The following article has been published in the Metchosin Muse:
Witty’s Beach joins other KBAs in the Victoria area :
 The other local KBA designation is at Race Rocks Ecological Reserve
The other local KBA designation is at Race Rocks Ecological Reserve

The following article has been published in the Metchosin Muse:
Witty’s Beach joins other KBAs in the Victoria area :
 The other local KBA designation is at Race Rocks Ecological Reserve
The other local KBA designation is at Race Rocks Ecological Reserve
Since the 25th of November, we have had 5 inches of precipitation and in the last two weeks an unusual number of South-Easterly storms providing great action at Taylor beach in front of the farm, especially at high tide. The view starts by looking towards William Head prison and ends with a view of Victoria in the distance
Last week we had a very high tide, and storms from the north-east which had temporarily blocked the exit to Gooch Creek on Taylor Beach. The water in Gooch creek swamp rose over a metre before breaking through and washing out on the beach. As the beach has eroded down, the record of the previous weeks of tide levels and storm surges is exposed in this eroding bank where the water exits on the beach.
During the past few weeks, we have experienced several storms out of the north east at high tide. These images were taken to document some of the on-going problems from the extensive rip-rapping and seawall construction on that beach. See this page for summer 2013 images for comparison.
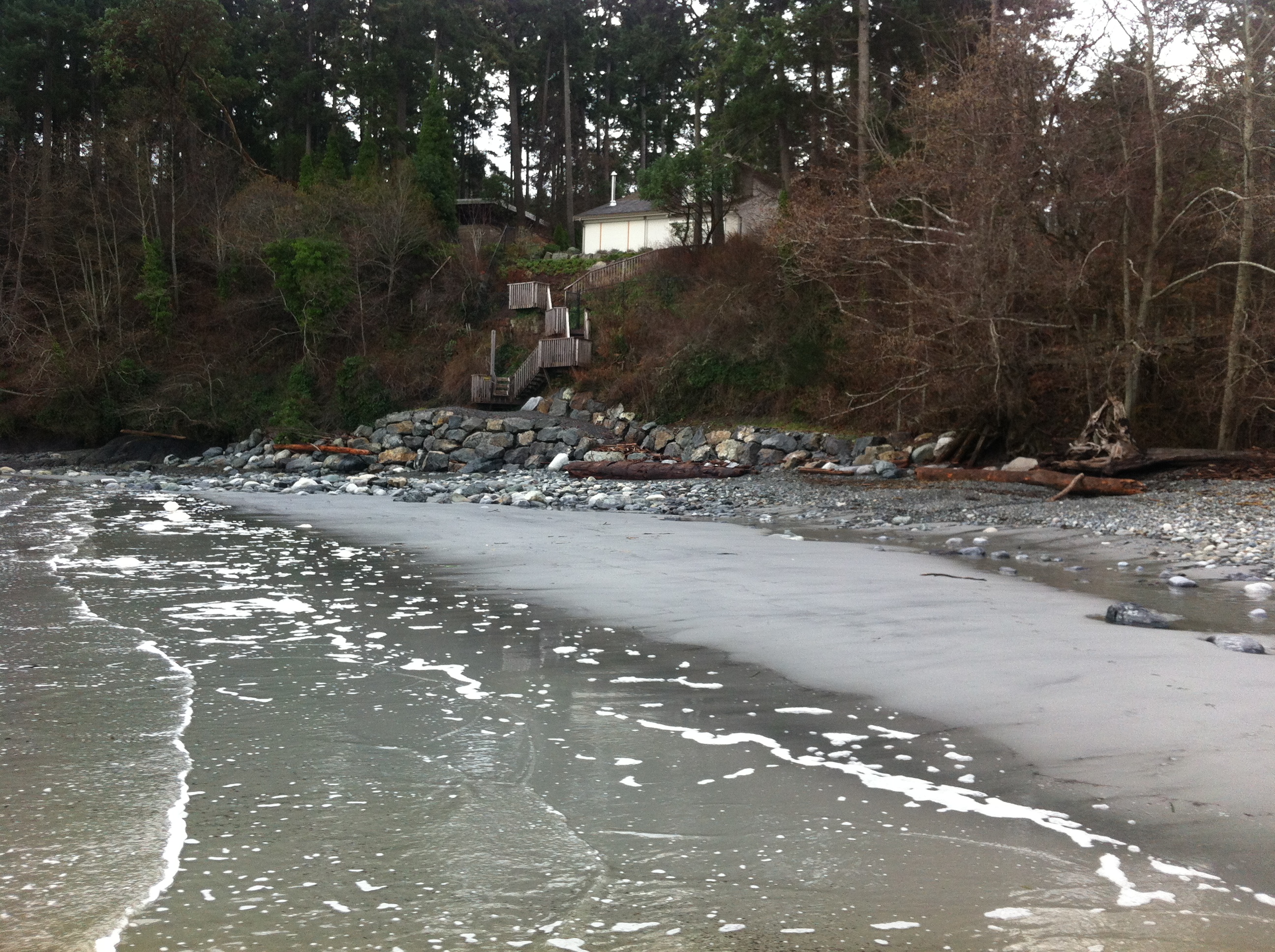

The solid sea-wall built only last year will lead to increased scouring and removal of sand. Unfortunately it will not only affect the crown land property in front of the wall, but the crown land foreshore adjacent to this property .
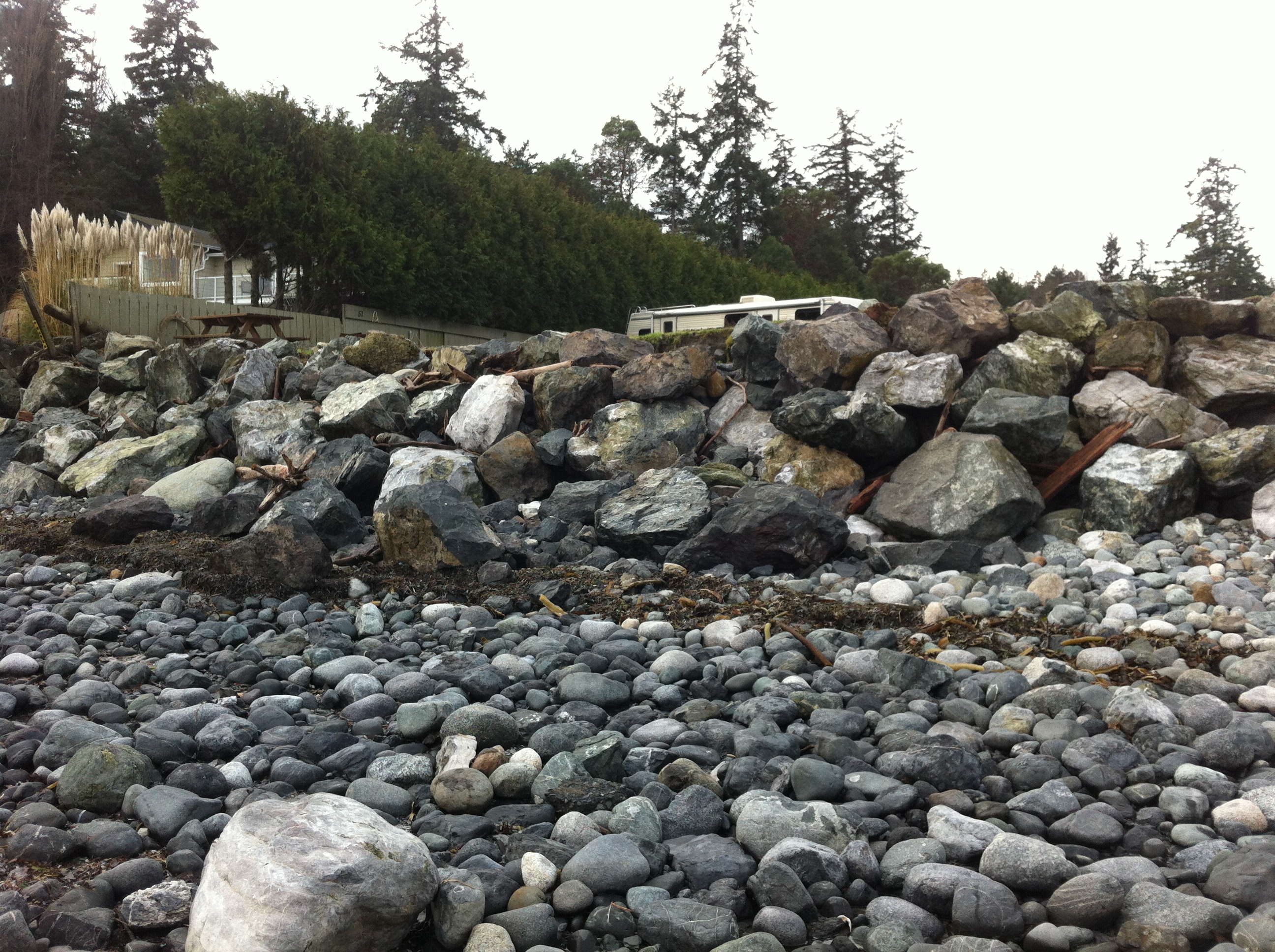

Recent storms have dislodged many of the boulders near the south end of the beach. Note the rubble foreground which was previously sand beach.
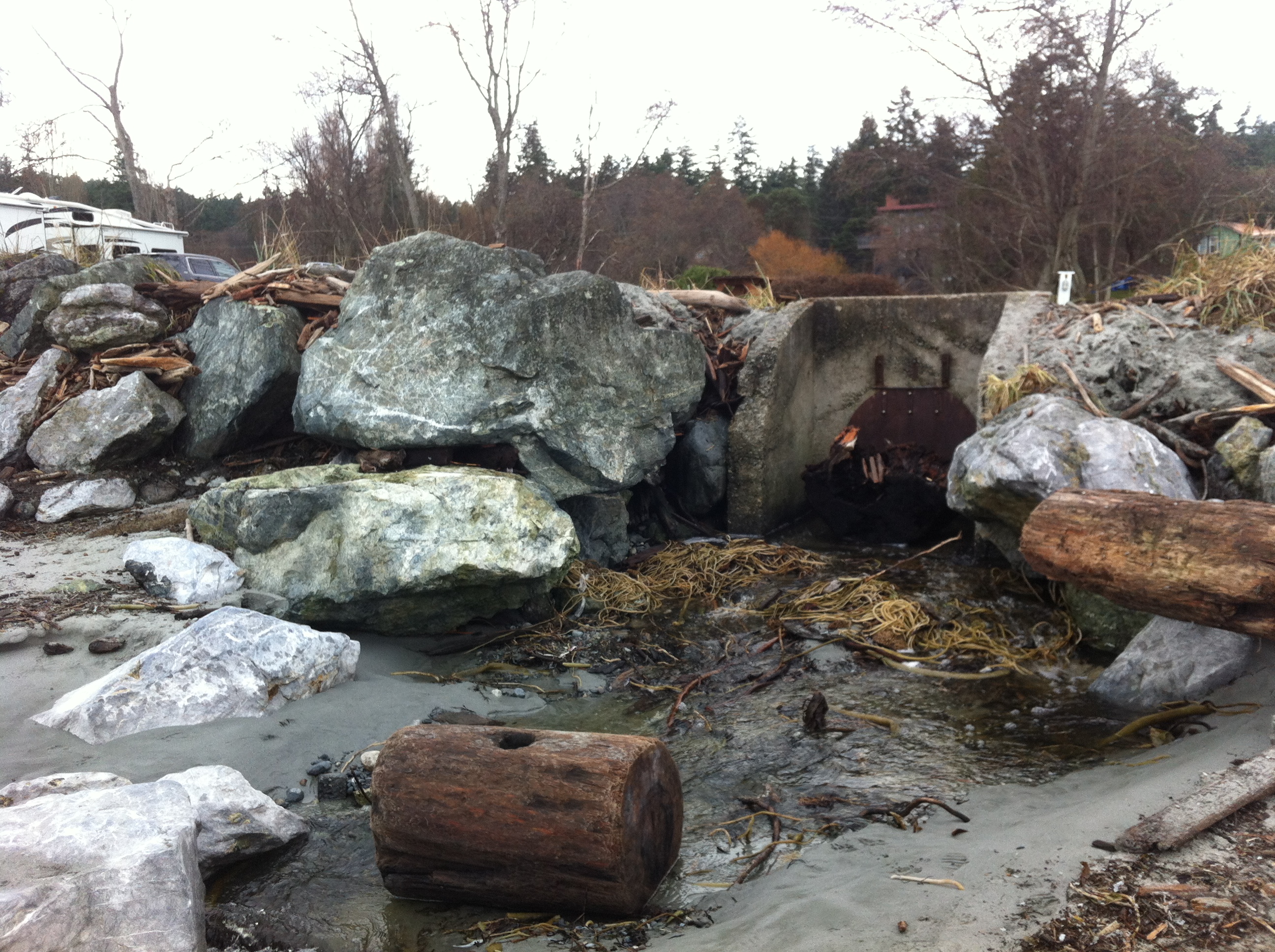

This concrete control gate was built many years ago to control flooding into a lagoon. The rip-rap boulders around it have been disturbed by wave action.
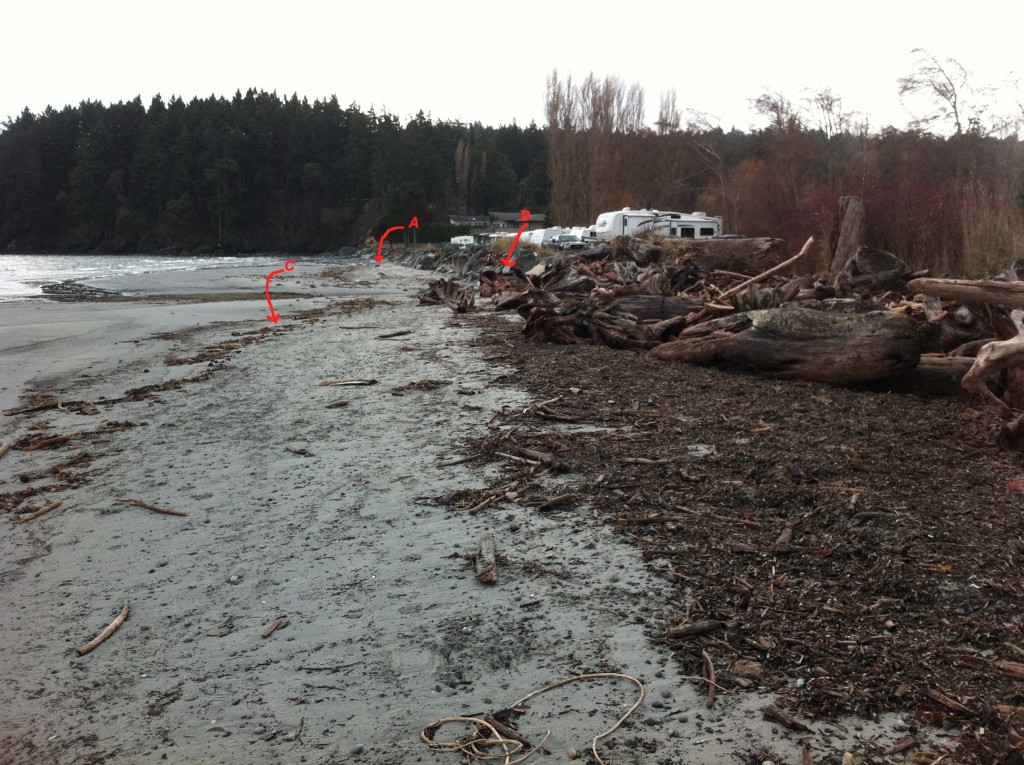

Site A= south end of the beach-sand eroded from base of rip-pap wall. Site B The border of where the rip-rap ends and the natural beach (going northward,) begins. C=the widened sand beach area backed by the natural beach. Scouring of the sand does not occur as it does further south on the beach.
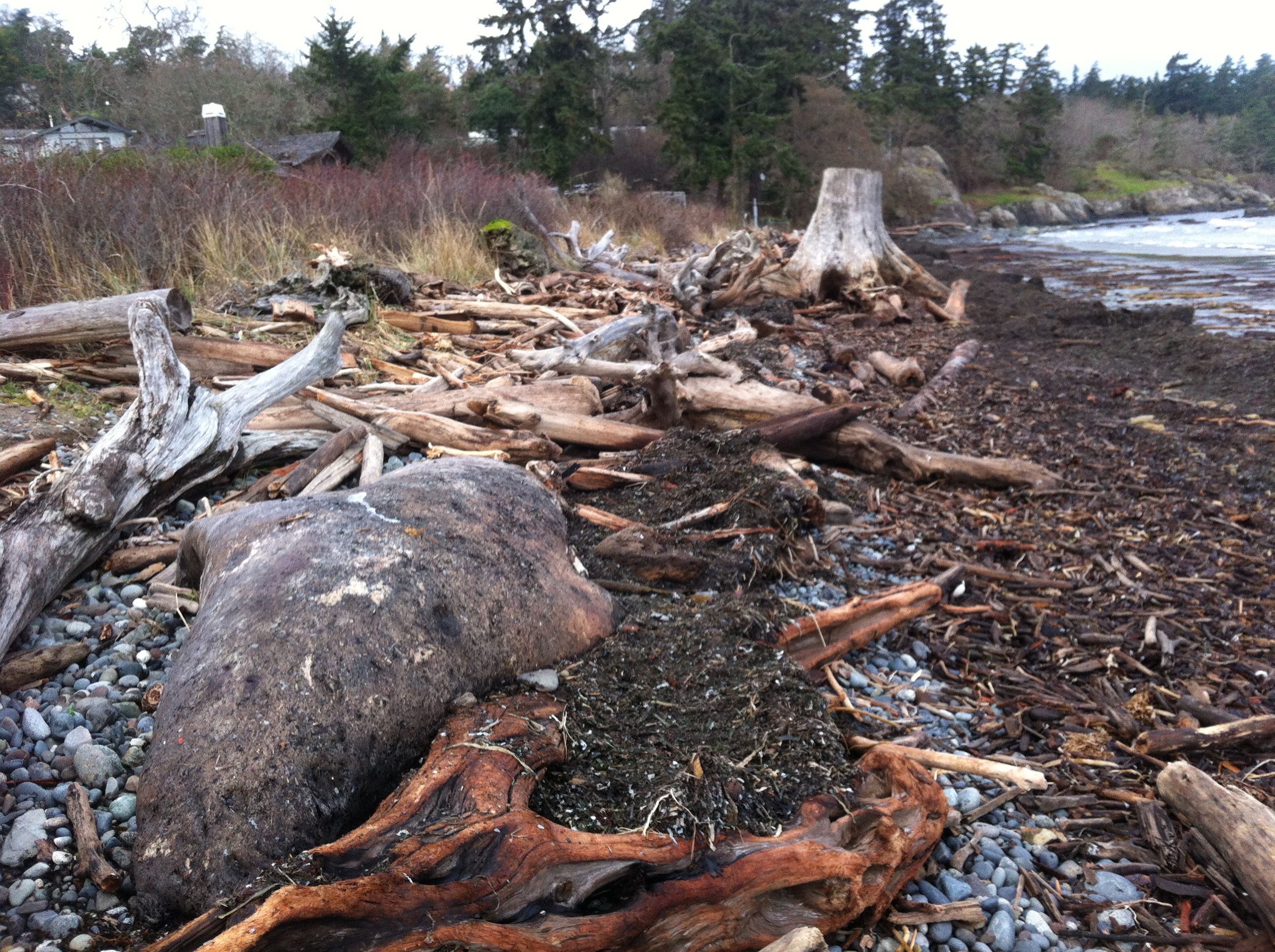

The berm on the North end of Weir’s beach is in a more natural state with logs and debris thrown up by storms. The and natural beach vegetation and debris absorbs the impact of the ocean energy and no scouring of the beach sand has occurred. This will lead to long-term beach stability and erosion-resistance.
See other posts and references on hardening of the shorelines by clicking on links below.
See this file on early pictures of Weir’s beach
Metchosin resident Jan Poulin reported a dead marine mammal today on Weir’s beach. Below are some pictures. It looks like a mature male, up to 4 m in length. It had been washed up in the swell form the North East storms over the last week. It has been dead for some time and will eventually probably cause a problem for the residents of the area. It has been reported to DFO.
Other images of the elephant seal : December 26, 2014
The skies are clear this week with out-flow winds from the northeast clearing the view of Mount Baker and the Olympic Mountains. With this comes colder temperatures and a few degrees of frost at night. Rains are expected to return next week.

The heavily impacted Weir’s Beach which has experienced considerable sand loss in recent years largely due to bad management of the shoreline.
This article highlights a good example how human interference ( anthropogenic) in a number of ways can result in the loss of Natural Capital and long term sustainability .
The beaches of Metchosin are not immune to the forces of Climate change and uninformed decisions of upland landowners and municipal governments which refuse to enact rigid Shoreline Development Bylaws.
This has been quoted from: The NYT Opinion Pages NOV. 4, 2014
It could once be said that “a beach is a place where sand stops to rest for a moment before resuming its journey to somewhere else,” as the naturalist D. W. Bennett wrote in the book “Living With the New Jersey Shore.” Sand moved along the shore and from beach to sea bottom and back again, forming shorelines and barrier islands that until recently were able to repair themselves on a regular basis, producing the illusion of permanence.
Today, however, 75 to 90 percent of the world’s natural sand beaches are disappearing, due partly to rising sea levels and increased storm action, but also to massive erosion caused by the human development of shores. Many low-lying barrier islands are already submerged.
Yet the extent of this global crisis is obscured because so-called beach nourishment projects attempt to hold sand in place and repair the damage by the time summer people return, creating the illusion of an eternal shore.
Before next summer, endless lines of dump trucks will have filled in bare spots and restored dunes. Virginia Beach alone has been restored more than 50 times. In recent decades, East Coast barrier islands have used 23 million loads of sand, much of it mined inland and the rest dredged from coastal waters — a practice that disturbs the sea bottom, creating turbidity that kills coral beds and damages spawning grounds, which hurts inshore fisheries.
The sand and gravel business is now growing faster than the economy as a whole. In the United States, the market for mined sand has become a billion-dollar annual business, growing at 10 percent a year since 2008. Interior mining operations use huge machines working in open pits to dig down under the earth’s surface to get sand left behind by ancient glaciers. But as demand has risen — and the damming of rivers has held back the flow of sand from mountainous interiors — natural sources of sand have been shrinking.
One might think that desert sand would be a ready substitute, but its grains are finer and smoother; they don’t adhere to rougher sand grains, and tend to blow away. As a result, the desert state of Dubai brings sand for its beaches all the way from Australia.
And now there is a global beach-quality sand shortage, caused by the industries that have come to rely on it. Sand is vital to the manufacturing of abrasives, glass, plastics, microchips and even toothpaste, and, most recently, to the process of hydraulic fracturing. The quality of silicate sand found in the northern Midwest has produced what is being called a “sand rush” there, more than doubling regional sand pit mining since 2009.
But the greatest industrial consumer of all is the concrete industry. Sand from Port Washington on Long Island — 140 million cubic yards of it — built the tunnels and sidewalks of Manhattan from the 1880s onward. Concrete still takes 80 percent of all that mining can deliver. Apart from water and air, sand is the natural element most in demand around the world, a situation that puts the preservation of beaches and their flora and fauna in great danger. Today, a branch of Cemex, one of the world’s largest cement suppliers, is still busy on the shores of Monterey Bay in California, where its operations endanger several protected species.
The huge sand mining operations emerging worldwide, many of them illegal, are happening out of sight and out of mind, as far as the developed world is concerned. But in India, where the government has stepped in to limit sand mining along its shores, illegal mining operations by what is now referred to as the “sand mafia” defy these regulations. In Sierra Leone, poor villagers are encouraged to sell off their sand to illegal operations, ruining their own shores for fishing. Some Indonesian sand islands have been devastated by sand mining.
It is time for us to understand where sand comes from and where it is going. Sand was once locked up in mountains and it took eons of erosion before it was released into rivers and made its way to the sea. As Rachel Carson wrote in 1958, “in every curving beach, in every grain of sand, there is a story of the earth.” Now those grains are sequestered yet again — often in the very concrete sea walls that contribute to beach erosion.
We need to stop taking sand for granted and think of it as an endangered natural resource. Glass and concrete can be recycled back into sand, but there will never be enough to meet the demand of every resort. So we need better conservation plans for shore and coastal areas. Beach replenishment — the mining and trucking and dredging of sand to meet tourist expectations — must be evaluated on a case-by-case basis, with environmental considerations taking top priority. Only this will ensure that the story of the earth will still have subsequent chapters told in grains of sand.
This Shiner Perch, Cymatogaster aggregata was at the water’s edge on Taylor Beach this morning. Cause of death is unknown. They are often found along our coast in shallow waters, and eel-grass communities, and serve as important forage fish, especially as juveniles.
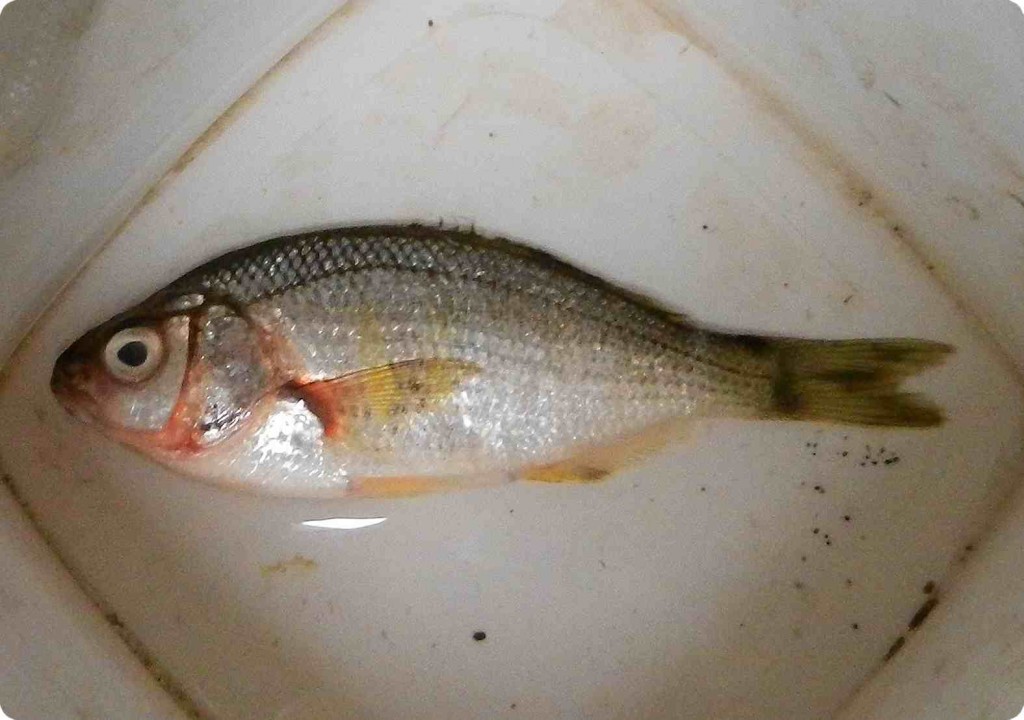

Classification from Species 2000 & ITIS Catalogue of Life: April 2013
Animalia
Chordata
Actinopterygii
Perciformes
Embiotocidae
Cymatogaster
Cymatogaster aggregata Gibbons, 1854
Today there is a strong swell from the North East on Taylor beach which has deposited a good sample of the diversity of the algae that live in the subtidal zone just below the low-tide level.
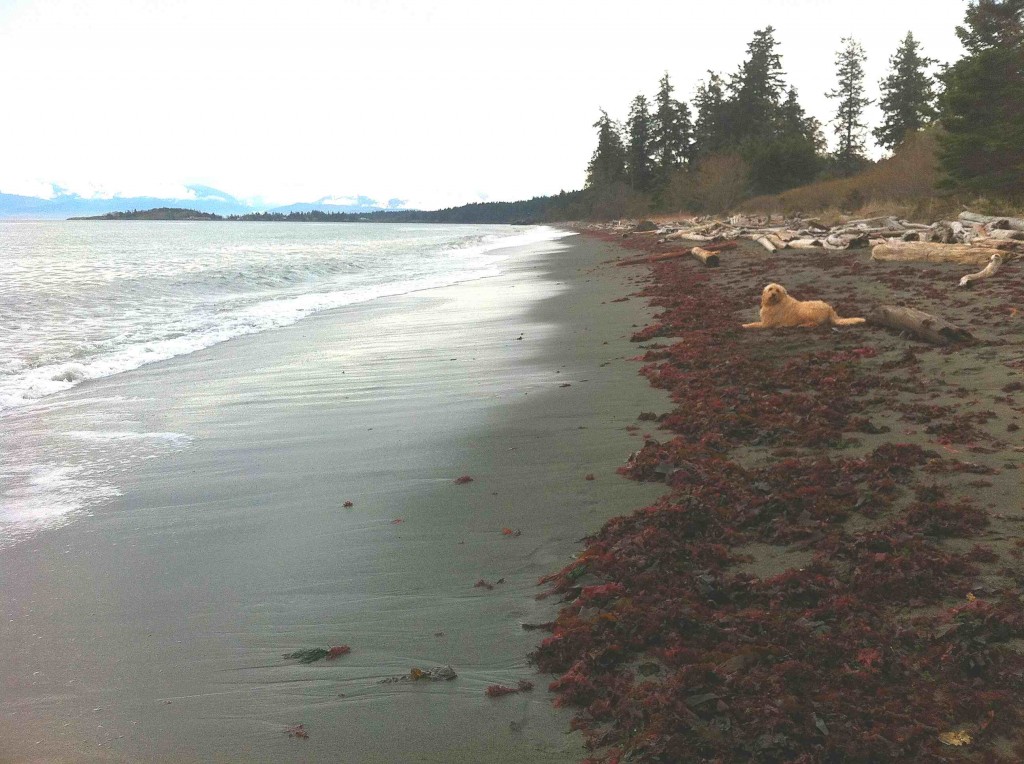

Taylor Beach in Parry Bay at the southern end of Vancouver Island. This beach gets winds and waves from the East in the fall, winter and spring months, but is protected by having only west winds from June to September. There is long-shore drift toward the north end of the beach in the summer as the energy from the westerlies refract around William Head, visible in the distance on the left.
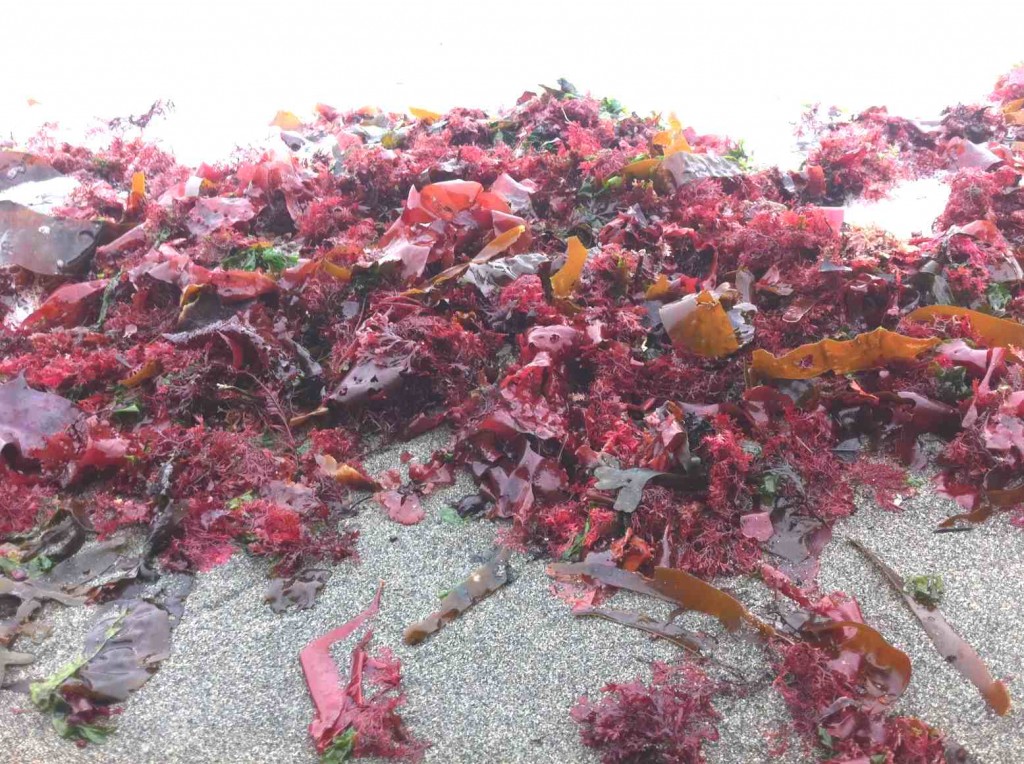

The Red algae as they lay in the strand line showing the upper limits of the last high tide and the swell which deposited the algae.
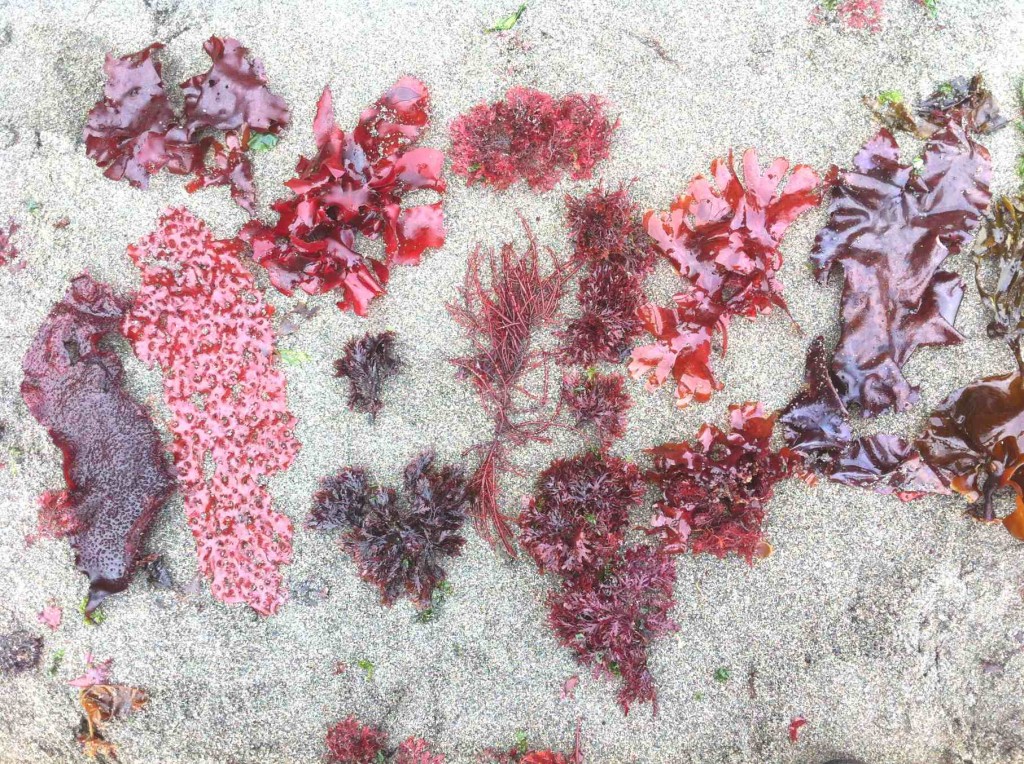

The greatest biodiversity is shown in the Rhodophytes or red algae shown here picked out from the strand line within a few square metres.
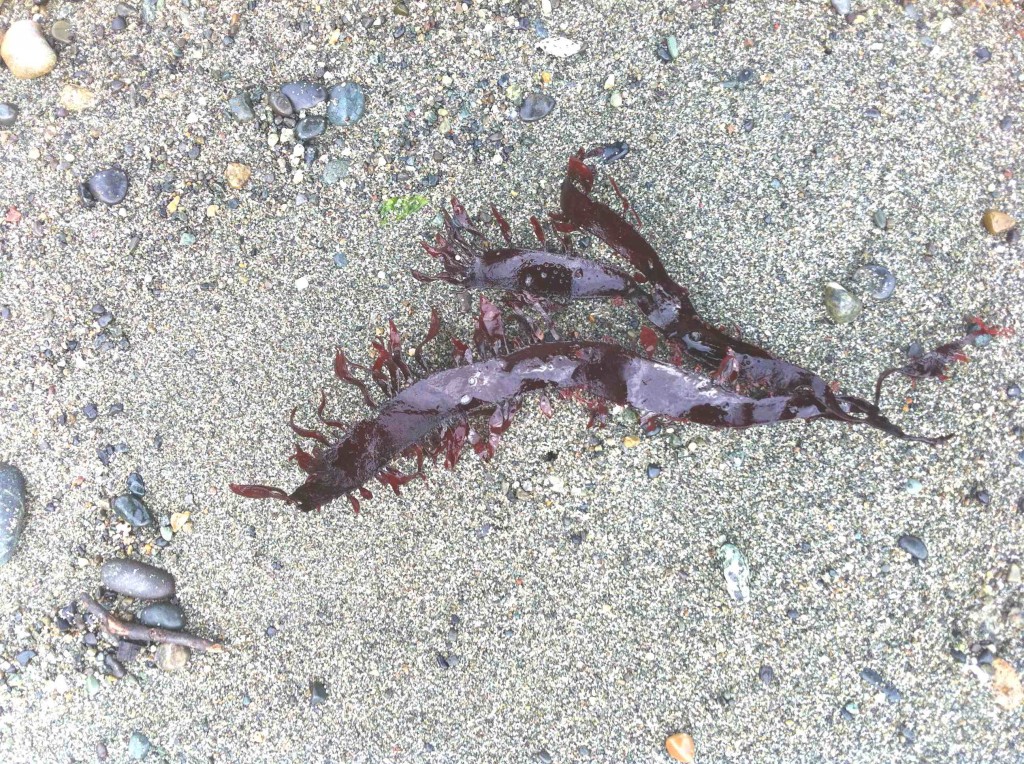

A sample of the red algae, Prionitis lanceolata . which is normally found on the low intertidal of rocky shores.