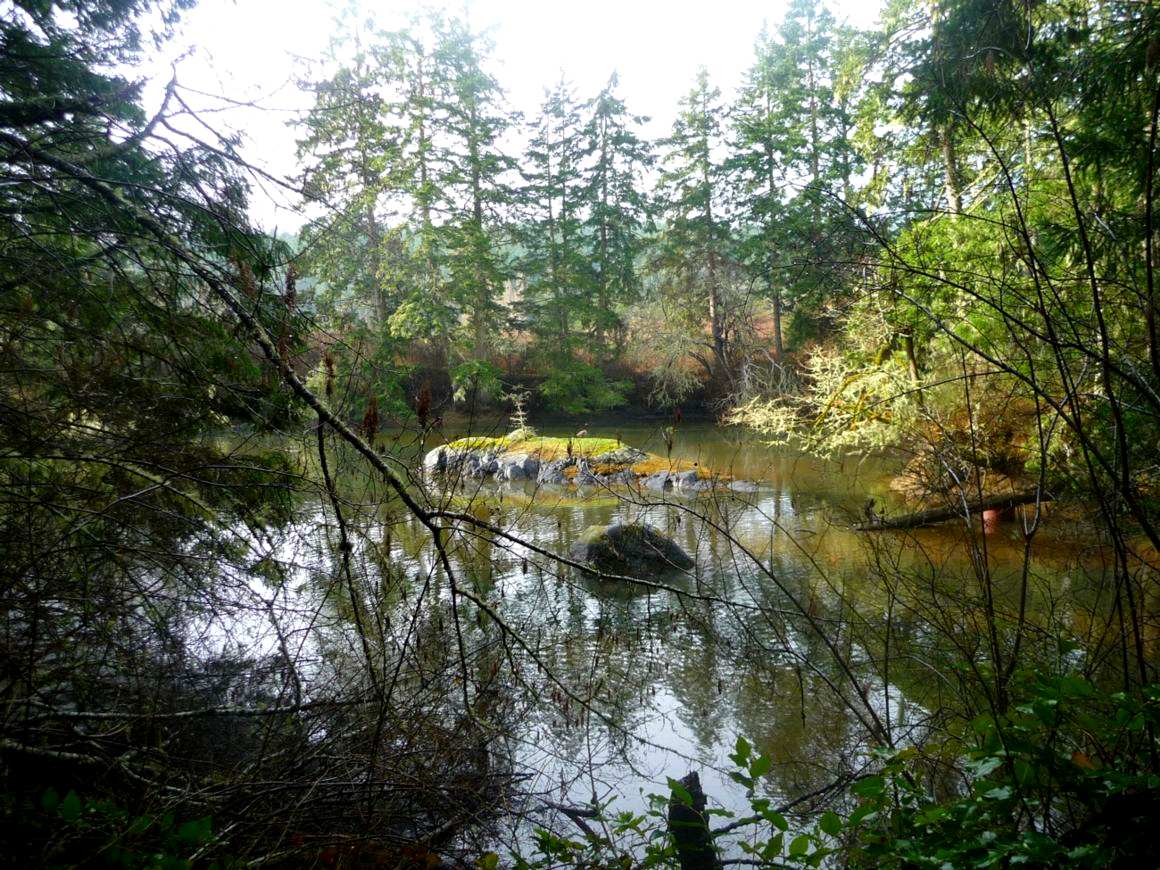
North side estuary looking west inland at high tide. The mudflats of this estuary provide a valuable source of food for waterfoul throughout the year
-

-
Canada Geese nest on the islands in upper art of the bay.
-

-
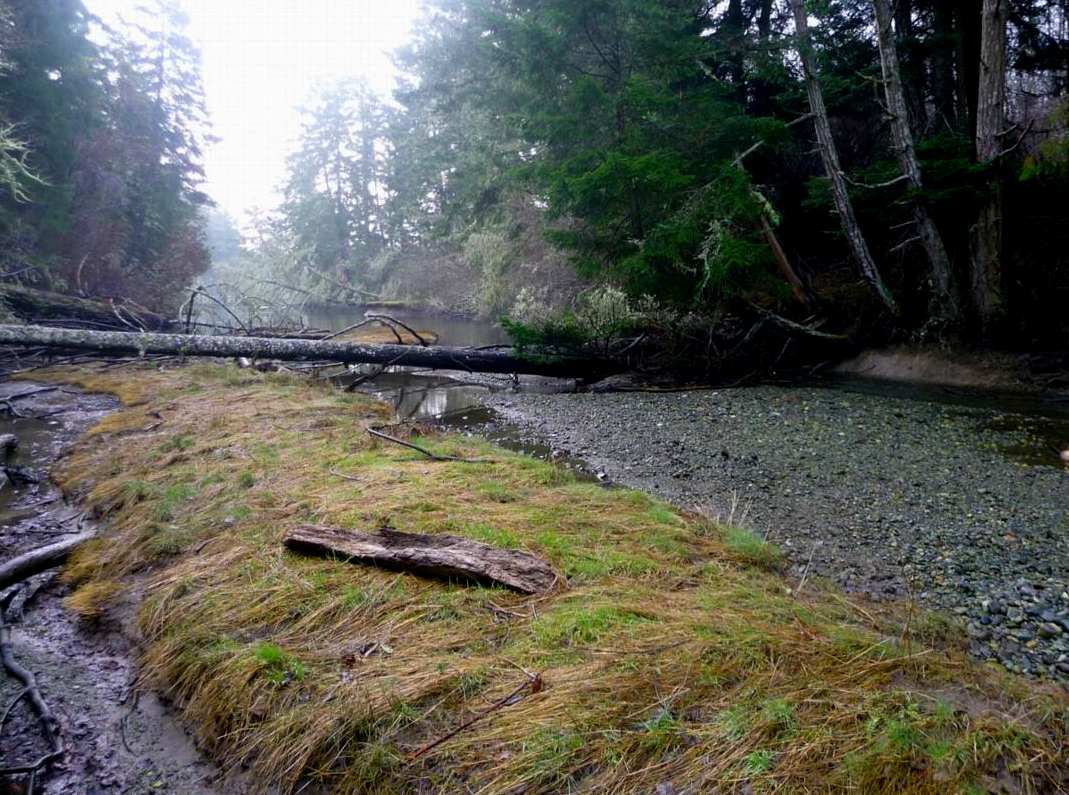
Burrowing worms and the large heart shaped cockles are part of the infauna of this ecosystem
-

-
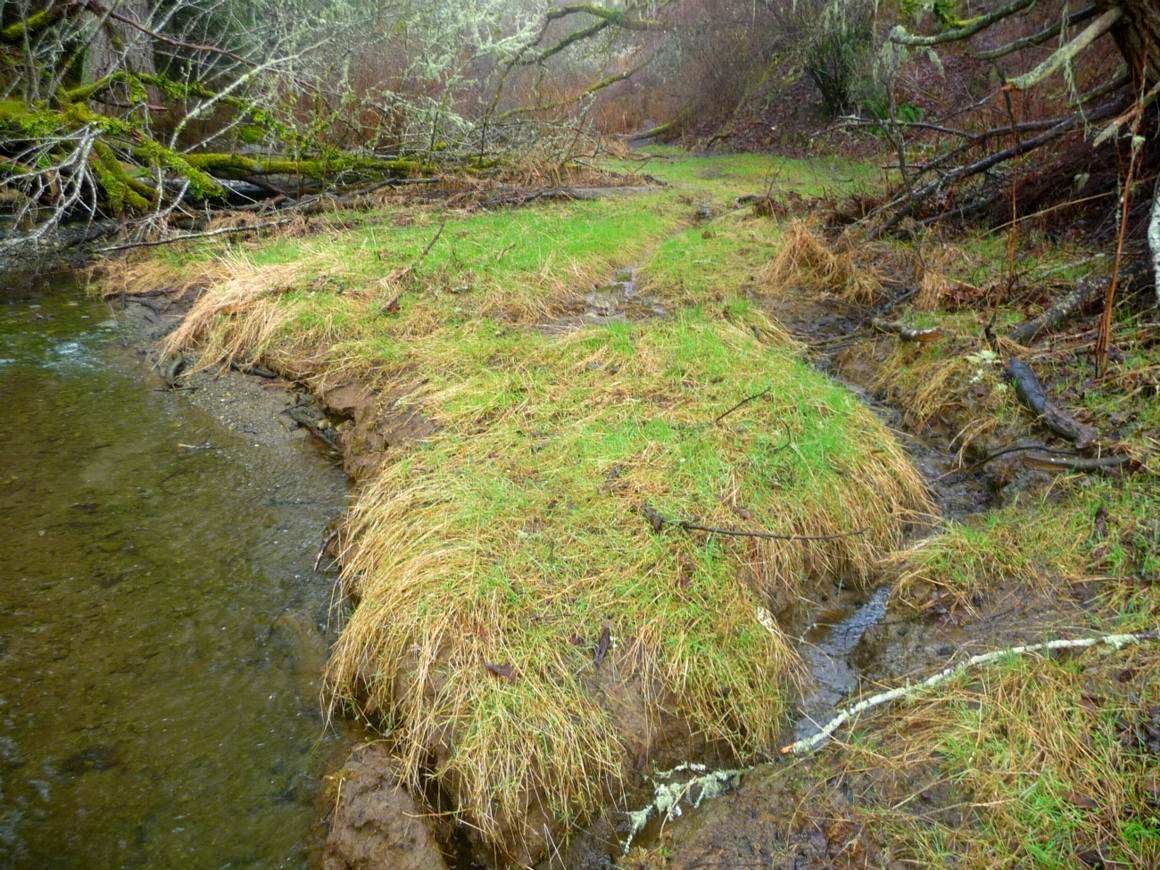
The estuary has typcal estuarine vegetation
-

-
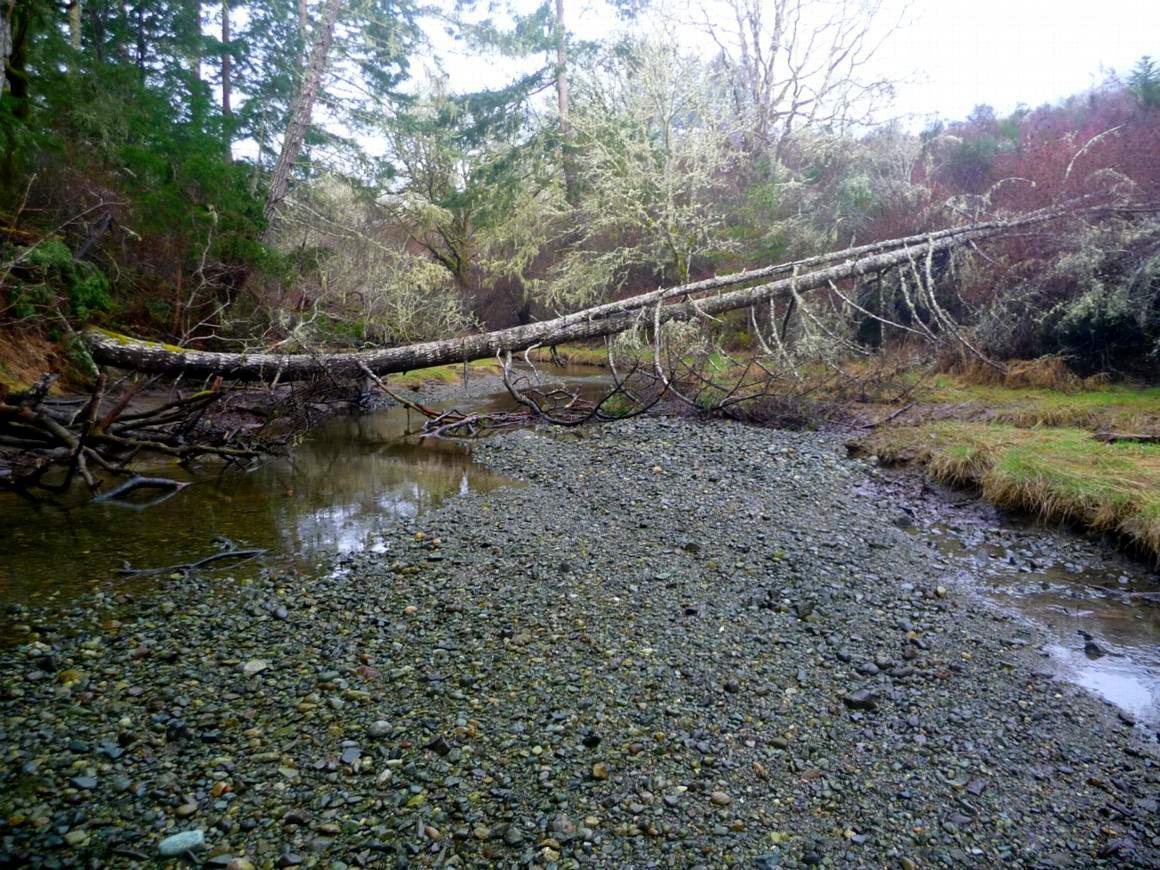
A mud mound in the estuary
-

-
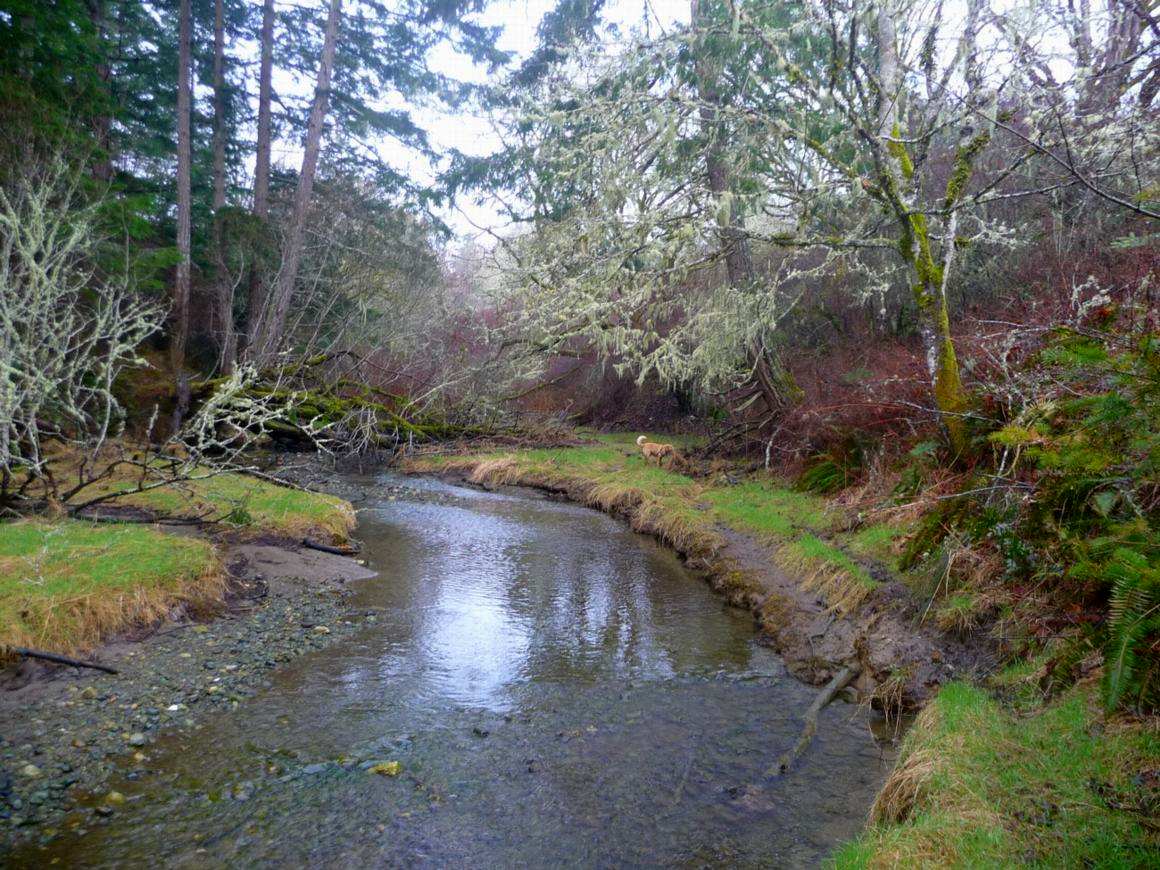
Looking east towards the bay
-

-
Looking west up the stream
-

-
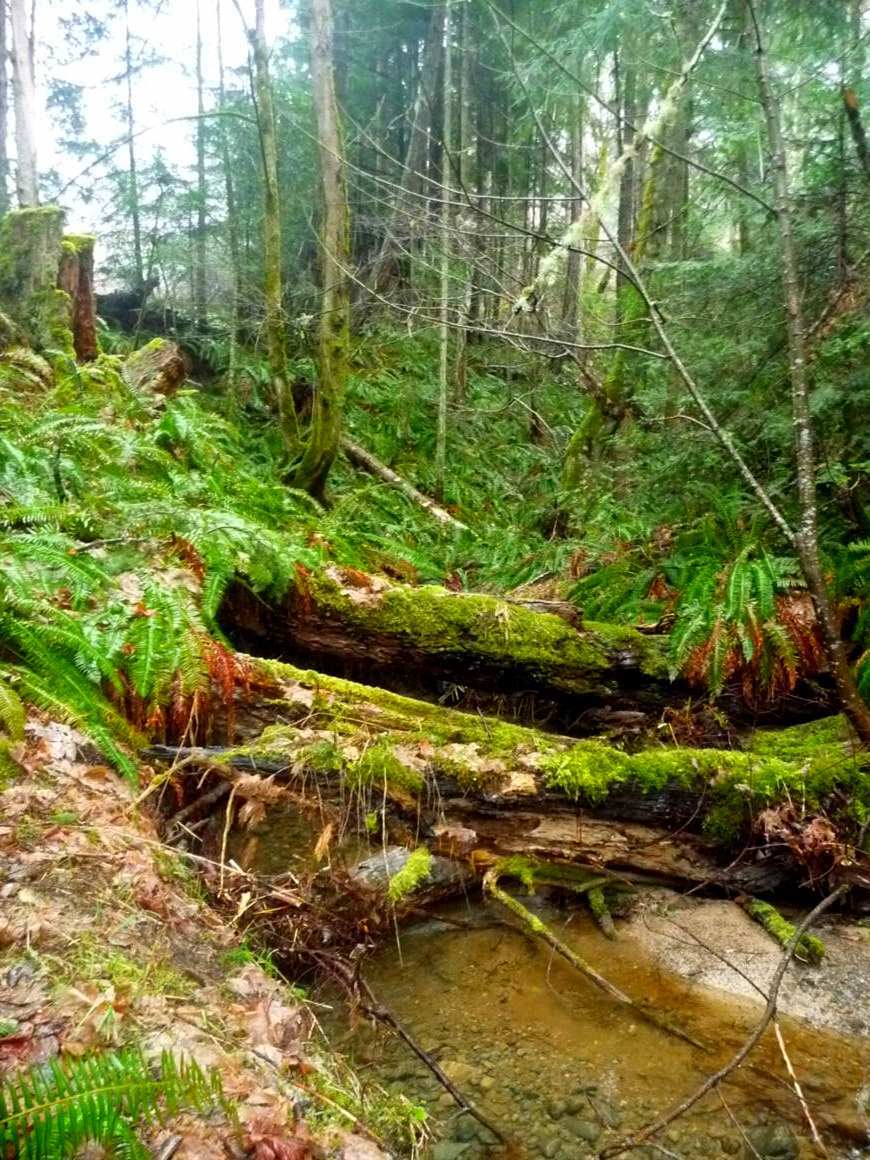
Looking west upstream on the north fork
-

-
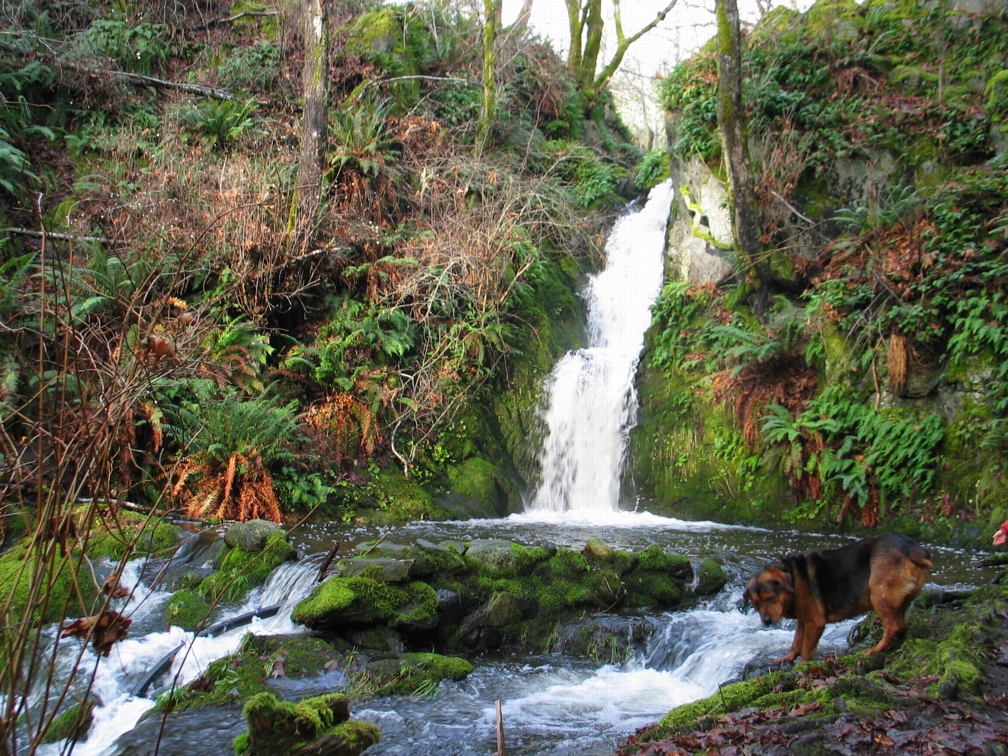
The waterfall that feeds into the estuary on the north side of Pedder Bay running at full capacity in December 2008.
-

-
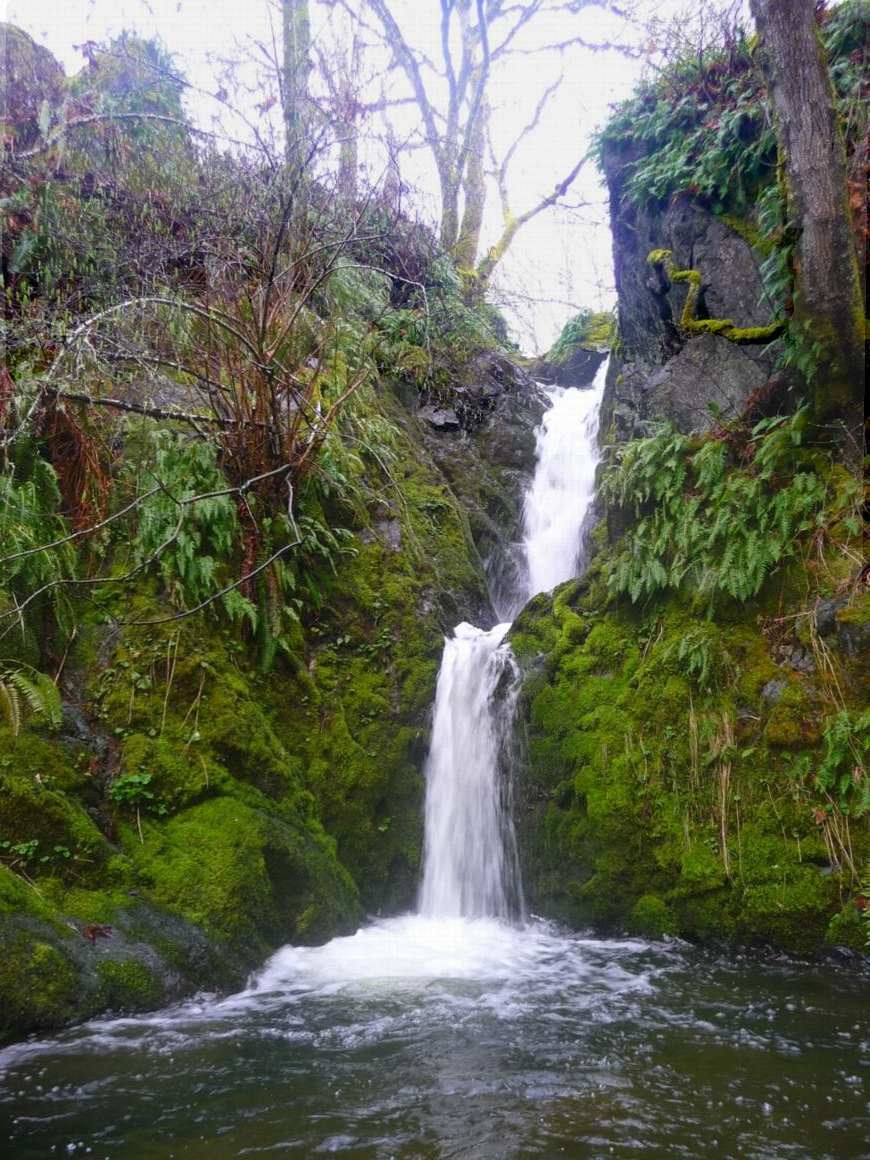
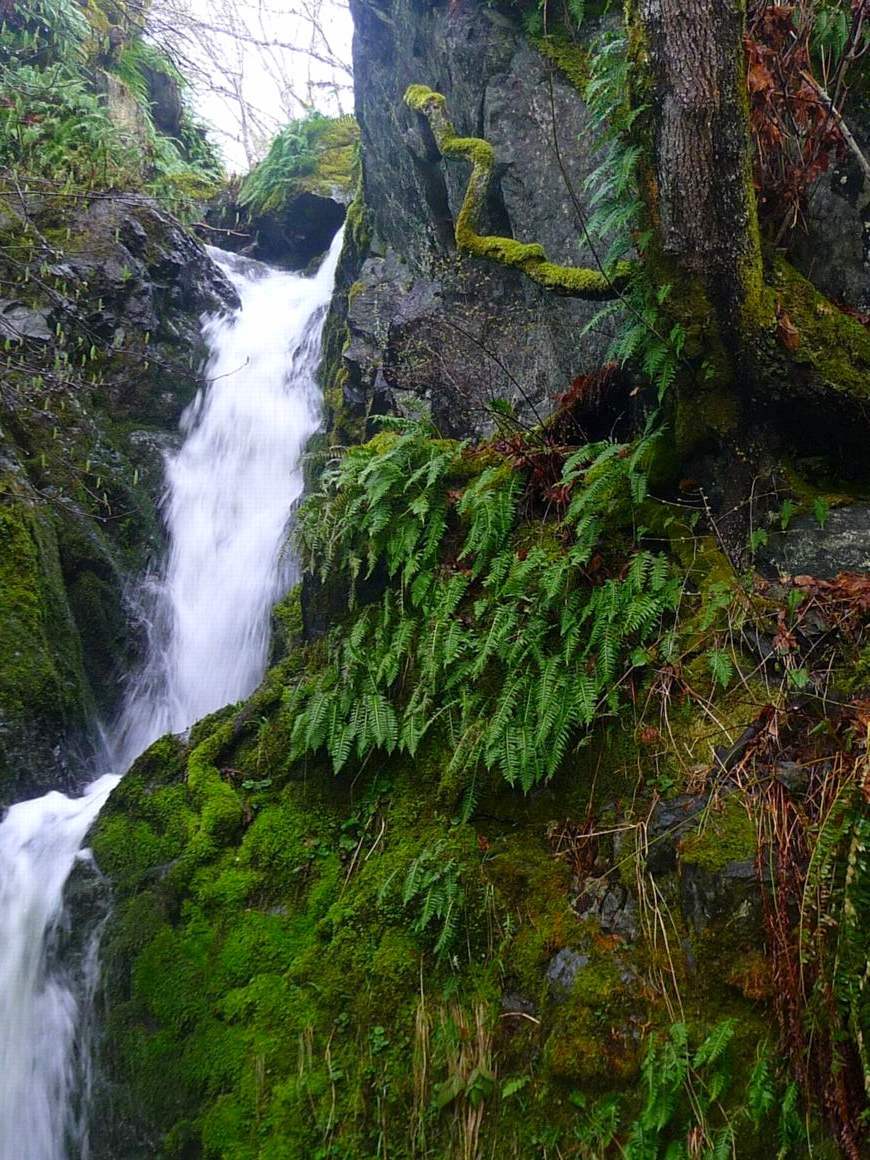
larvae and adult invertebrates which serve as a reliable food source for cutthroat trout coming to the stream. The waterfall, March 18, 2009
-

-
Licorice Ferns on the cliff beside the waterfall
-

-
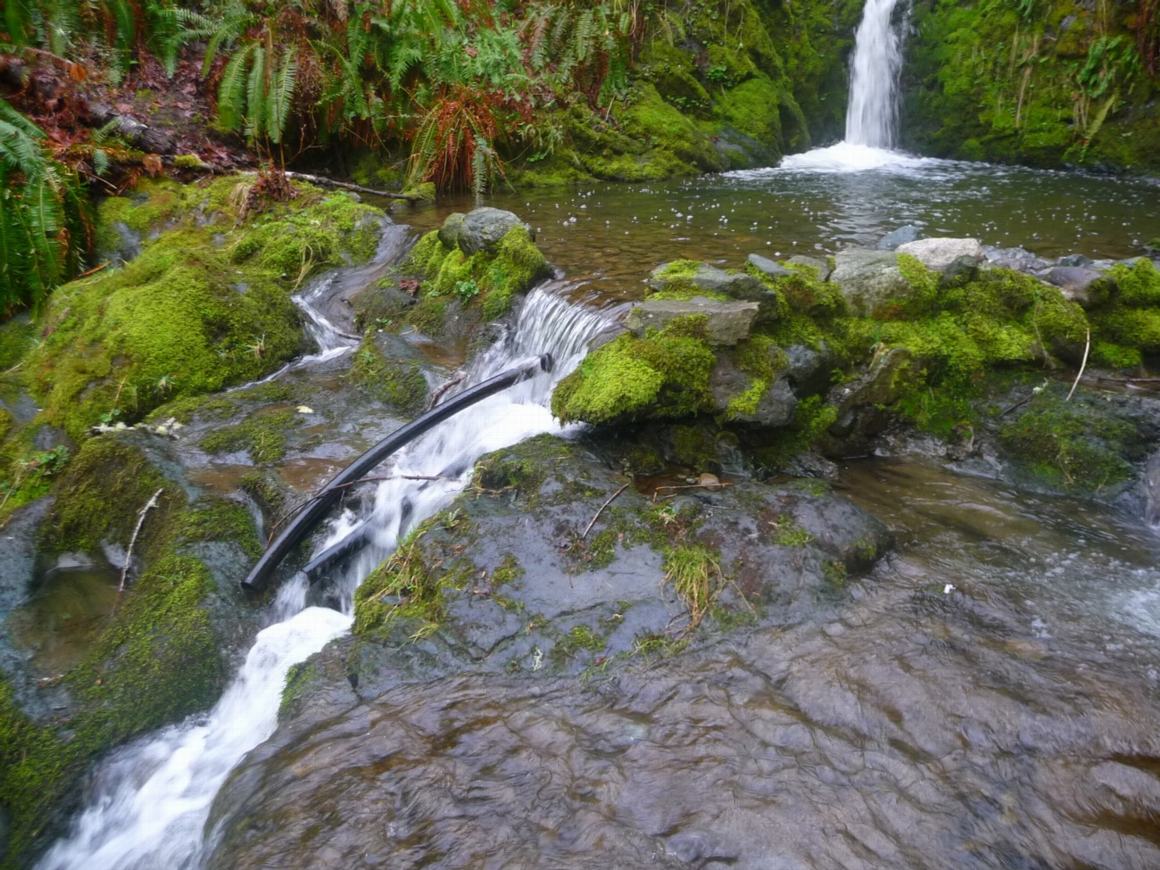
The pool at the base of the waterfall
-

-
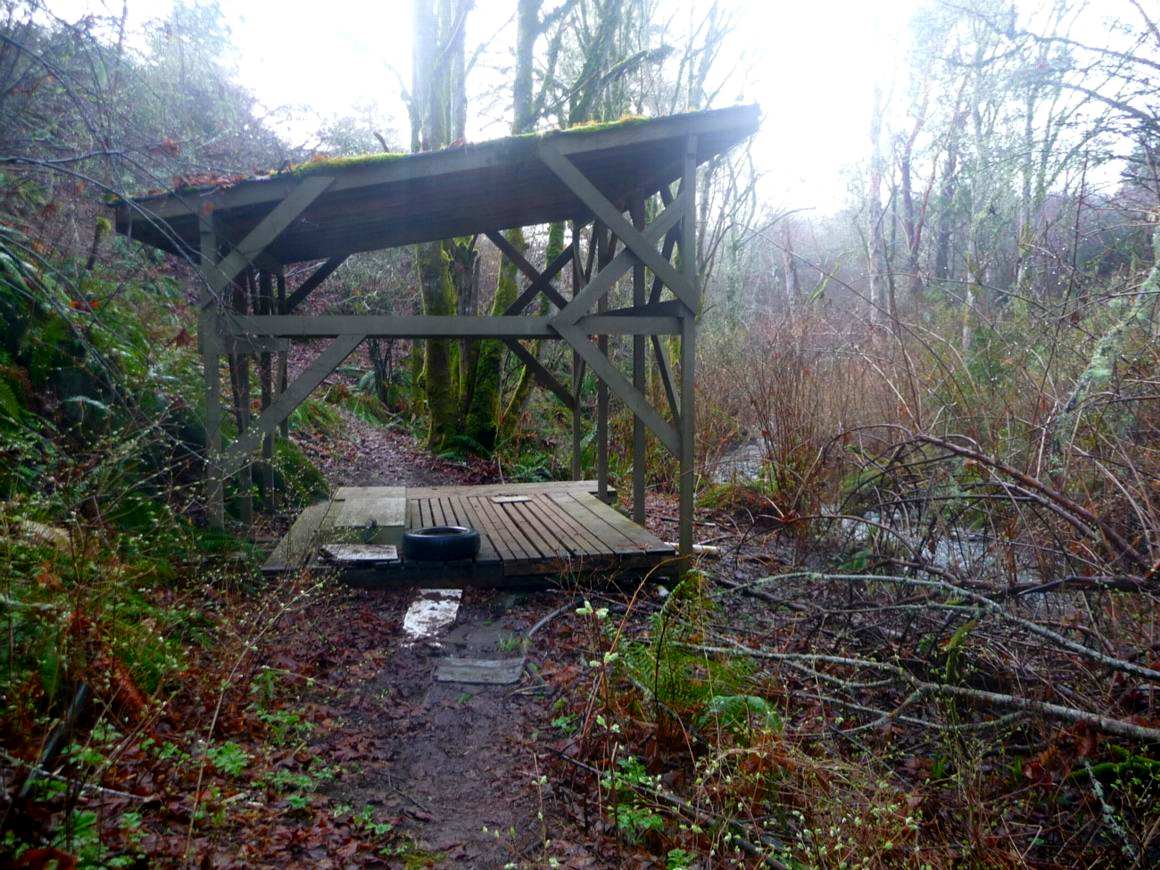
Salmon enhancement shed built by Pearson College in the early 1990s
========================================================
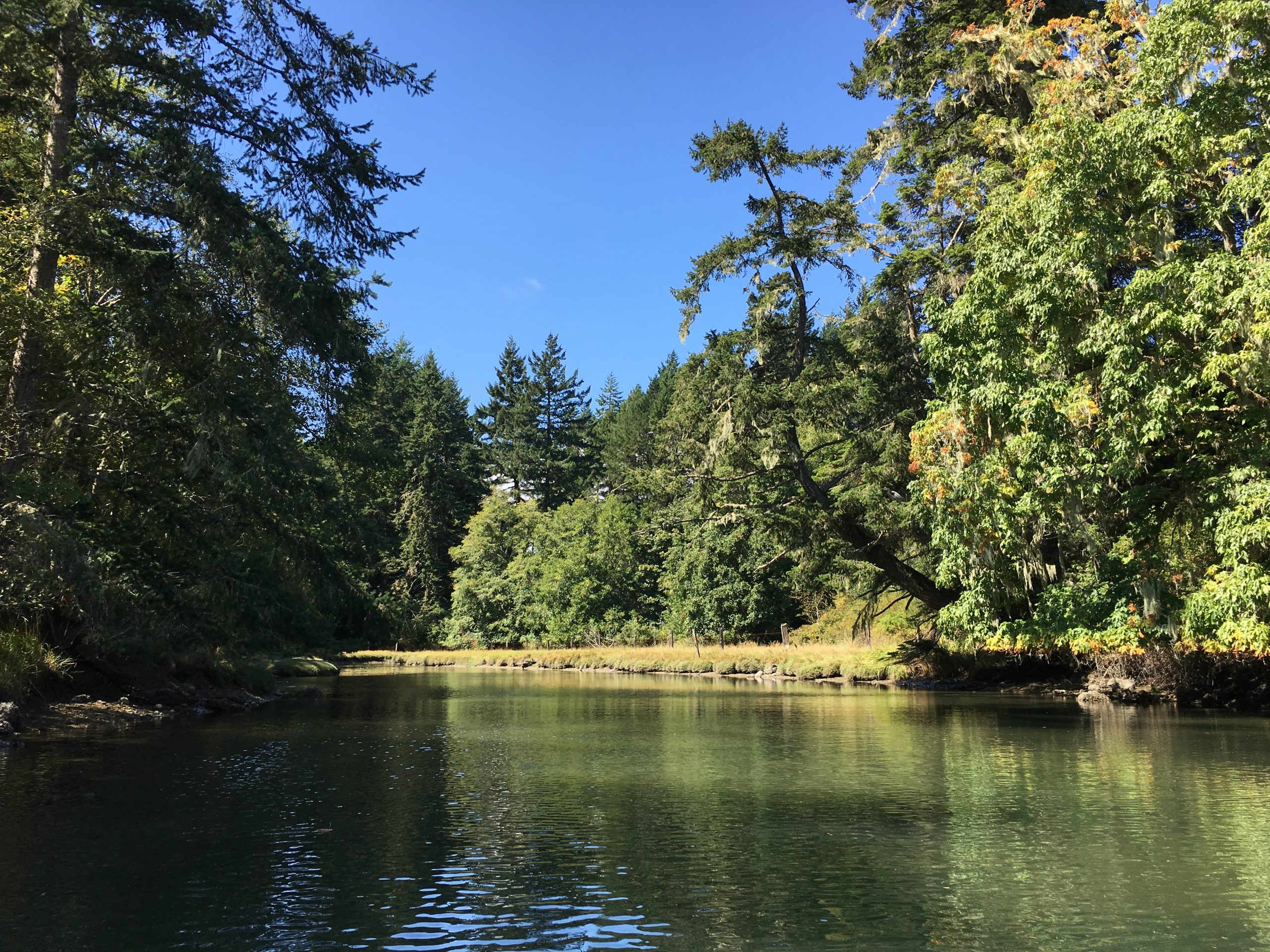 South arm of the Pedder Bay Estuary
South arm of the Pedder Bay Estuary
-

-
Entering the upper estuary
-
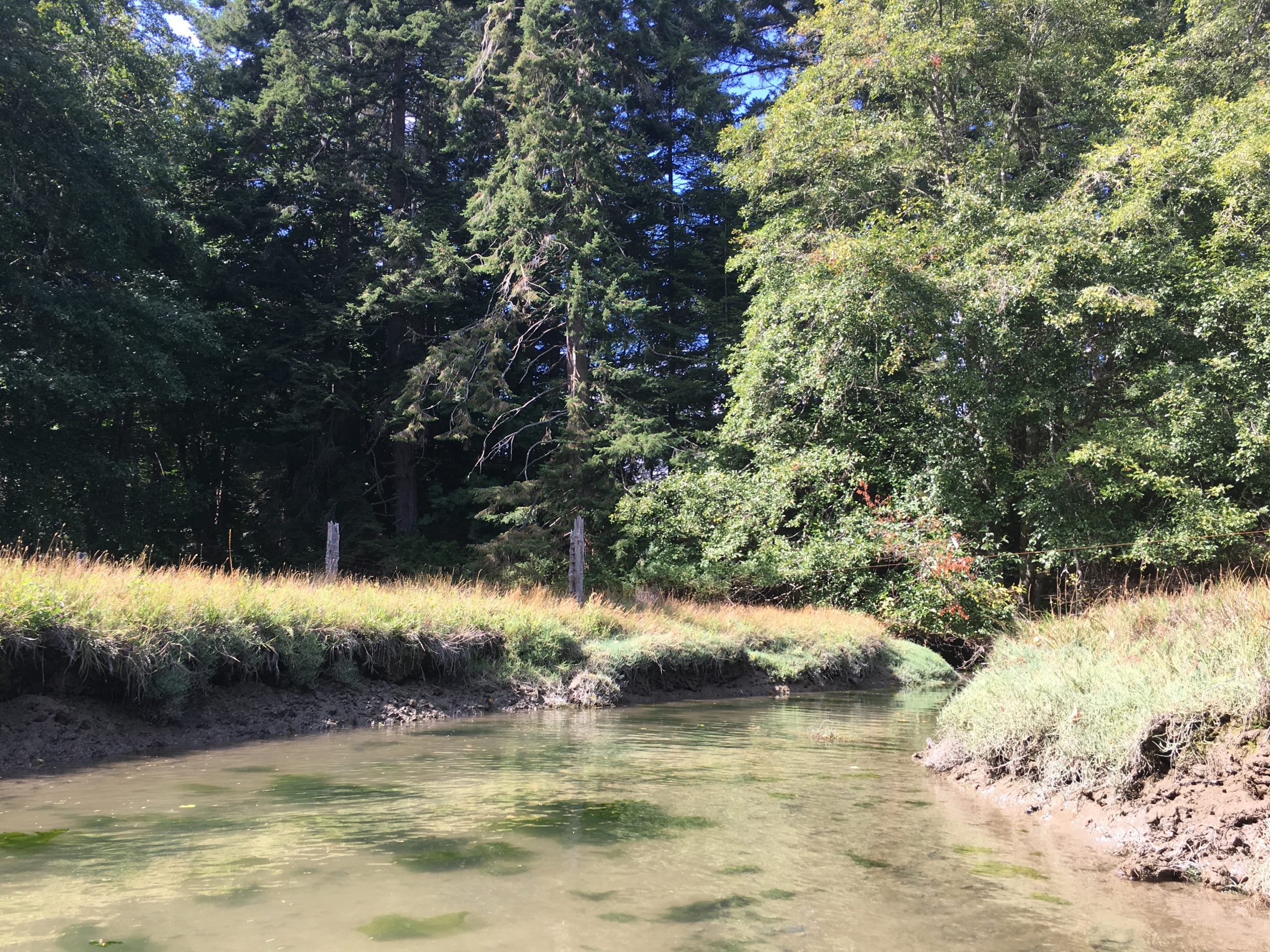

-
about as far as you can go in a kayak..
-
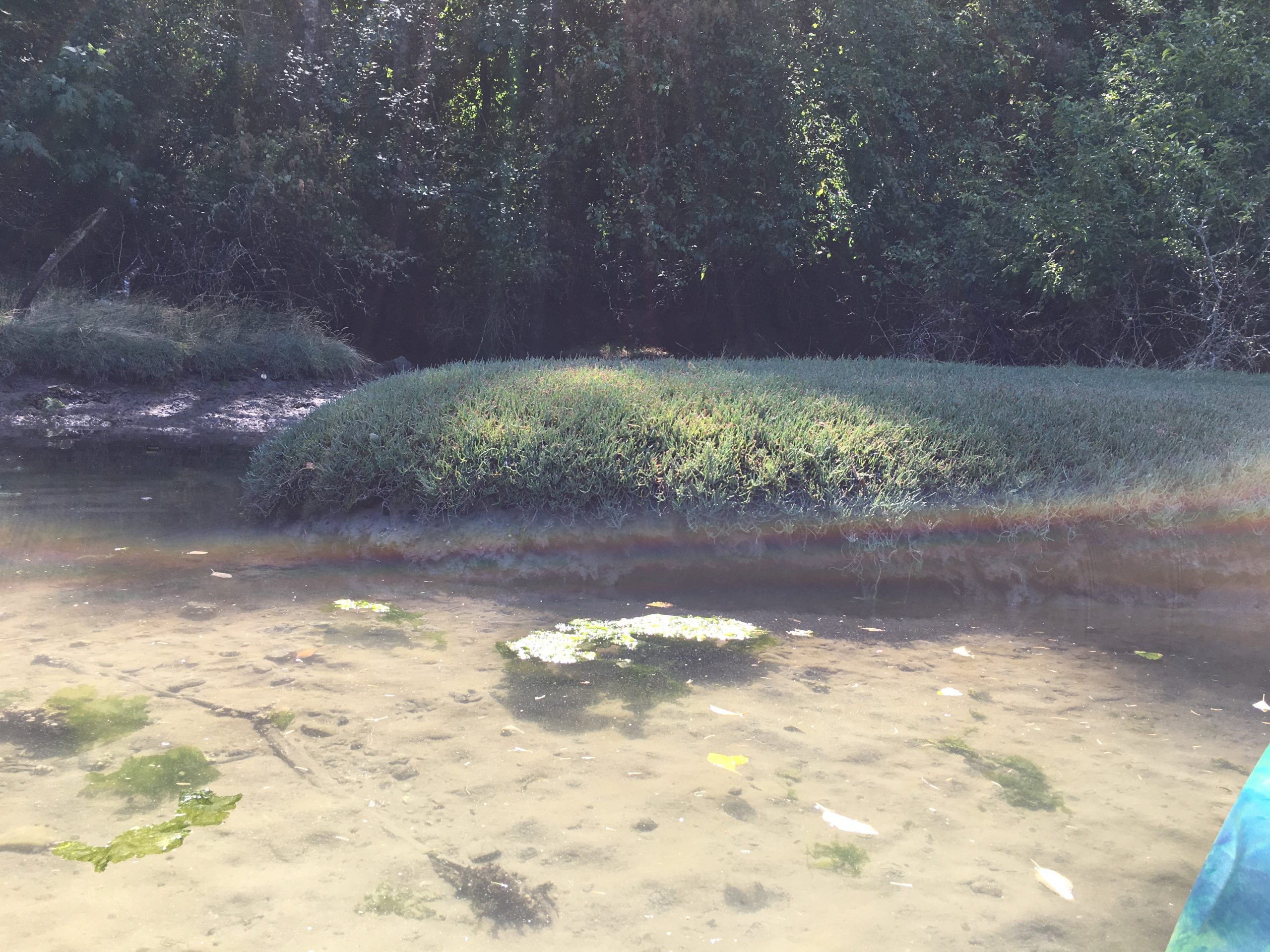

-
Salicornia on south shore
-
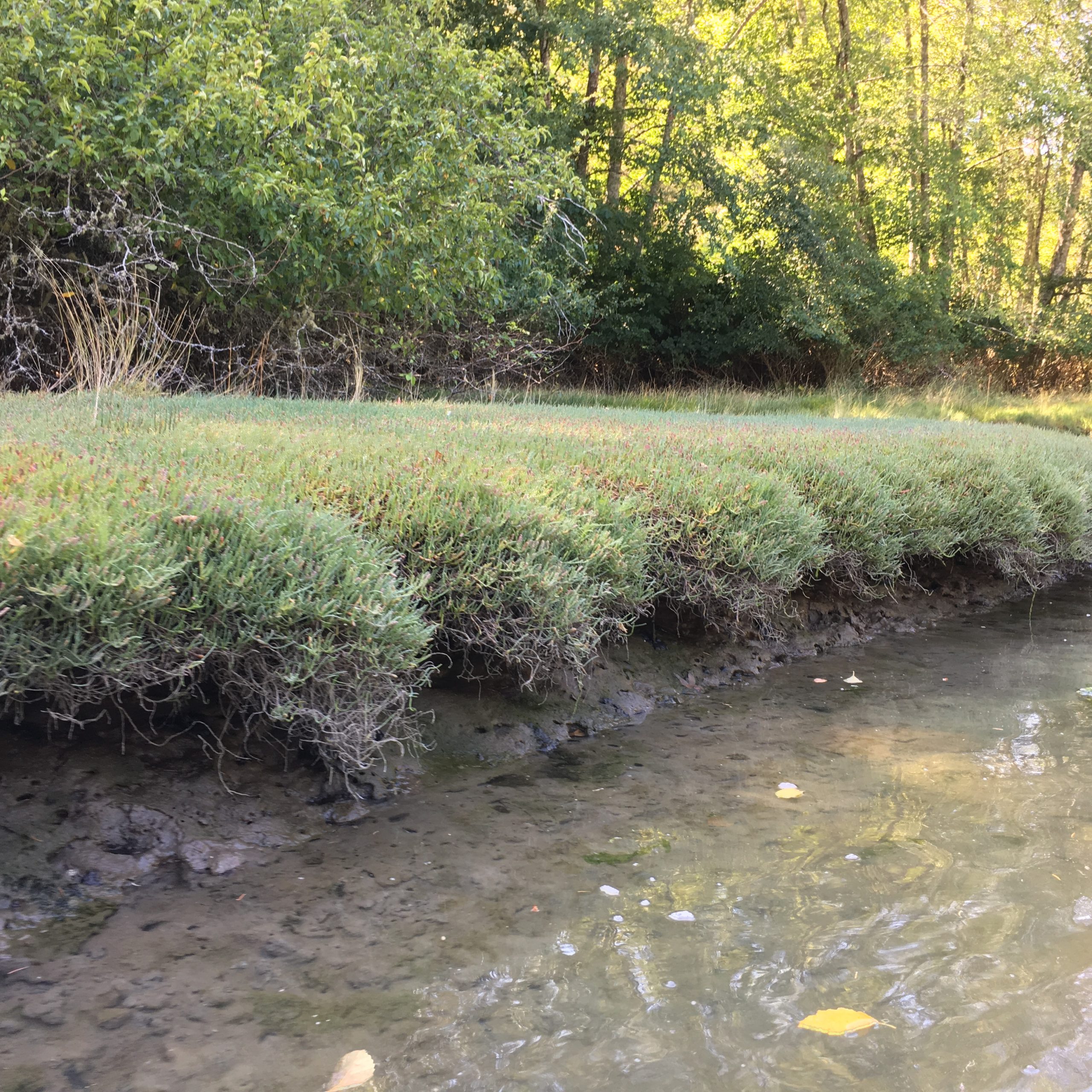

-
mounds of Salicornia spp.in the upper estuary
=========================================================
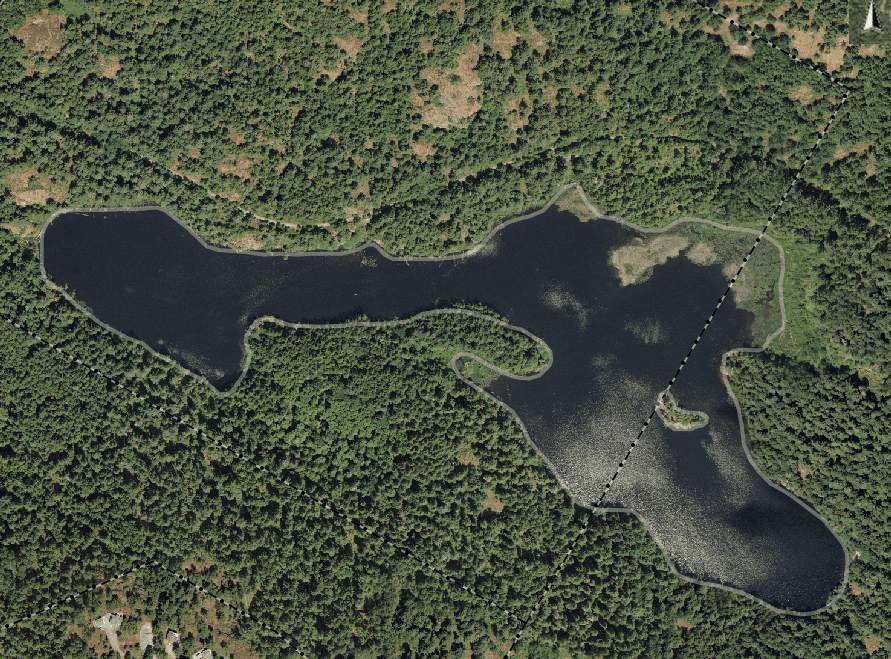 MATHESON LAKE -connected by a stream from the South arm (above) of the Estuary
MATHESON LAKE -connected by a stream from the South arm (above) of the Estuary
-

-
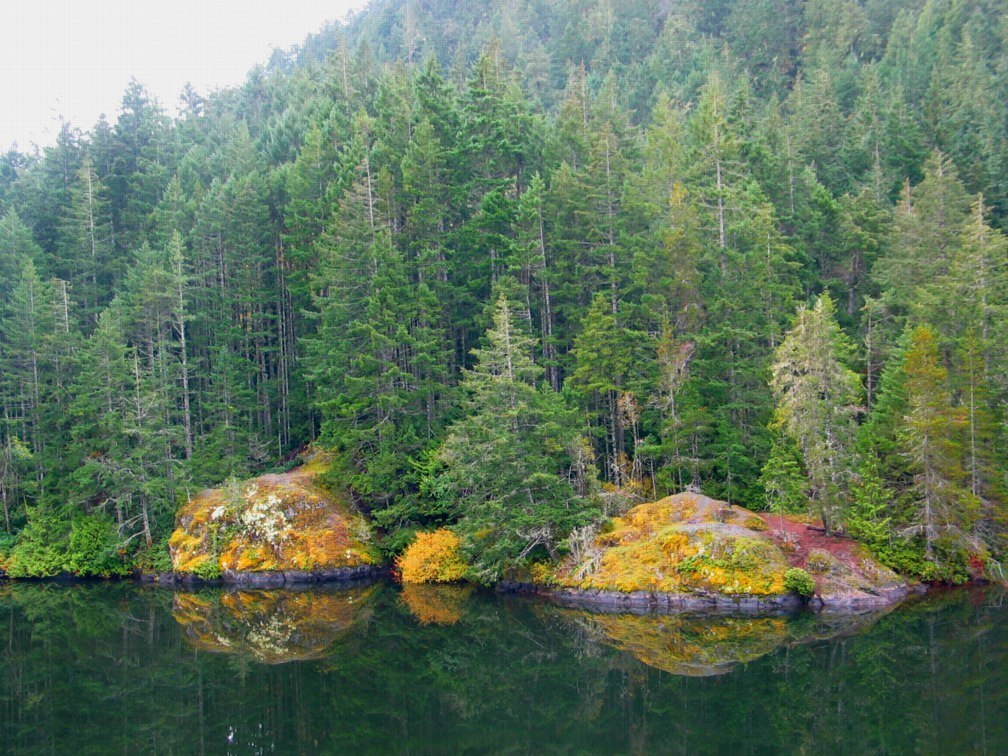
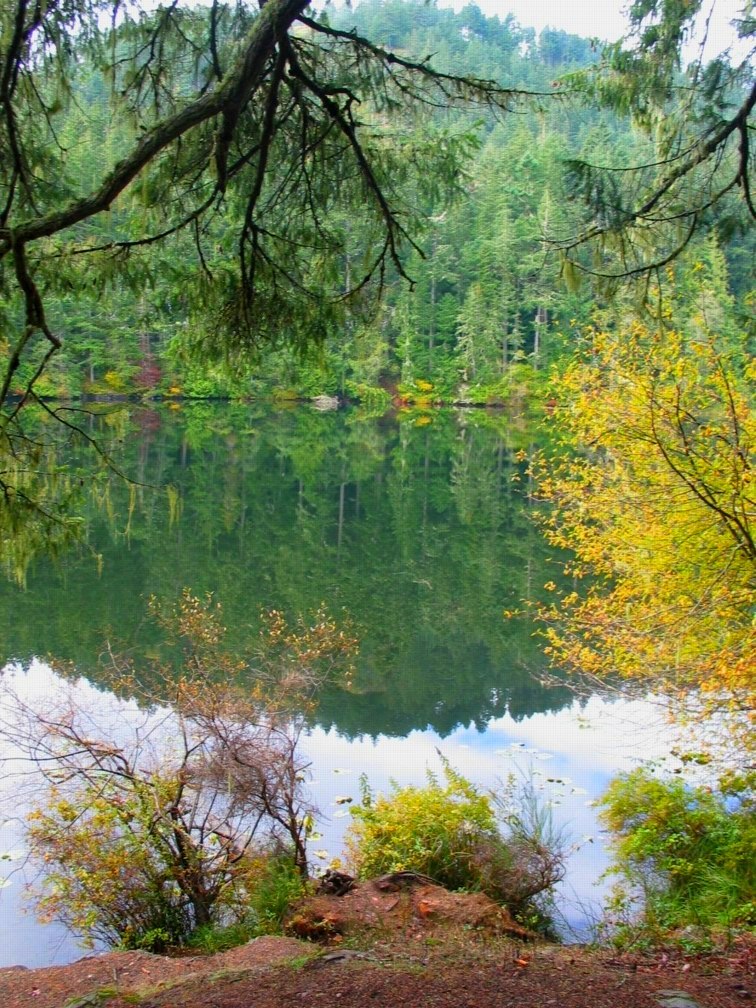
Matheson Lake
-

-

-
Matheson lake, Fall 2007
==================================================
NORTH SIDE INNER PEDDER BAY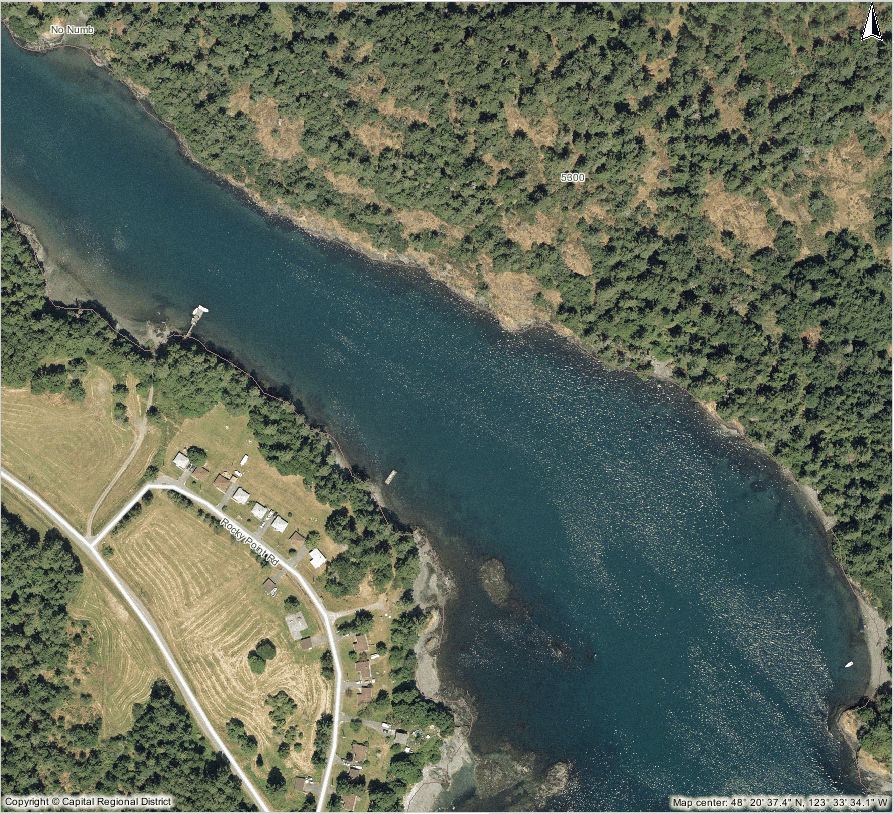
====================================================
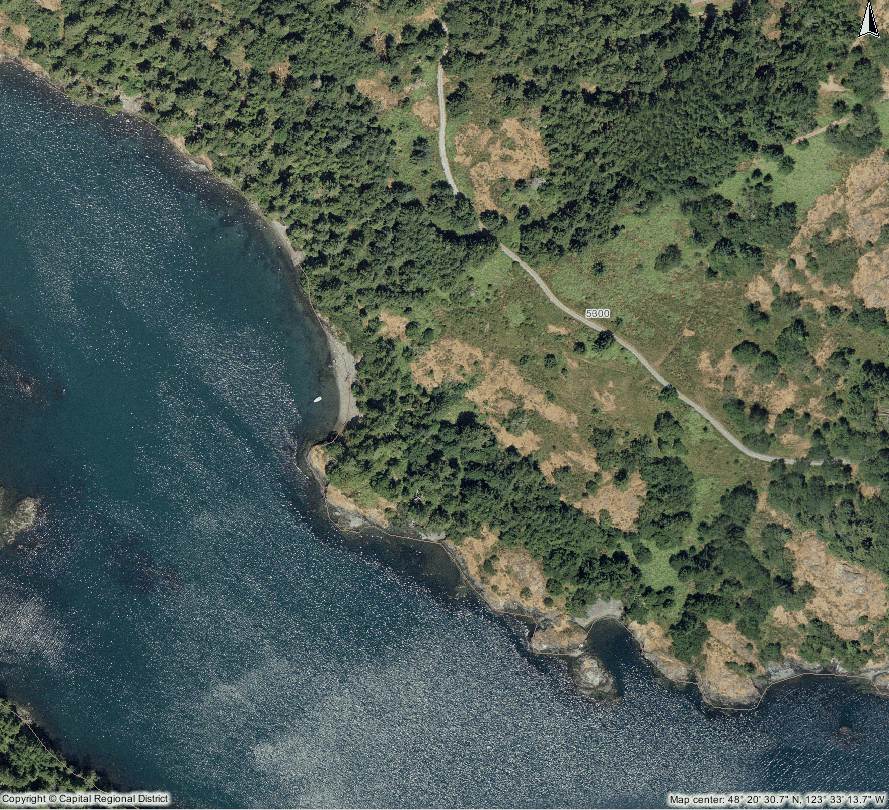 WEIR POINT and beach to North Outer Shore
WEIR POINT and beach to North Outer Shore

Weir point from south side of Pedder Bay
-

-
Weir Point
-

-
Beach just out from Weir Point under Mary Hill
-

-
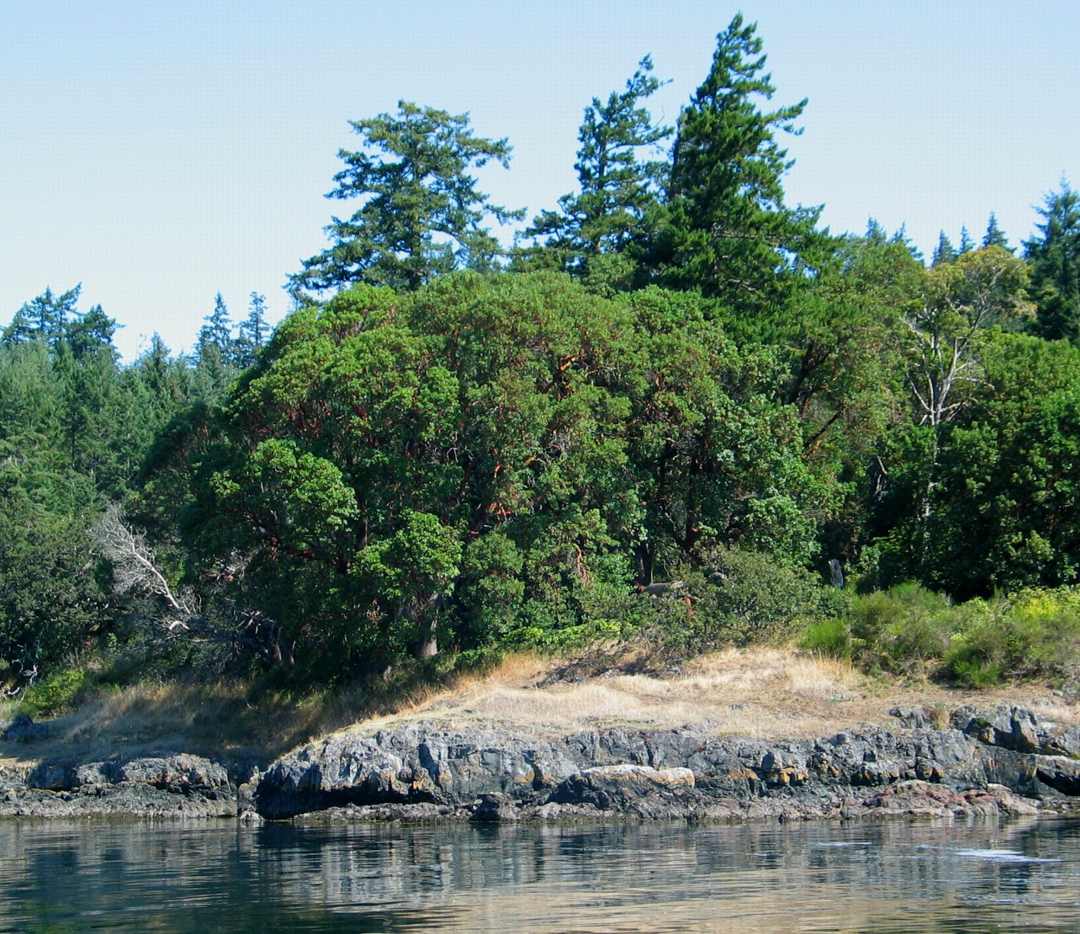
Islands at the outer north corner of Pedder Bay, and the start of William Head.
==================================================
ANTHROPOGENIC HABITAT MODIFICATION in PEDDER BAY
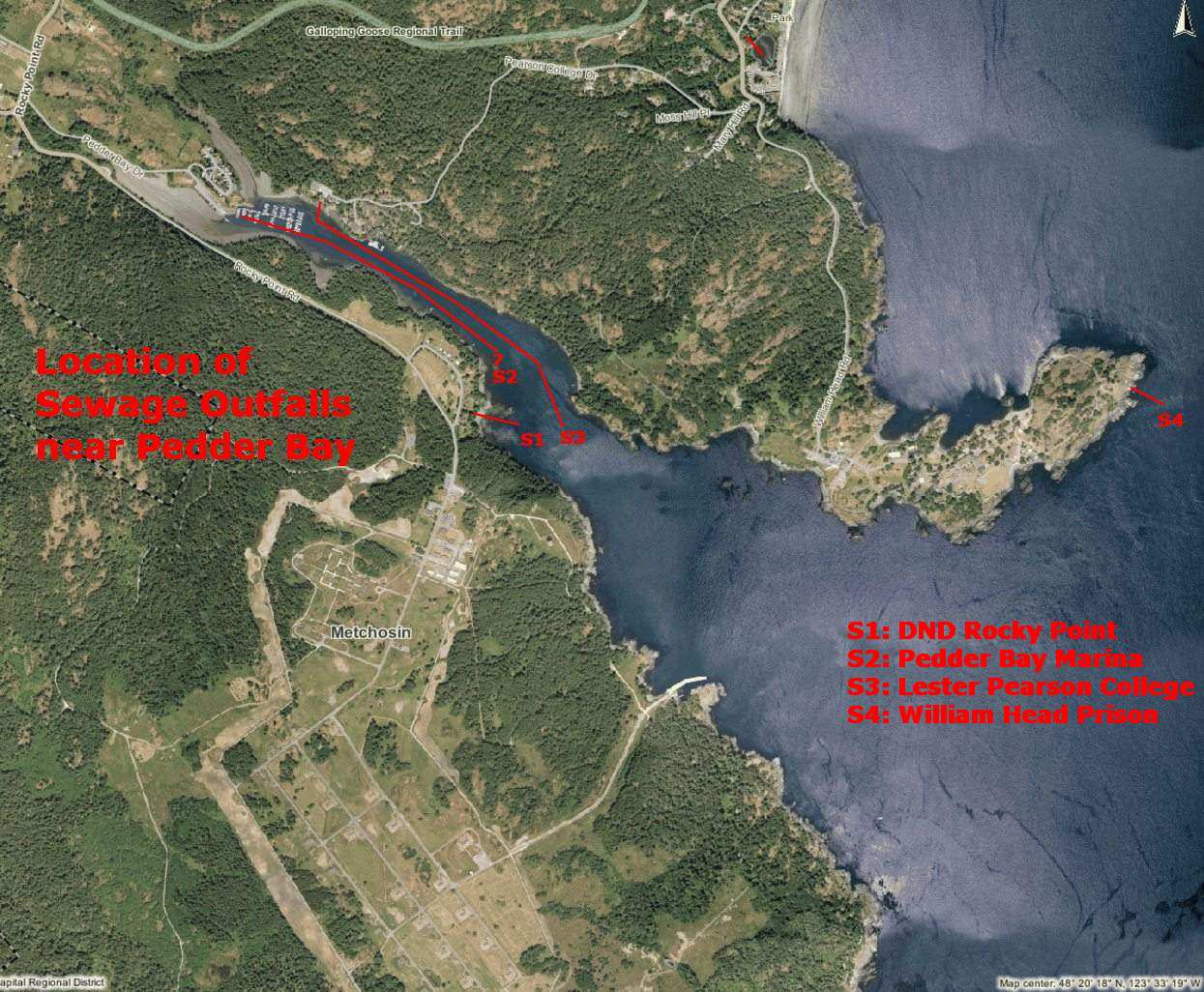 Sewage Outfalls in Pedder Bay
Sewage Outfalls in Pedder Bay
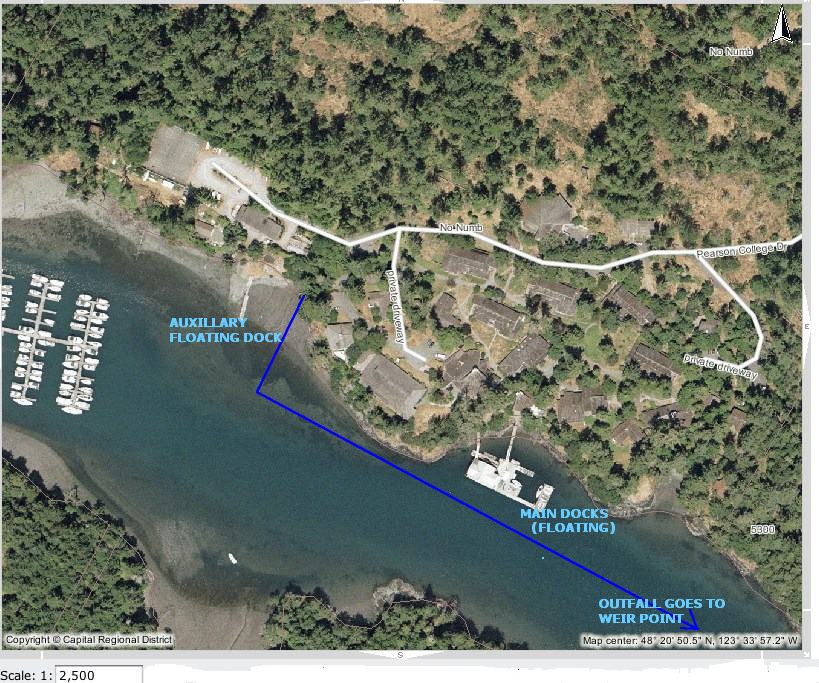 Pearson College fronts on the bay on the north side. Modifications to the shoreline have changed the habitat of the bay. The floating docks provide a large substrate for additional growth of biomass. Boats, diesel and gasoline, provide additional hydrocarbon discharge into the bay. Introduction of efficient four stroke engines in recent years have helped to mitigate boat engine pollution. No Inorganic fertilizers or pesticides are used on the campus, so surface runoff is not an issue.
Pearson College fronts on the bay on the north side. Modifications to the shoreline have changed the habitat of the bay. The floating docks provide a large substrate for additional growth of biomass. Boats, diesel and gasoline, provide additional hydrocarbon discharge into the bay. Introduction of efficient four stroke engines in recent years have helped to mitigate boat engine pollution. No Inorganic fertilizers or pesticides are used on the campus, so surface runoff is not an issue.
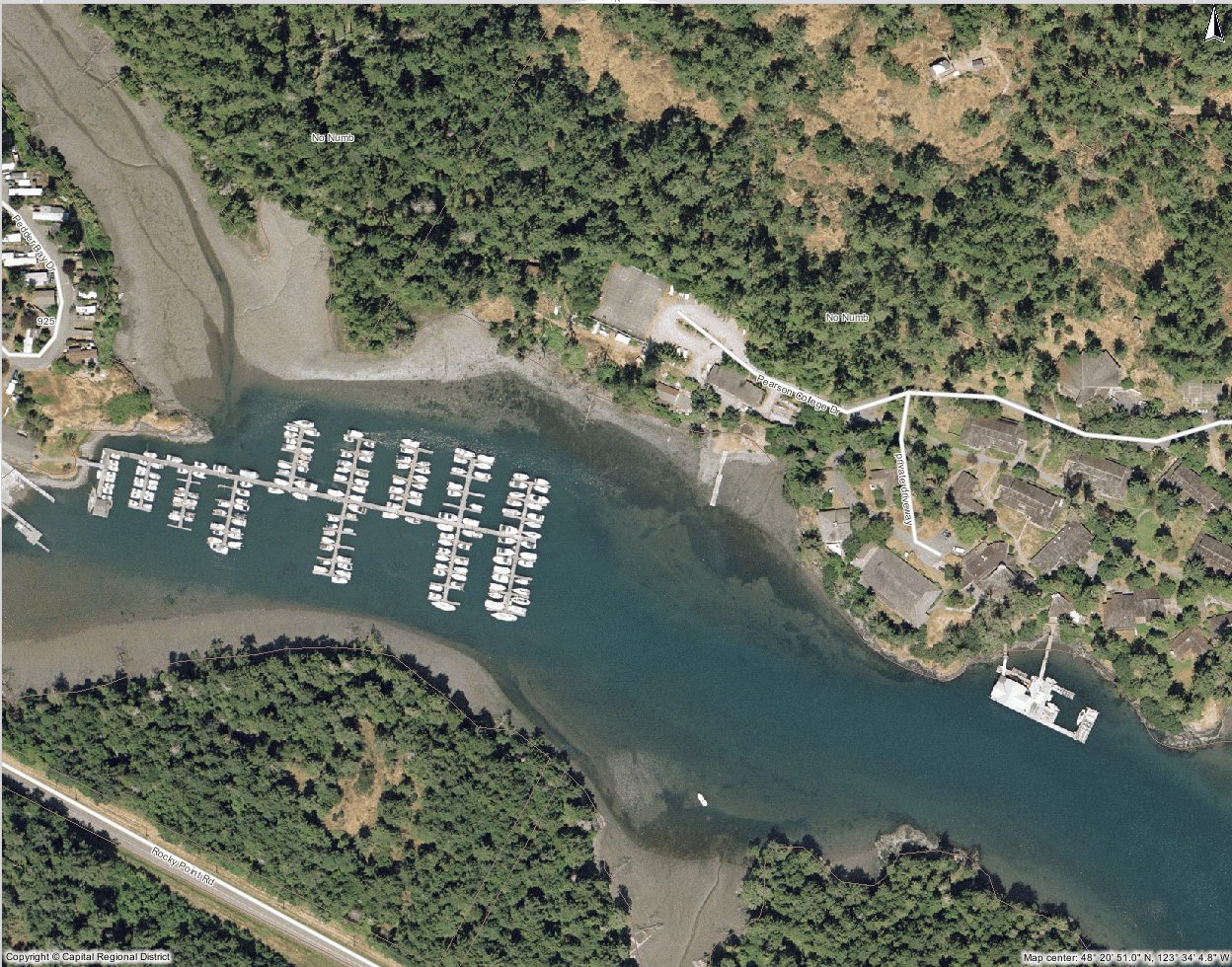 Pedder Bay marina docks have a great number of boats which provide a large potential input of hydrocarbons. Chronic oil pollution from bilge systems of boats in marinas such as this provide a continual hazard to marine life.
Pedder Bay marina docks have a great number of boats which provide a large potential input of hydrocarbons. Chronic oil pollution from bilge systems of boats in marinas such as this provide a continual hazard to marine life.
Location of Sewage outfall is not known, although it is believed that it runs at least part way out of the bay.
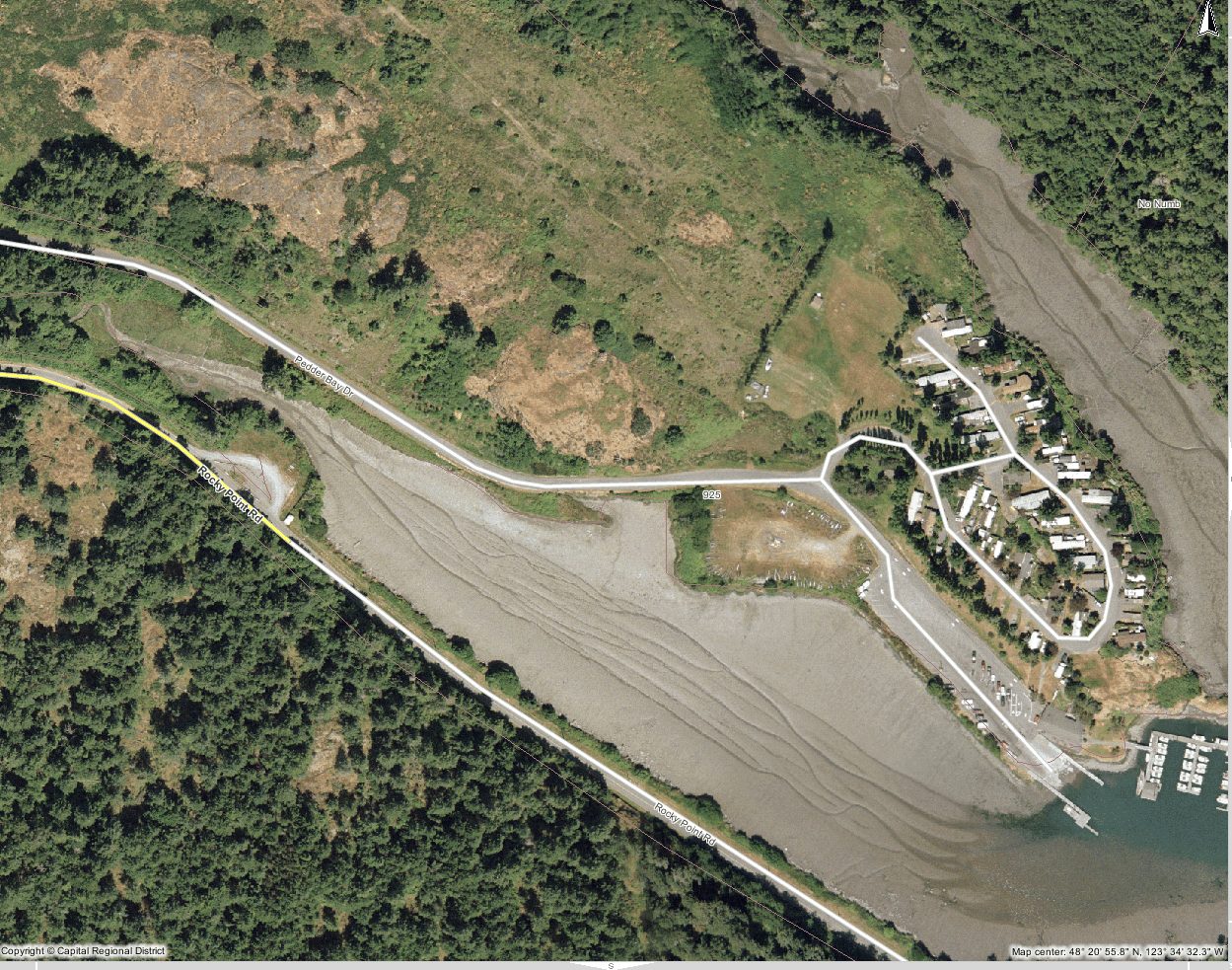 The trailer court at Pedder Bay sits on the bank of the estuary . Sewage from this location is pumped seaward and terminates in middle Pedder Bay. Primary sewage treatment only is available.
The trailer court at Pedder Bay sits on the bank of the estuary . Sewage from this location is pumped seaward and terminates in middle Pedder Bay. Primary sewage treatment only is available.
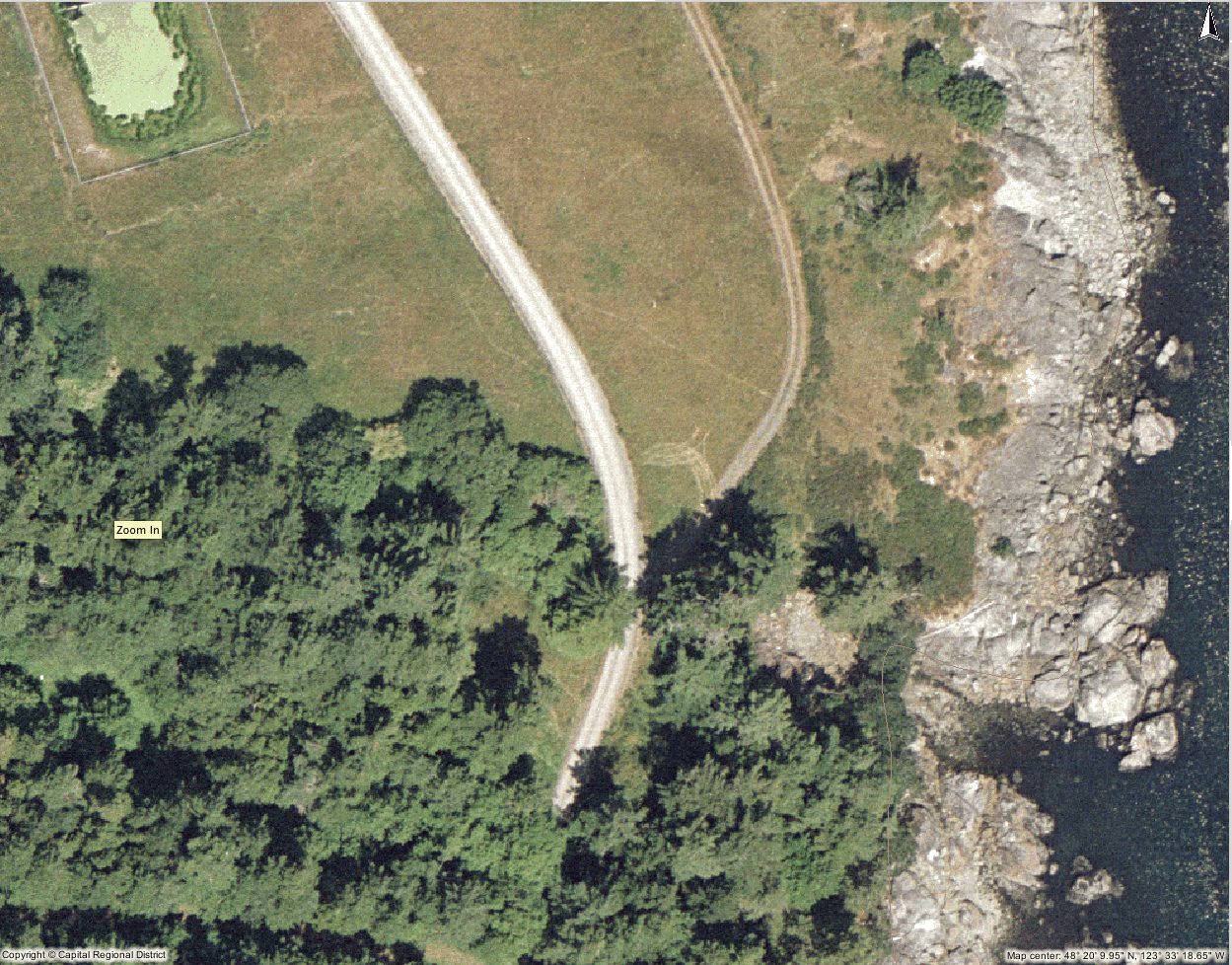 The Rocky Point DND sewage outfall runs down the shore in a buried pipe, and terminates over 100 meters seaward in the bay. It is presumed that secondary treatment has been done on this effluent. runs down the shore in a buried pipe, and terminates over 100 meters seaward in the bay. It is presumed that secondary treatment has been done on this effluent.
The Rocky Point DND sewage outfall runs down the shore in a buried pipe, and terminates over 100 meters seaward in the bay. It is presumed that secondary treatment has been done on this effluent. runs down the shore in a buried pipe, and terminates over 100 meters seaward in the bay. It is presumed that secondary treatment has been done on this effluent.
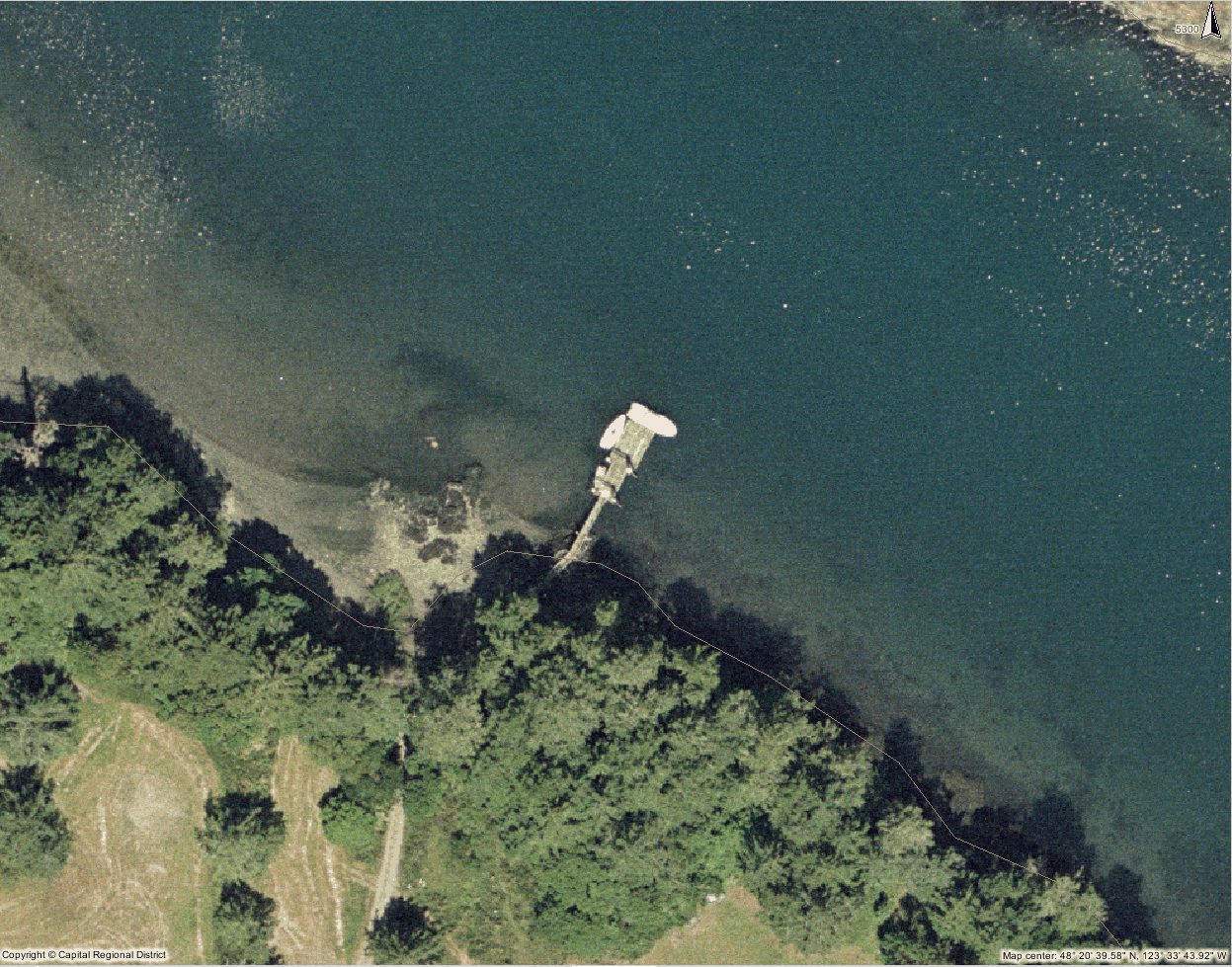 The small DND floating dock on the south side of inner Pedder Bay, now no longer used.
The small DND floating dock on the south side of inner Pedder Bay, now no longer used.
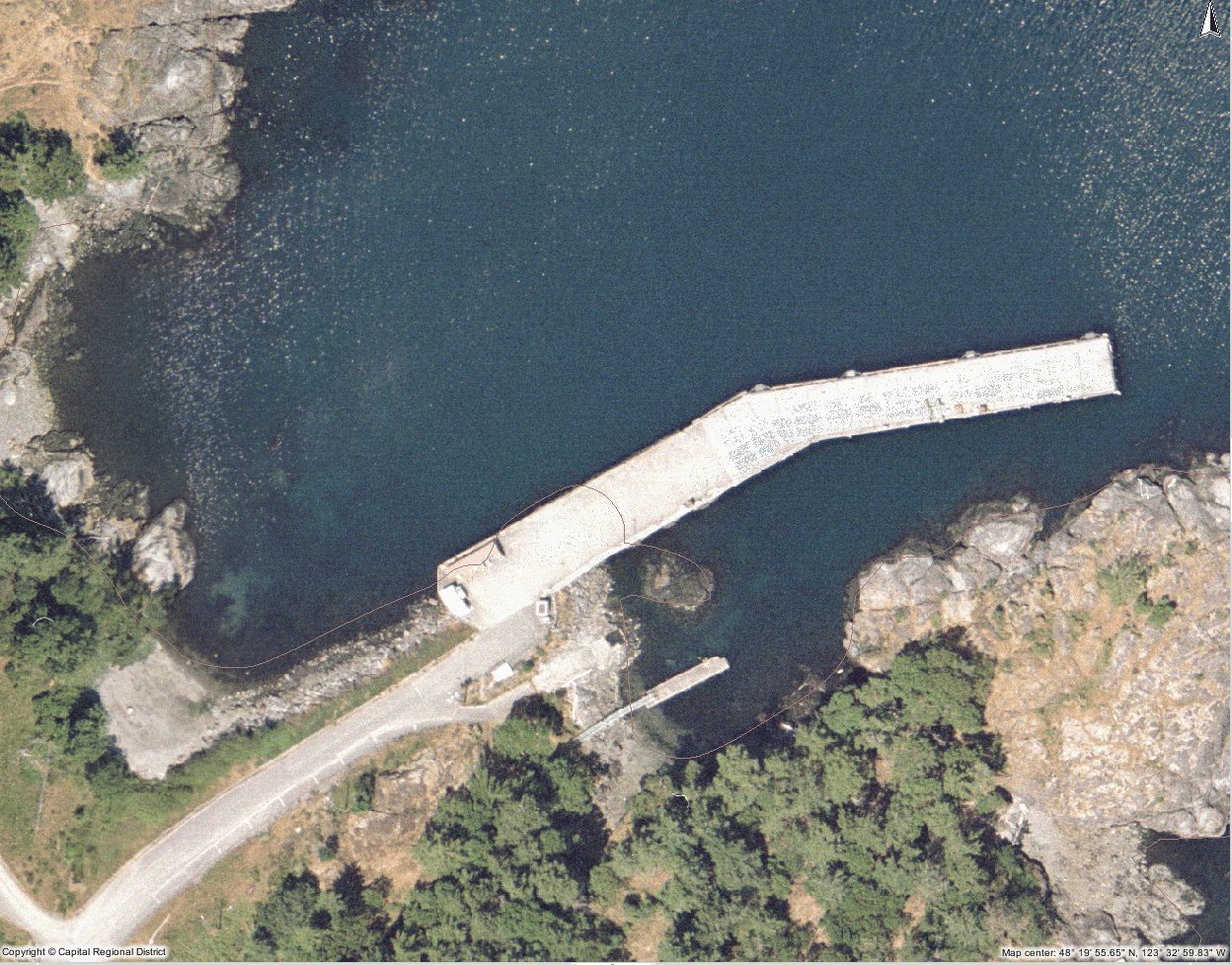 The bottom of the ocean at the DND Jetty has been dredged to deepen it for ocean going vessels. This is a fixed concrete pier.
The bottom of the ocean at the DND Jetty has been dredged to deepen it for ocean going vessels. This is a fixed concrete pier.
======================================================
This site has been created to represent the contiguous ecosystems of the Race Rocks Ecological Reserve/Marine Protected Area and for the use of the Green Blue Spaces sub committee of the Metchosin Environmental Advisory Select Committee ( MEASC
















































































 Often in the spring when the sunlight levels are adequate, the nutrient laden water from winter run-off may support a non-poisonous red tide. A deep reddish bloom caused by the organism Mesodinium rubrum will cover parts of the bay. This is a unique marine photosynthetic ciliate which can fix energy because it has a cryptophyte endosymbiontic red algae inside it. A good example of a mutualistic relationship occurring on a massive scale within the bay.
Often in the spring when the sunlight levels are adequate, the nutrient laden water from winter run-off may support a non-poisonous red tide. A deep reddish bloom caused by the organism Mesodinium rubrum will cover parts of the bay. This is a unique marine photosynthetic ciliate which can fix energy because it has a cryptophyte endosymbiontic red algae inside it. A good example of a mutualistic relationship occurring on a massive scale within the bay.